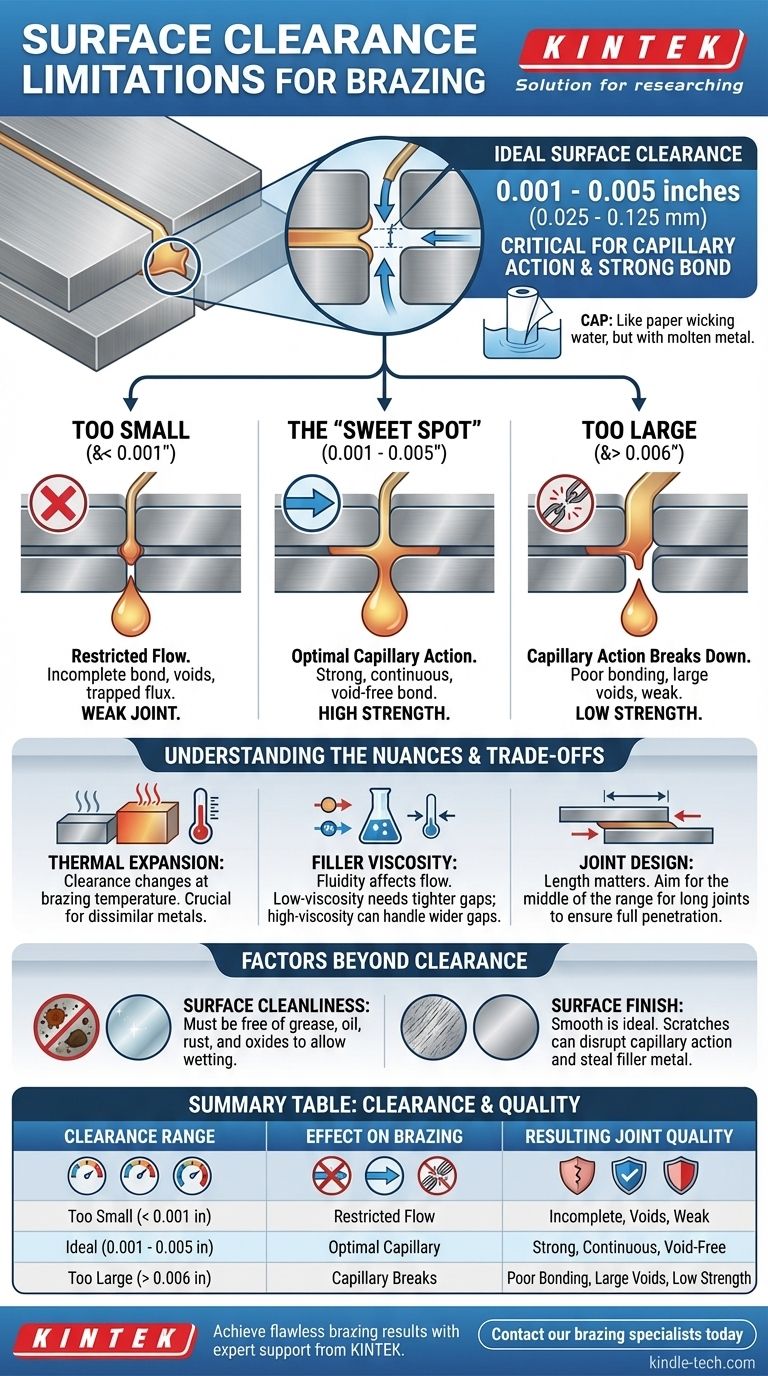
For a successful brazed joint, the ideal surface clearance is typically between 0.001 and 0.005 inches (0.025 mm to 0.125 mm). This precise gap is not arbitrary; it is the single most critical factor for enabling capillary action, the physical force that draws the molten filler metal into the joint to create a strong, continuous bond.
The challenge in brazing isn't simply meeting a clearance specification, but understanding that this gap is the environment that makes the process work. Your goal is to create the perfect channel for capillary action to pull the filler metal uniformly throughout the entire joint.

The Principle of Capillary Action: Why Clearance Matters
The entire brazing process relies on the physical phenomenon of capillary action. This is the tendency of a liquid to be drawn into a very narrow space, even against the force of gravity. The clearance you design directly controls the effectiveness of this force.
The "Sweet Spot" for Filler Flow
The optimal range of 0.001" to 0.005" creates the ideal conditions for capillary action. Think of it like a paper towel wicking up water; the narrow spaces between the fibers pull the water in.
In brazing, this force is strong enough to pull the molten filler metal deep into the joint, ensuring complete coverage and a void-free, high-strength bond.
The Problem with Too Little Clearance
If the gap is too small (typically below 0.001"), the molten filler metal cannot flow freely.
The filler may solidify before it fully penetrates the joint, trapping flux or creating voids. This results in an incomplete, unreliable bond that is significantly weaker than intended.
The Problem with Too Much Clearance
When the gap is too large (often above 0.006"), the force of capillary action breaks down.
Instead of being drawn in, the filler metal will not be able to bridge the gap effectively. This leads to large voids, inconsistent bonding, and a joint whose strength relies only on the filler metal itself, not the powerful bond with the base materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Nuances
While the general range is a reliable guide, several factors can influence the ideal clearance for your specific application. A true expert accounts for these variables.
Dissimilar Metal Thermal Expansion
This is the most common pitfall. The clearance you measure at room temperature is not the clearance at brazing temperature.
If you are joining two different materials, like steel and copper, their different rates of thermal expansion will change the gap. You must calculate the joint clearance at the brazing temperature to ensure it falls within the optimal range.
Filler Metal Viscosity
Different brazing alloys have different flow characteristics. A very fluid, low-viscosity filler metal might perform better in the tighter end of the clearance range, while a more sluggish alloy may require a slightly larger gap.
Joint Design and Length
The type of joint also plays a role. For a long lap joint, you may want to aim for the middle of the clearance range to ensure the filler metal has a clear path to travel the full distance without solidifying prematurely.
Factors Beyond Clearance That Ensure Success
Perfect clearance is necessary but not sufficient. The condition of the joint surfaces is equally important for enabling capillary action.
Critical Surface Cleanliness
As the references note, components must be completely clean and free from grease, oil, rust, and oxides. Any contaminant acts as a barrier, effectively blocking the filler metal from wetting the base material and stopping capillary flow in its tracks.
The Importance of Surface Finish
A smooth, uniform surface is ideal. Score marks, deep scratches, or rough, shot-blasted areas can disrupt capillary action. The filler metal can be pulled away from the joint and into these imperfections, starving the bond line of the material it needs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the target clearance requires balancing ideal strength with manufacturing reality. Use your primary objective as your guide.
- If your primary focus is maximum joint strength: Target the tighter end of the range, around 0.001" to 0.002", as this produces the strongest metallurgical bond.
- If your primary focus is accommodating production tolerances: A slightly wider clearance, from 0.002" to 0.005", may be more practical and cost-effective for high-volume manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is brazing dissimilar metals: Your first step must be to calculate the joint clearance at the brazing temperature to account for thermal expansion before selecting a target.
Mastering joint clearance is the key to creating consistent, reliable, and high-strength brazed assemblies.
Summary Table:
| Clearance Range | Effect on Brazing | Resulting Joint Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Too Small (< 0.001 in) | Filler metal flow is restricted | Incomplete bond, voids, weak joint |
| Ideal (0.001 - 0.005 in) | Optimal capillary action | Strong, continuous, void-free bond |
| Too Large (> 0.006 in) | Capillary action breaks down | Poor bonding, large voids, low strength |
Achieve flawless brazing results with expert support from KINTEK.
Perfect joint clearance is critical for creating strong, reliable bonds in your laboratory or production assemblies. Whether you're working with standard or dissimilar metals, KINTEK's expertise in lab equipment and consumables can help you optimize your brazing process for maximum strength and consistency.
Contact our brazing specialists today to discuss your specific application and discover how our solutions can enhance your results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety
- What is the purpose of inert atmosphere? A Guide to Protecting Your Materials and Processes
- What is an example of an inert atmosphere? Discover the Best Gas for Your Process
- What provides an inert atmosphere? Achieve Safety and Purity with Nitrogen, Argon, or CO2
- What gases are used in inert atmospheres? Choose the Right Gas for Non-Reactive Environments



















