The primary types of compression molds are flash, positive, semi-positive, and landed positive. Each design is defined by how it contains the raw material and manages the flow of excess material, known as "flash," during the molding cycle. The selection of a specific mold type is a critical engineering decision that directly impacts part quality, material usage, and overall manufacturing cost.
The fundamental difference between compression mold types lies in how they control material pressure and overflow. Your choice moves along a spectrum from the economical but less precise flash mold to the exacting but higher-density positive mold, with semi-positive designs offering a versatile middle ground.
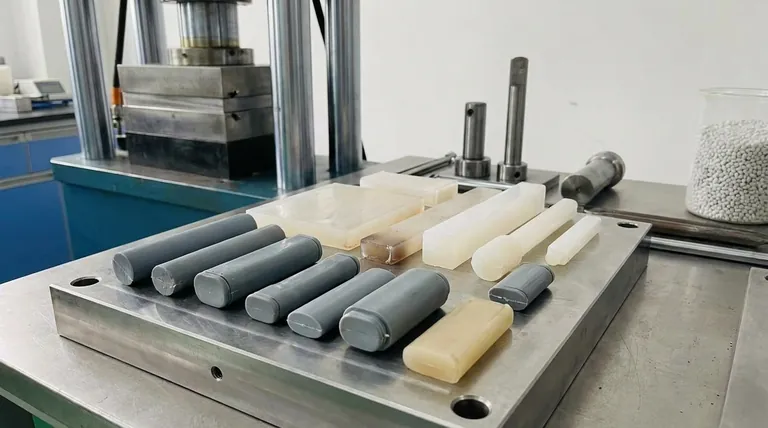

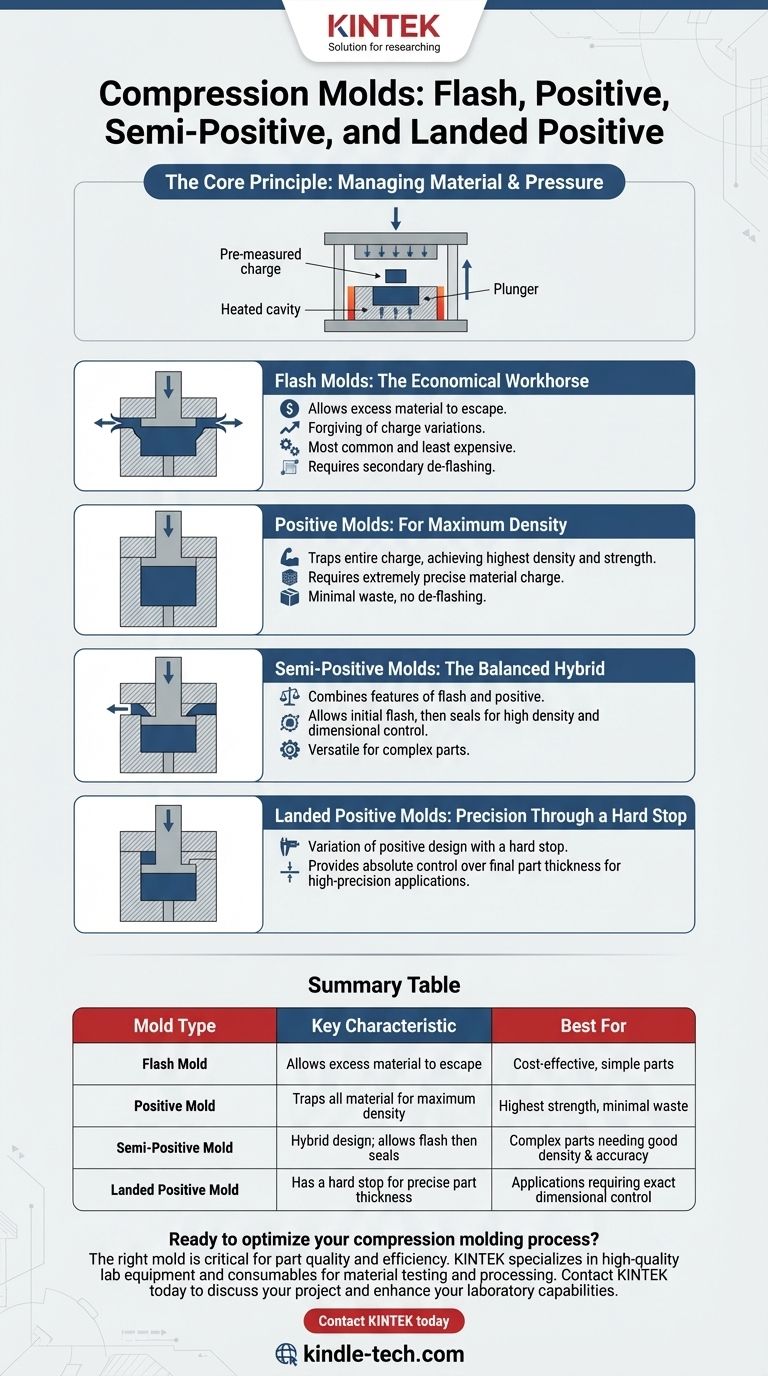
The Core Principle: Managing Material and Pressure
Compression molding fundamentally involves placing a pre-measured amount of material (the "charge") into a heated mold cavity. A plunger or top force then closes the mold, applying immense pressure that forces the material to conform to the cavity's shape.
The key differentiator among mold types is how they handle the fact that the material charge is rarely perfect. This leads to different strategies for controlling pressure and dealing with any excess material.
Flash Molds: The Economical Workhorse
A flash mold is designed so the two halves of the mold do not seal perfectly. A small, horizontal gap known as a "flash land" surrounds the cavity.
As pressure is applied, excess material is allowed to flow out of the cavity and into this land area, forming a thin sheet of flash. This makes the mold forgiving to slight variations in material charge. It is the most common and least expensive type of compression mold.
Positive Molds: For Maximum Density
A positive mold functions like a piston in a cylinder. The plunger fits tightly within the vertical walls of the cavity, leaving no room for material to escape.
This design traps the entire material charge, forcing all of it to be consolidated within the part. It achieves the highest possible part density and strength but requires an extremely precise material charge. Too little material results in an incomplete part; too much can damage the mold or press.
Semi-Positive Molds: The Balanced Hybrid
A semi-positive mold combines features of both flash and positive designs. It allows for a small amount of flash to escape initially, but as the mold closes further, the plunger enters the cavity, creating a positive seal.
This "best of both worlds" approach provides good dimensional control and high density while still being more forgiving of charge variations than a true positive mold. It is excellent for complex parts that require good surface quality and internal integrity.
Landed Positive Molds: Precision Through a Hard Stop
Also known as a "landed plunger" mold, this is a variation of the positive design. The key feature is a physical "land" or stop that halts the plunger's travel at a precise, predetermined depth.
This provides absolute control over the final part thickness, which is critical for many high-precision applications. While it still traps most material like a positive mold, the hard stop ensures dimensional consistency from part to part.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a mold type is not about which is "best," but which is best for a specific application. The decision involves balancing cost, part complexity, and quality requirements.
Cost vs. Precision
Flash molds are the least expensive to manufacture and operate because they don't require precise material weighing. However, they create material waste (the flash) and necessitate a secondary trimming operation, adding labor costs.
Positive molds are more expensive to build and demand strict process control for the material charge. The benefit is a net-shape part with minimal material waste and no secondary de-flashing.
Material Flow and Properties
The viscosity and flow characteristics of your chosen polymer (e.g., thermoset BMC, SMC, or thermoplastics) are critical. A very stiff or low-flow material may not fill the intricate features of a part if a flash mold allows too much pressure to bleed off.
In such cases, a semi-positive or positive mold is necessary to build the pressure required to ensure the cavity is completely filled.
Part Geometry
Simple, shallow parts are ideal candidates for flash molds.
Deep-draw parts or those with complex features, tall vertical walls, or varying thicknesses benefit from the superior pressure control of semi-positive and positive molds. These designs ensure that material is forced into every corner of the cavity, preventing voids and ensuring uniform density.
Selecting the Right Mold for Your Application
Your final choice depends on a clear understanding of your project's primary goal.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for high-volume, simple parts: A flash mold offers the lowest tooling cost and is forgiving in production.
- If your primary focus is maximum part density, strength, and minimal material waste: A positive mold is the ideal choice, but you must invest in precise charge control.
- If your primary focus is a balance of dimensional accuracy, good density, and design complexity: A semi-positive mold provides the most versatile and robust solution.
- If your primary focus is absolute control over a critical part thickness: A landed positive mold is the only design that guarantees this level of dimensional stability.
Choosing the correct mold is the first step toward efficient, high-quality production.
Summary Table:
| Mold Type | Key Characteristic | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Flash Mold | Allows excess material (flash) to escape | Cost-effective, simple parts |
| Positive Mold | Traps all material for maximum density | Highest strength, minimal waste |
| Semi-Positive Mold | Hybrid design; allows flash then seals | Complex parts needing good density & accuracy |
| Landed Positive Mold | Has a hard stop for precise part thickness | Applications requiring exact dimensional control |
Ready to optimize your compression molding process? The right mold is critical for achieving the perfect balance of part quality, material efficiency, and cost-effectiveness for your specific application. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including solutions for material testing and processing that support advanced molding techniques.
Let our experts help you select the ideal equipment for your needs. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project and discover how we can enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Isostatic Molding Pressing Molds for Lab
- Lab Sterile Slapping Type Homogenizer for Tissue Mashing and Dispersing
- Custom PTFE Wafer Holders for Lab and Semiconductor Processing
- Vacuum Cold Trap Direct Cold Trap Chiller
People Also Ask
- What are the factors affecting molding? Master the 4 Keys to Perfect Plastic Parts
- What are the different types of molds? A Guide to Choosing the Right Process for Your Product
- What are the two structures of molds? Understanding Hyphae and Mycelium
- What are molds used for? Unlock Mass Production of Precision Parts
- What are three-plate molds? Precision Injection Molding for Complex Parts



