Rotary vane vacuum pumps are versatile workhorses used in a vast range of industrial and scientific applications, from automotive manufacturing and food packaging to laboratory research and plastics forming. They are the go-to solution for processes requiring a consistent and strong "rough vacuum" level, which is the pressure range between atmospheric pressure and approximately 1 milliTorr.
Rotary vane pumps are the foundational tool for achieving rough vacuum. Their primary role is either to perform tasks that only require this level of vacuum or to act as a "roughing" pump that prepares a system for a more powerful high-vacuum pump.

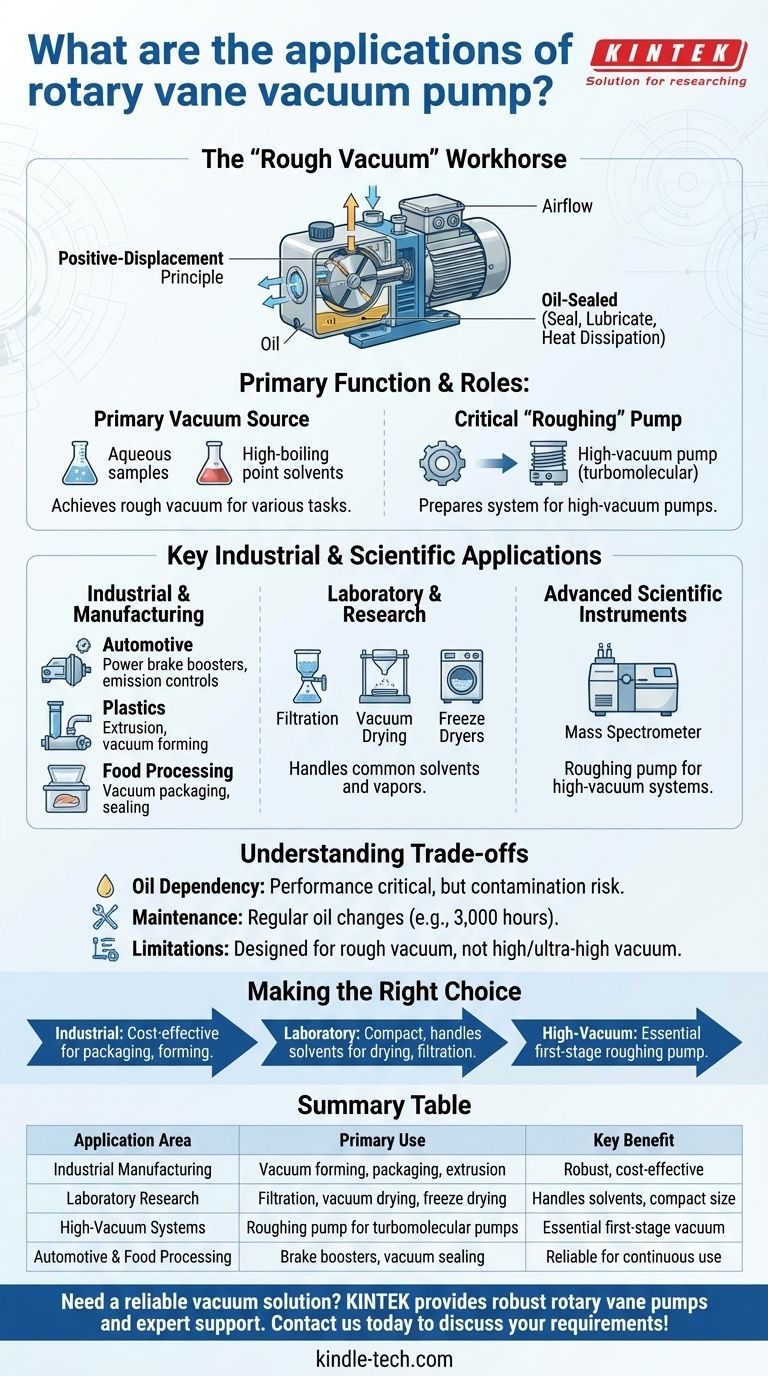
The Core Principle: The "Rough Vacuum" Workhorse
The primary function of a rotary vane pump is to remove air molecules from a sealed volume, creating a rough vacuum. This capability defines its role across all applications.
How a Rotary Vane Pump Works
This pump operates on a positive-displacement principle. Inside a chamber, an off-center rotor with sliding vanes traps, compresses, and then expels gas.
These are oil-sealed pumps. A specially formulated mineral oil fills the chamber, acting as a sealant for an airtight seal, a lubricant for the moving parts, and a medium for heat dissipation.
The Role as a Primary Vacuum Source
For many applications, the rough vacuum achieved by a rotary vane pump is all that is required. The pump acts as the primary and only vacuum source.
Its ability to handle aqueous samples and high-boiling point solvents is particularly valuable, as it can remove these vapors from a system effectively.
The Critical Role as a "Roughing" Pump
Many high-vacuum pumps, like turbomolecular or diffusion pumps, cannot start operating at atmospheric pressure. They would be damaged.
A rotary vane pump serves as the essential "roughing" pump, reducing the system pressure from atmospheric levels to a point where the high-vacuum pump can safely take over to achieve much lower pressures.
Key Industrial and Scientific Applications
The combination of cost-effectiveness, robust construction, and reliable performance makes these pumps fixtures in numerous fields.
Industrial and Manufacturing
In the automotive industry, these pumps are used for systems like power brake boosters and emission controls.
The plastics industry relies on them for processes like extrusion and vacuum forming, where a vacuum is needed to shape materials.
In food processing, they are critical for vacuum packaging and sealing, which extends the shelf life of products by removing air.
Laboratory and Research
Rotary vane pumps are standard equipment in labs for processes like vacuum drying, filtration, and operating freeze dryers.
Their compact size and performance make them ideal for benchtop applications where a consistent vacuum source is needed.
Advanced Scientific Instruments
In high-tech research, their most important role is as a roughing pump. Systems like mass spectrometers require a high vacuum to function, and a rotary vane pump is the indispensable first stage in that process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, rotary vane pumps have specific operational requirements and limitations that are important to understand.
The Need for Oil
Being oil-sealed is both a strength and a maintenance point. The oil is critical for performance, but it can become contaminated over time.
Maintenance Requirements
Regular maintenance is necessary for longevity and optimal performance. This primarily involves periodic oil changes, typically recommended after every 3,000 hours of operation, to prevent wear and ensure a strong vacuum seal.
Performance Limitations
It is critical to remember that these pumps are designed for the rough vacuum range. They cannot, on their own, achieve the high or ultra-high vacuum levels required for more sensitive applications like surface science or particle accelerators.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right vacuum technology depends entirely on your pressure requirements and operational context.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective industrial processes: A rotary vane pump is an excellent choice for applications like packaging, forming, or filtration due to its robust nature and good airflow.
- If your primary focus is general laboratory work: Its compact size and ability to handle common solvents and vapors make it a reliable and practical tool for drying, concentration, and filtration.
- If your primary focus is achieving high vacuum: You will need a rotary vane pump as a critical first-stage roughing pump, which must be paired with a secondary high-vacuum pump.
Understanding the role and limits of the rotary vane pump empowers you to build a more effective and reliable vacuum system.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Primary Use | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial Manufacturing | Vacuum forming, packaging, extrusion | Robust, cost-effective performance |
| Laboratory Research | Filtration, vacuum drying, freeze drying | Handles solvents, compact size |
| High-Vacuum Systems | Roughing pump for turbomolecular pumps | Essential first-stage vacuum source |
| Automotive & Food Processing | Brake boosters, vacuum sealing | Reliable operation for continuous use |
Need a reliable vacuum solution for your lab or production line? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing robust rotary vane pumps and expert support for your specific application. Whether you require a primary vacuum source for filtration or a roughing pump for advanced instruments, we have the right solution to enhance your system's efficiency and reliability. Contact us today to discuss your vacuum requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rotary Vane Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Electric Heated Hydraulic Vacuum Heat Press for Lab
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of rotary vane pumps? Unlock Cost-Effective, High-Performance Vacuum
- What are the common configurations and typical performance specifications of Rotary Vane Vacuum Pumps? Expert Guide
- How do you inspect a vacuum pump? A Step-by-Step Guide to Ensure Peak Performance
- What are the limitations of rotary vane pumps? Understanding Oil Dependence and Gas Compatibility
- What is the primary use of a Rotary Vane Vacuum Pump? Expert Guide to Gas Evacuation and Rough Vacuum Ranges



















