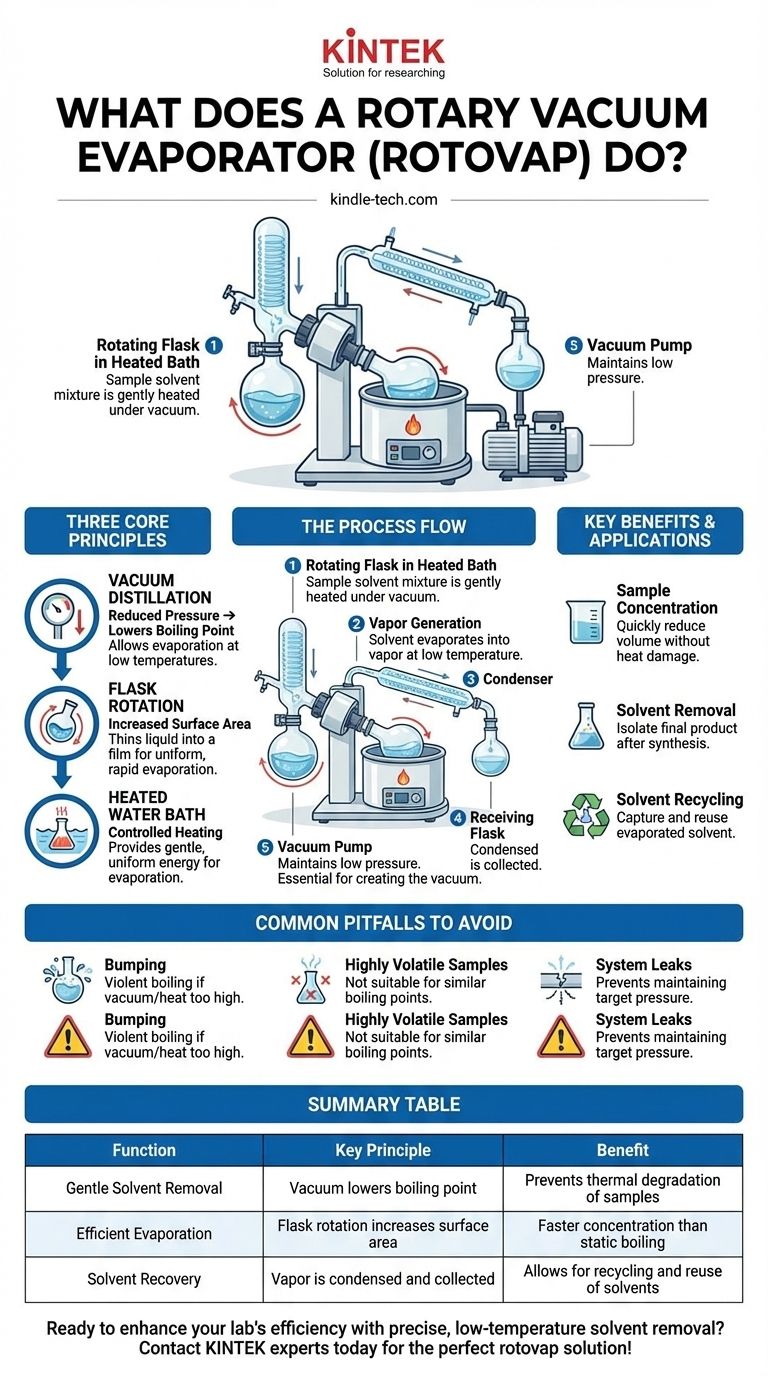
A rotary vacuum evaporator, often called a "rotovap," is a laboratory instrument designed to gently and efficiently remove solvents from a sample. It works by reducing the pressure over a liquid, which lowers its boiling point, allowing it to evaporate at a much lower temperature than normal. This process is combined with flask rotation to increase the surface area and ensure uniform, rapid evaporation without damaging heat-sensitive compounds.
The fundamental purpose of a rotary evaporator is to separate a volatile solvent from a non-volatile sample with speed and precision, all while preventing thermal degradation of the desired compound.

How a Rotary Evaporator Achieves Gentle Evaporation
A rotovap's effectiveness comes from the combination of three core principles: reduced pressure, increased surface area, and controlled heating.
The Principle of Vacuum Distillation
The heart of the process is vacuum distillation. By connecting the apparatus to a vacuum pump, the pressure inside is significantly lowered.
Lowering the pressure directly lowers a liquid's boiling point. This allows solvents like water or ethanol to boil at room temperature or with very mild heat, preventing the high temperatures that would destroy delicate chemical compounds.
The Role of Rotation
The rotation of the sample flask is what gives the instrument its name and is critical to its efficiency.
As the flask spins, it constantly spreads the liquid sample into a thin film on the interior wall. This dramatically increases the surface area available for evaporation, making the process much faster than static boiling. This rotation also provides gentle agitation, ensuring the sample is heated evenly.
The Importance of the Heated Bath
To facilitate evaporation, the rotating flask is partially submerged in a heated water bath.
This bath provides a gentle and highly controlled source of energy (heat) to the sample. It prevents the formation of "hot spots" that could cause decomposition and ensures the temperature remains just high enough to encourage evaporation at the reduced pressure.
The Condenser's Function
Once the solvent evaporates into a vapor, it must be removed from the system. The vapor travels into a condenser, which is a glass coil chilled with a circulating coolant.
Here, the vapor cools rapidly, turns back into a liquid, and is collected in a separate receiving flask. This not only isolates the solvent but also protects the vacuum pump from corrosive solvent vapors.
The Critical Role of the Vacuum Pump
It's important to understand that the rotary evaporator glassware and the vacuum pump are two parts of a single system. The rotovap itself cannot create a vacuum.
Creating the Low-Pressure Environment
The system relies on an external vacuum pump to evacuate the air and create the low-pressure environment needed for vacuum distillation.
Typically, a rotary vane pump is used to achieve the necessary "rough vacuum" range (from atmospheric pressure down to about 1 Torr) required for most solvent evaporations.
Why This System is Essential
This combination is indispensable in chemical and pharmaceutical labs. It's the standard method for concentrating a solution after an extraction or for removing the solvent after a chemical synthesis to isolate the final product.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
While highly effective, proper technique is essential for successful operation and to avoid damaging your sample.
The Risk of "Bumping"
If the vacuum is applied too quickly or the heat is too high, the liquid can boil violently. This phenomenon, known as bumping, can splash the sample out of the rotating flask and into the rest of the apparatus, resulting in sample loss and contamination.
Not for Highly Volatile Samples
If your desired compound is also volatile (has a low boiling point), it can evaporate along with the solvent. This makes the rotovap unsuitable for separating two liquids with similar boiling points.
System Integrity is Key
The entire glass apparatus must be perfectly sealed. Any air leaks will prevent the system from reaching and maintaining the target pressure, making the evaporation process slow or impossible.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
The rotary evaporator is a versatile tool used to achieve several common laboratory objectives.
- If your primary focus is sample concentration: The rotovap allows you to quickly reduce the volume of a solution to increase the concentration of your solute without heat damage.
- If your primary focus is solvent removal: After a chemical reaction or extraction, this is the standard method for stripping away the process solvent to isolate your crude product for purification.
- If your primary focus is solvent recycling: The condenser efficiently captures the evaporated solvent in a separate flask, allowing it to be recovered and reused.
Ultimately, the rotary evaporator is an indispensable tool for any process requiring precise, low-temperature solvent removal.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Principle | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Gentle Solvent Removal | Vacuum lowers boiling point | Prevents thermal degradation of samples |
| Efficient Evaporation | Flask rotation increases surface area | Faster concentration than static boiling |
| Solvent Recovery | Vapor is condensed and collected | Allows for recycling and reuse of solvents |
Ready to enhance your lab's efficiency with precise, low-temperature solvent removal? KINTEK specializes in high-quality rotary evaporators and lab equipment designed to meet the demanding needs of research and pharmaceutical laboratories. Contact our experts today to find the perfect rotovap solution for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rotary Vane Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Laboratory Benchtop Water Circulating Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of rotary vane pumps? Unlock Cost-Effective, High-Performance Vacuum
- How does a Rotary Vane Pump operate? Discover Efficient Vacuum Technology for Your Lab
- What is the primary use of a Rotary Vane Vacuum Pump? Expert Guide to Gas Evacuation and Rough Vacuum Ranges
- How do you inspect a vacuum pump? A Step-by-Step Guide to Ensure Peak Performance
- Why is a gas ballast valve necessary on a rotary vane vacuum pump? Protect Your Oil and Extend Pump Life



















