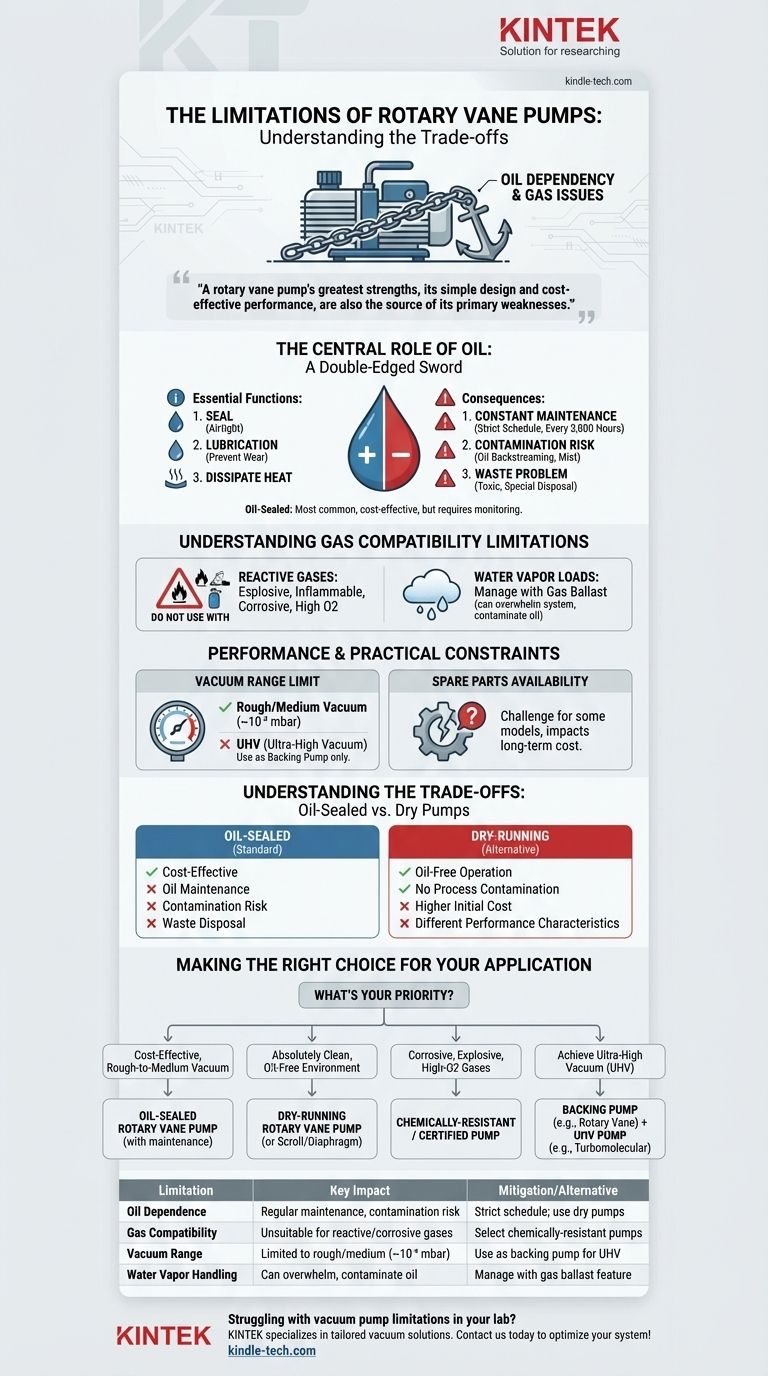
While rotary vane pumps are workhorses for achieving rough and medium vacuum, their limitations are significant and stem directly from their core design. The most critical drawbacks are their dependency on oil—which introduces maintenance requirements and contamination risks—and their incompatibility with certain types of gases.
A rotary vane pump's greatest strengths, its simple design and cost-effective performance, are also the source of its primary weaknesses. Understanding the trade-offs associated with its oil-based operation is the key to determining if it's the right tool for your specific application.

The Central Role of Oil: A Double-Edged Sword
The vast majority of rotary vane pumps are oil-sealed. This oil is not just a lubricant; it's a fundamental component of the pump's operation, but its presence creates several unavoidable challenges.
Why Oil is Essential
Oil serves three critical functions in these pumps: it creates an airtight seal between the vanes and the pump housing, it provides lubrication to prevent wear, and it helps dissipate heat generated during gas compression.
The Consequence: Constant Maintenance
This reliance on oil necessitates a strict maintenance schedule. The oil must be monitored and periodically changed, typically after every 3,000 hours of operation, to ensure the pump performs optimally and to prevent premature wear.
The Inevitable Risk of Contamination
Even with advanced filters and separators, oil-sealed pumps can introduce contamination. Small amounts of oil vapor, known as oil backstreaming, can migrate from the pump into your vacuum chamber, potentially contaminating sensitive samples or processes. They can also release an oil mist into the laboratory environment.
The Problem of Waste
The used pump oil is considered toxic waste and requires special handling and disposal procedures, adding an operational and environmental cost.
Understanding Gas Compatibility Limitations
A rotary vane pump cannot be used with all types of gases. The oil and internal components can react with or be damaged by certain substances, making gas compatibility a critical safety and operational constraint.
Unsuitability for Reactive Gases
Standard oil-sealed rotary vane pumps are not suitable for pumping explosive, inflammable, corrosive, or high-concentration oxygen gases. These substances can react with the pump oil or degrade the pump's internal components, leading to pump failure or a hazardous situation.
Managing High Water Vapor Loads
While these pumps can handle water vapor, especially with a feature called a gas ballast, this must be managed correctly. A gas ballast introduces a small amount of air to help flush vapors through the pump without condensing, but high vapor loads can still overwhelm the system and contaminate the oil, reducing performance.
Performance and Practical Constraints
Beyond oil and gas handling, there are practical limits to where and how a rotary vane pump can be deployed effectively.
The Vacuum Range Limit
Rotary vane pumps provide excellent, consistent pressure for rough and medium vacuum applications (down to about 10⁻³ mbar). However, they cannot achieve the ultra-high vacuum (UHV) ranges required for applications like particle accelerators or surface science research. In those systems, they are used only as "roughing" or "backing" pumps for a UHV pump.
Sourcing Spare Parts
Depending on the manufacturer and model, finding replacement spare parts can sometimes be a challenge. This can impact the long-term serviceability and total cost of ownership.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Oil-Sealed vs. Dry Pumps
It is crucial to distinguish between the two main types of rotary vane pumps, as their limitations differ significantly.
The Oil-Sealed Standard
Most of the limitations discussed—oil maintenance, contamination risk, and waste disposal—apply to oil-sealed pumps. They are the most common and cost-effective type.
The Dry-Running Alternative
Dry-running rotary vane pumps exist to solve the oil problem. They operate without any oil in the compression chamber, eliminating the risk of process contamination. However, this advantage comes with its own trade-offs, often including a higher initial cost and potentially different performance characteristics.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your decision must be based on a clear-eyed assessment of your process requirements against the pump's inherent limitations.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective rough-to-medium vacuum: An oil-sealed rotary vane pump is an excellent choice, provided you can implement a consistent maintenance schedule and your process is not sensitive to trace oil contamination.
- If your application demands an absolutely clean, oil-free environment: You must select a dry-running rotary vane pump or a different oil-free technology, such as a scroll or diaphragm pump.
- If you are working with corrosive, explosive, or high-oxygen gases: A standard rotary vane pump is unsuitable. You must specify a pump chemically-resistant or certified for your specific process gas.
- If you need to achieve ultra-high vacuum: A rotary vane pump will only serve as a backing pump and must be paired with a UHV pump like a turbomolecular or ion pump.
Ultimately, selecting the right vacuum pump means matching its operational design and inherent trade-offs with the non-negotiable demands of your goal.
Summary Table:
| Limitation | Key Impact | Mitigation/Alternative |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Dependence | Requires regular maintenance, risk of sample contamination | Strict oil change schedule; use dry pumps for clean processes |
| Gas Compatibility | Unsuitable for reactive/corrosive gases | Select chemically-resistant pumps for specific gases |
| Vacuum Range | Limited to rough/medium vacuum (down to ~10⁻³ mbar) | Use as backing pump for ultra-high vacuum systems |
| Water Vapor Handling | Can overwhelm system without proper gas ballast | Manage vapor loads with gas ballast feature |
Struggling with vacuum pump limitations in your lab? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing tailored vacuum solutions that address oil contamination, gas compatibility, and maintenance challenges. Our experts can help you select the right pump—whether oil-sealed, dry, or a specialized model—to ensure reliable performance and protect your sensitive processes. Contact us today to optimize your lab's vacuum system!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rotary Vane Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Electric Heated Hydraulic Vacuum Heat Press for Lab
People Also Ask
- Why is a gas ballast valve necessary on a rotary vane vacuum pump? Protect Your Oil and Extend Pump Life
- What is a Rotary Vane Vacuum Pump? Efficiency and Performance for Laboratory Vacuum Systems
- What are the advantages of rotary vane pumps? Unlock Cost-Effective, High-Performance Vacuum
- What are the fundamental differences between low-cost and high-end industrial rotary vane vacuum pumps? | KINTEK
- How does a Rotary Vane Pump operate? Discover Efficient Vacuum Technology for Your Lab



















