In short, creating THC isolate from distillate is an advanced chemical purification process performed in a laboratory setting. It involves dissolving the distillate in a solvent and then using a technique called chromatography to separate the individual THC molecules from all other remaining cannabinoids, terpenes, and impurities. The resulting highly-purified THC solution is then put through a crystallization and solvent-purging process to yield a solid, crystalline isolate.
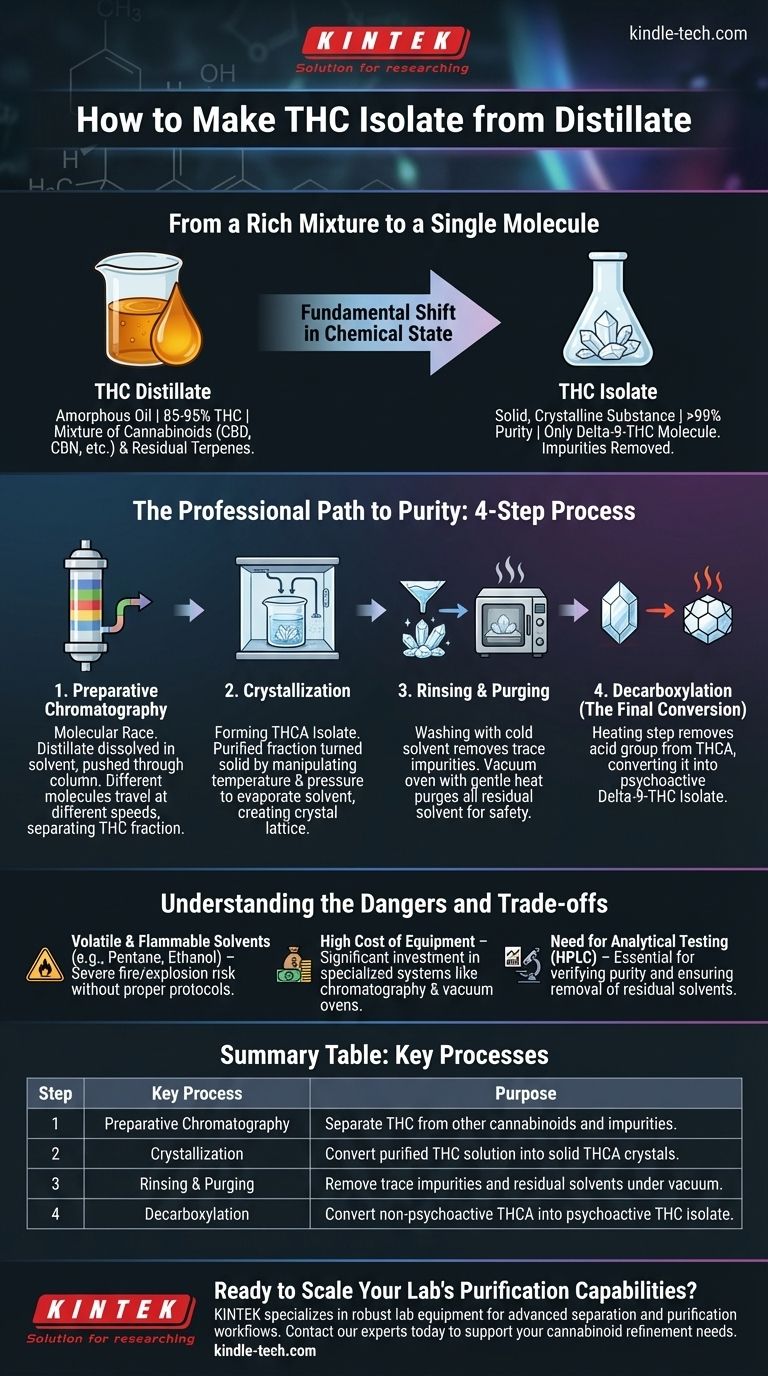
The transition from distillate to isolate is not a simple filtering step, but a fundamental shift in chemical state. It is the process of forcing a specific molecule (THCA) out of a complex mixture to form a solid, crystalline structure of exceptionally high purity, which is then converted to THC.

From a Rich Mixture to a Single Molecule
To understand the process, it's essential to first clarify the starting and ending points. They are fundamentally different products.
What is THC Distillate?
THC distillate is a highly refined cannabis oil. While it is very potent—often containing 85-95% THC—it is still an amorphous oil.
This oil is a mixture containing THC alongside other cannabinoids (like CBD or CBN) and sometimes residual terpenes. It is pure relative to raw extract, but it is not chemically pure.
What is THC Isolate?
THC isolate is the purest form of THC possible, often testing above 99% purity. It is a solid, crystalline substance at room temperature.
Isolate contains only one molecule: delta-9-THC. All other plant compounds, cannabinoids, and terpenes have been meticulously removed.
The Core Challenge: Separating Similar Molecules
The primary difficulty is that cannabinoids are very similar in chemical structure and properties. This makes separating them from each other extremely challenging using simple methods like distillation or filtration. It requires a more precise technique.
The Professional Path to Purity
Achieving over 99% purity is a multi-step process that demands precision, specialized equipment, and a deep understanding of chemistry. This is exclusively the domain of professional labs.
Step 1: Preparative Chromatography
The workhorse of this process is preparative chromatography. Think of it as a molecular race.
The distillate is dissolved in a solvent (the "mobile phase") and pushed through a large column packed with a filter material (the "stationary phase," often silica).
Because each type of molecule (THC, CBD, terpenes, etc.) interacts with the filter material differently, they travel through the column at different speeds. The THC molecules are collected as a separate, highly-purified "fraction" as they exit the column.
Step 2: Crystallization
The collected THC fraction is now extremely pure, but it is still dissolved in a solvent. The next goal is to turn it into a solid.
Interestingly, delta-9-THC itself does not crystallize well. Labs instead create THCA isolate, as the acidic form (THCA) crystallizes readily under the right conditions.
This is achieved by manipulating temperature and pressure to slowly evaporate the solvent, encouraging the pure THCA molecules to stack together into a highly organized crystal lattice, leaving any remaining impurities behind in the residual solvent.
Step 3: Rinsing and Purging
The newly formed THCA crystals are then "washed" with a very cold, non-polar solvent. This final rinse removes any trace impurities that may have clung to the crystal surfaces.
After rinsing, the crystals are placed in a vacuum oven. The combination of gentle heat and vacuum purges any and all residual solvent from the final product, which is critical for safety and purity.
Step 4: Decarboxylation (The Final Conversion)
The end product of crystallization is pure THCA isolate. To create THC isolate, a final, carefully controlled heating step is required.
This process, called decarboxylation, removes the acid group (the "A" in THCA) and converts the molecule into the psychoactive delta-9-THC. The result is a pure, solid THC isolate.
Understanding the Dangers and Trade-offs
This is not a process that can or should be attempted outside of a purpose-built, licensed laboratory environment with trained chemists.
Volatile and Flammable Solvents
The solvents used in chromatography and crystallization (such as pentane, heptane, or ethanol) are highly volatile and flammable. Without proper ventilation and handling protocols, the risk of fire or explosion is severe.
High Cost of Equipment
Preparative chromatography systems, rotary evaporators, and laboratory-grade vacuum ovens represent a significant capital investment, costing tens or even hundreds of thousands of dollars.
The Need for Analytical Testing
Verifying the purity of the final product and ensuring the complete removal of residual solvents is impossible without analytical equipment like High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC). Without this, you cannot know what you have truly created.
How to Apply This Understanding
This knowledge is most valuable not for replication, but for context as a professional or discerning consumer.
- If your focus is on production: Recognize that creating isolate is a major operational step-up from distillate, requiring significant investment in a specialized lab, skilled personnel, and rigorous safety protocols.
- If your focus is on product selection: You can now understand why isolate-based products command a premium price. The cost reflects the complex, multi-stage refinement process required to achieve that level of purity.
- If your focus is on scientific knowledge: The key principle to study is separation science, specifically preparative chromatography, which is the cornerstone of purifying any single chemical compound from a complex mixture.
Ultimately, the journey from distillate to isolate is a testament to the power of precise chemical refinement.
Summary Table:
| Step | Key Process | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Preparative Chromatography | Separate THC from other cannabinoids and impurities. |
| 2 | Crystallization | Convert the purified THC solution into solid THCA crystals. |
| 3 | Rinsing & Purging | Remove trace impurities and residual solvents under vacuum. |
| 4 | Decarboxylation | Convert non-psychoactive THCA into psychoactive THC isolate. |
Ready to Scale Your Lab's Purification Capabilities?
This complex process requires precision equipment and expertise. KINTEK specializes in providing the robust lab equipment and consumables needed for advanced separation and purification workflows, including chromatography and solvent evaporation. Our solutions help laboratories achieve the highest levels of purity and efficiency.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs in cannabinoid refinement and beyond.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- Why Use Controlled Drying for Zr-doped CaO? Preserve Porosity and Prevent Agglomeration
- How much does biochar pyrolysis cost? Unpacking the $230/Ton Production Price
- What is the difference between centrifugation and filtration based on force used? A Guide to Choosing the Right Separation Method
- What are the advantages of using Extremely fast Joule Heating (EJH) equipment? Precision in Thin Film Synthesis
- What is the definition of sintering? Master Thermal Manufacturing for High-Density Solids
- Is biomass electricity cheap? The True Cost of Dispatchable Renewable Power
- What precautions should be taken when using FTIR analysis? Essential Steps for Reliable Spectroscopic Results
- Why is a powerful magnetic stirrer essential during photocatalytic degradation? Ensure Accurate Catalyst Performance















