Yes, aluminum can be sputtered, and it is a very common process used to create thin films for applications ranging from reflective coatings on mirrors to electrical interconnects in microelectronics. However, successfully sputtering aluminum requires careful control over the process because of its high chemical reactivity, particularly with oxygen.
The central challenge in sputtering aluminum is not the process itself, but managing the metal's tendency to instantly react with any residual oxygen in the vacuum chamber. This reaction can "poison" the sputtering target, drastically reducing deposition rates and compromising film quality.

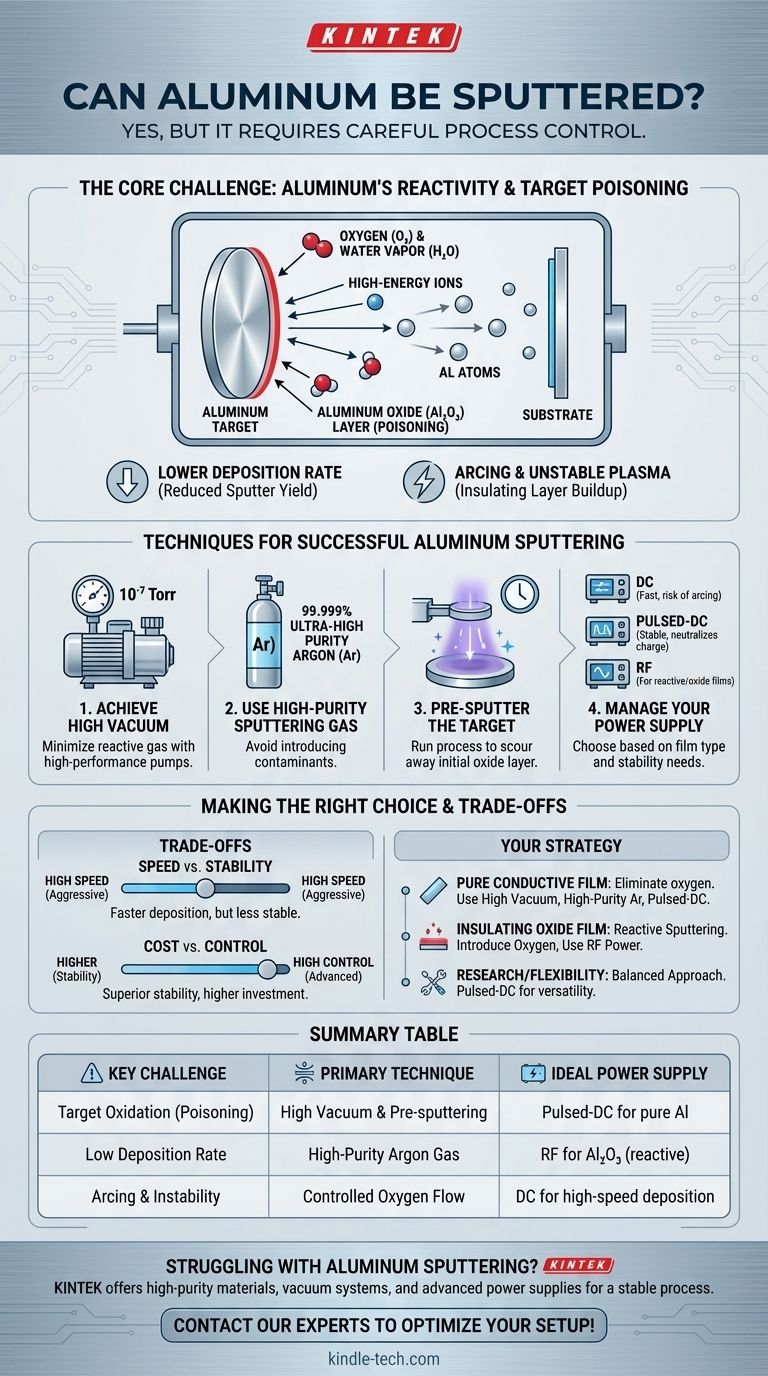
The Core Challenge: Aluminum's Reactivity
Sputtering is a physical vapor deposition (PVD) process. It works by bombarding a solid material, known as the target (in this case, aluminum), with high-energy ions from a plasma. This bombardment physically ejects or "sputters" atoms from the target, which then travel and deposit onto a substrate, forming a thin film.
The Oxidation Problem
Aluminum is a highly reactive metal. When an aluminum surface is exposed to even trace amounts of oxygen or water vapor, it almost instantly forms a very thin, tough, and electrically insulating layer of aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃).
This natural characteristic is the primary obstacle in sputtering. The vacuum chamber where sputtering occurs always contains trace amounts of residual gases, including oxygen and water.
Understanding "Target Poisoning"
When the rate of oxide formation on the aluminum target surface becomes faster than the rate at which it's sputtered away, the target is said to be "poisoned."
This is problematic for two key reasons. First, aluminum oxide has a much lower sputter yield than pure aluminum, meaning it's harder to eject atoms from it. This causes the deposition rate to plummet.
Second, the oxide layer is an electrical insulator. If you are using the common Direct Current (DC) sputtering method, positive charge can build up on these insulating patches, leading to unstable plasma and destructive arcing events.
Techniques for Successful Aluminum Sputtering
Controlling the chamber environment and the sputtering parameters is essential for achieving a stable and repeatable process. The goal is to keep the target in its clean, metallic state.
Achieve High Vacuum
The first line of defense is to minimize the amount of reactive gas available. This means starting with a very low base pressure in the deposition chamber, typically in the range of 10⁻⁷ Torr or lower. High-performance vacuum pumps, such as cryopumps, are often used to effectively remove water vapor.
Use High-Purity Sputtering Gas
The sputtering process itself is conducted in a controlled atmosphere of an inert gas, almost always high-purity argon (Ar). Using ultra-high purity (99.999% or "five-nines") argon is critical to avoid introducing oxygen or moisture contaminants with the process gas.
Pre-Sputter the Target
Before opening the shutter to deposit the film onto your substrate, it's standard practice to run the sputtering process for several minutes. This pre-sputtering step acts as a final cleaning, using the argon plasma to scour away any residual oxide layer that formed on the target's surface.
Manage Your Power Supply
For pure metallic aluminum films, DC magnetron sputtering is the fastest and most common method. However, due to the risk of arcing from oxide poisoning, pulsed-DC power supplies are often preferred. They rapidly cycle the voltage, which helps to neutralize charge buildup on any insulating spots that may form, providing a more stable process.
If the goal is to intentionally create an aluminum oxide film (a process called reactive sputtering), an RF (Radio Frequency) power supply is typically used because it is designed to effectively sputter insulating materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice of process parameters involves balancing competing factors.
Speed vs. Stability
Operating at very high deposition rates (using high power) helps keep the target surface clean, as aluminum is sputtered away faster than it can oxidize. However, this aggressive approach can be less stable and may not be suitable for all applications.
Cost vs. Control
A simple DC power supply is the least expensive option but offers the least protection against target poisoning and arcing. Advanced pulsed-DC or RF power supplies provide superior process stability and control but represent a greater investment in equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your sputtering strategy should be dictated by the type of film you intend to create.
- If your primary focus is a pure, conductive aluminum film: Your goal is to eliminate all sources of oxygen. Prioritize achieving a high vacuum, use high-purity argon, and employ a thorough pre-sputter clean with a high-power DC or pulsed-DC supply.
- If your primary focus is a durable, insulating aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃) film: You will use reactive sputtering. This involves intentionally introducing a controlled flow of oxygen into the chamber alongside the argon and typically requires an RF power supply to manage the insulating target.
- If you need a mix of properties or are in a research environment: A system equipped with a pulsed-DC power supply offers the most flexibility, providing stability for sputtering pure aluminum while also being capable of handling some reactive processes.
Ultimately, mastering aluminum sputtering is a matter of precisely controlling the vacuum environment to overcome the metal's powerful affinity for oxygen.
Summary Table:
| Key Challenge | Primary Technique | Ideal Power Supply |
|---|---|---|
| Target Oxidation (Poisoning) | High Vacuum & Pre-sputtering | Pulsed-DC for pure Al |
| Low Deposition Rate | High-Purity Argon Gas | RF for Al₂O₃ (reactive) |
| Arcing & Instability | Controlled Oxygen Flow | DC for high-speed deposition |
Struggling with aluminum sputtering in your lab? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing the high-purity argon, robust vacuum systems, and advanced power supplies you need for a stable, repeatable process. Whether you're depositing conductive interconnects or durable insulating layers, our expertise ensures high-quality thin films. Contact our experts today to optimize your sputtering setup!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating
- What are the components of PECVD? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition Systems
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What is plasma CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for Sensitive Materials
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process



















