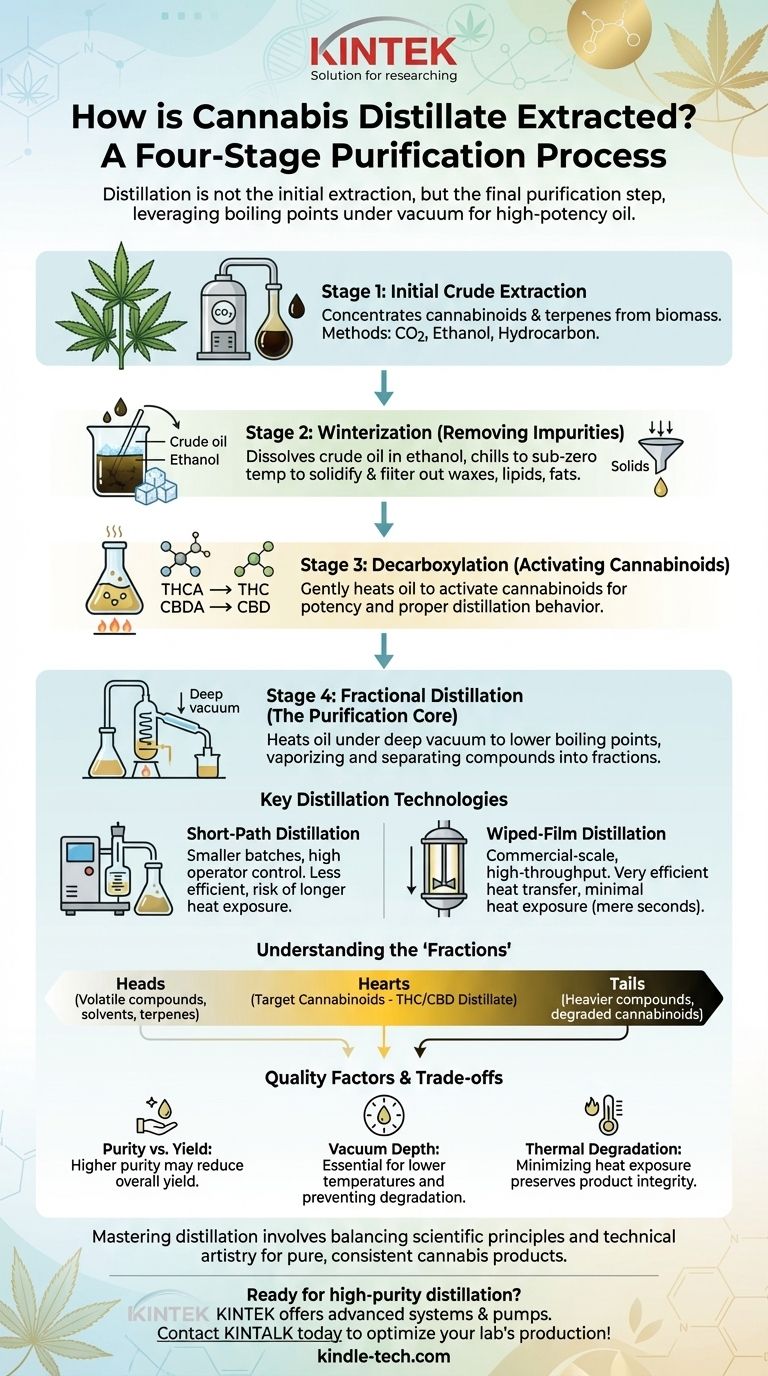
In short, creating cannabis distillate is a multi-stage purification process. It begins with a crude cannabis extract, which is then refined through winterization and decarboxylation before undergoing fractional distillation under a deep vacuum to isolate the desired cannabinoids like THC or CBD.
The term "extracting distillate" is a slight misnomer. Distillation is not the initial extraction from the plant; it is the ultimate step in purifying a crude extract. The core principle is to leverage the different boiling points of various compounds under vacuum to separate cannabinoids from everything else, resulting in a highly potent, refined oil.
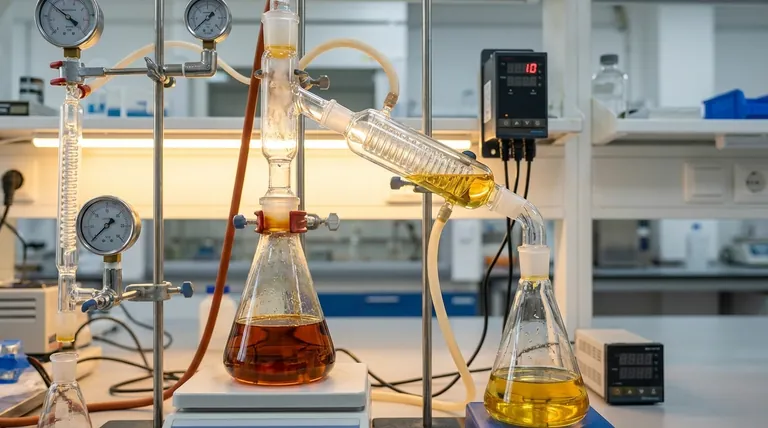

The Four Essential Stages of Distillate Production
Creating high-quality distillate is a systematic workflow. Skipping or poorly executing any of the initial stages will compromise the quality of the final product, regardless of how advanced your distillation equipment is.
Stage 1: Initial Crude Extraction
You cannot distill raw plant material. The first step is to create a concentrated crude oil by extracting the cannabinoids and terpenes from the cannabis or hemp biomass.
Common methods include CO2 extraction, ethanol extraction, or hydrocarbon (butane/propane) extraction. Each method yields a crude oil with a unique profile of cannabinoids, terpenes, waxes, and lipids.
Stage 2: Winterization (Removing Impurities)
Crude oil contains undesirable compounds like plant fats, waxes, and lipids. Winterization, also known as dewaxing, is the process of removing them.
The crude oil is dissolved in a solvent, typically ethanol, and then chilled to sub-zero temperatures for 24-48 hours. The low temperature causes the fats and waxes to solidify and precipitate, allowing them to be filtered out, leaving a cleaner, more refined oil.
Stage 3: Decarboxylation (Activating Cannabinoids)
Cannabinoids in their raw form exist in an acidic state (e.g., THCA, CBDA). These molecules are not psychoactive (in the case of THCA) and behave differently during distillation.
Decarboxylation is the process of gently heating the oil to a specific temperature. This removes the carboxyl acid group, converting THCA into the target THC and CBDA into CBD. This step is critical for ensuring the final product is potent and distills properly.
Stage 4: Fractional Distillation (The Purification Core)
This is the final and most crucial stage. The fully prepared oil is placed into a distillation apparatus where it is heated under a deep vacuum.
The vacuum is essential because it dramatically lowers the boiling points of the cannabinoids. This allows them to be vaporized at temperatures that do not cause thermal degradation. As the oil is heated, different compounds (fractions) vaporize at different temperatures and are condensed and collected separately.
Key Distillation Technologies
The two dominant methods for cannabis distillation are short-path and wiped-film distillation. Both operate under vacuum but differ in their mechanics and ideal use cases.
Short-Path Distillation
In a short-path system, the oil is heated in a boiling flask. The resulting vapor travels a very short distance—the "short path"—to a condenser, where it is cooled back into a liquid and collected.
This method is well-suited for smaller, batch-based production. It gives a skilled operator a high degree of control but can be less efficient and risks longer heat exposure for the oil compared to wiped-film systems.
Wiped-Film Distillation
Also known as thin-film distillation, this is the standard for high-throughput, commercial-scale operations. In this system, the crude oil is fed into a heated vertical cylinder.
Rotating wipers continuously spread the oil into a very thin film against the heated interior surface. This creates incredibly efficient heat transfer and immediately vaporizes the target cannabinoids, which are then collected on an internal condenser. The residence time under heat is mere seconds, drastically minimizing the risk of thermal degradation.
Understanding the "Fractions": Heads, Hearts, and Tails
Distillation is the art of separating the oil into distinct parts, or "fractions," based on their boiling points.
The "Heads" Fraction
As the oil first heats up, the most volatile compounds with the lowest boiling points vaporize. This fraction, known as the "heads," typically contains residual solvents, water, and lighter terpenes. It is collected and set aside.
The "Hearts" Fraction
After the heads are removed, the temperature is raised to the target boiling point of the desired cannabinoid (e.g., THC or CBD). This main fraction is the "hearts" or the main body. This is the clear, golden distillate that is the goal of the entire process.
The "Tails" Fraction
What remains in the boiling flask after the hearts have been distilled is the "tails." This thick, dark residue consists of heavier compounds with higher boiling points, such as sterols, pigments, and degraded cannabinoids.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Quality Factors
The quality of your final distillate depends on balancing several key variables.
Purity vs. Yield
Achieving extremely high purity (e.g., 95%+) often requires a "second pass," where the "hearts" fraction is distilled a second time. While this increases potency and clarity, it inevitably results in some loss of material, reducing the overall yield.
The Critical Role of Vacuum Depth
The single most important variable for quality is the vacuum. A deep vacuum (measured in microns) is non-negotiable. An inadequate vacuum forces the operator to use higher temperatures, which is the primary cause of cannabinoid degradation, leading to a darker color and lower potency.
Thermal Degradation
Cannabinoids are sensitive to heat. The longer the oil is exposed to high temperatures, the more it degrades. This is why wiped-film systems, with their extremely short residence time, are often considered superior for preserving the integrity of the final product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your production goals will determine the ideal approach and equipment.
- If your primary focus is boutique, small-batch production: Short-path distillation offers a lower initial investment and precise control for a skilled operator to create high-quality products.
- If your primary focus is large-scale, continuous manufacturing: Wiped-film distillation is the industry standard for its efficiency, high throughput, and superior protection against thermal degradation.
- If your primary focus is maximizing product quality: Invest in a high-performance vacuum pump and master the art of separating fractions, potentially using a two-pass distillation process for ultimate purity.
Ultimately, mastering distillation is a blend of scientific principle and technical artistry, enabling the creation of exceptionally pure and consistent cannabis products.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Process | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Crude Extraction | CO2, Ethanol, or Hydrocarbon Extraction | Concentrate cannabinoids from plant material. |
| 2. Winterization | Dissolve in ethanol, chill, filter | Remove waxes, lipids, and fats for a cleaner oil. |
| 3. Decarboxylation | Gentle heating | Activate cannabinoids (convert THCA to THC, CBDA to CBD). |
| 4. Fractional Distillation | Heat under deep vacuum | Separate and purify target cannabinoids based on boiling points. |
Ready to produce high-purity cannabis distillate with precision and efficiency? The right lab equipment is critical for maximizing yield and preventing thermal degradation. KINTEK specializes in advanced distillation systems, including wiped-film and short-path setups, and the high-performance vacuum pumps necessary for superior results. Whether you're scaling up production or optimizing for small-batch quality, our experts can help you build the ideal solution for your laboratory's needs. Contact KINTALK today to discuss your distillation goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab Scale Rotary Single Punch Tablet Press Machine TDP Tablet Punching Machine
- Evaporation Crucible for Organic Matter
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Multi-Punch Rotary Tablet Press Mold Ring for Rotating Oval and Square Molds
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is a sputtering machine? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What are the different parts of a single punch tablet machine? The Core Components Explained
- What are pill presses called? The Correct Term is Tablet Press for Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
- What is the difference between single punch and rotary tablet press? Choose the Right Machine for Your Lab or Production
- What is tablet pressing in pharmaceutical industry? The Core Process for Producing Solid Oral Dosage Forms



















