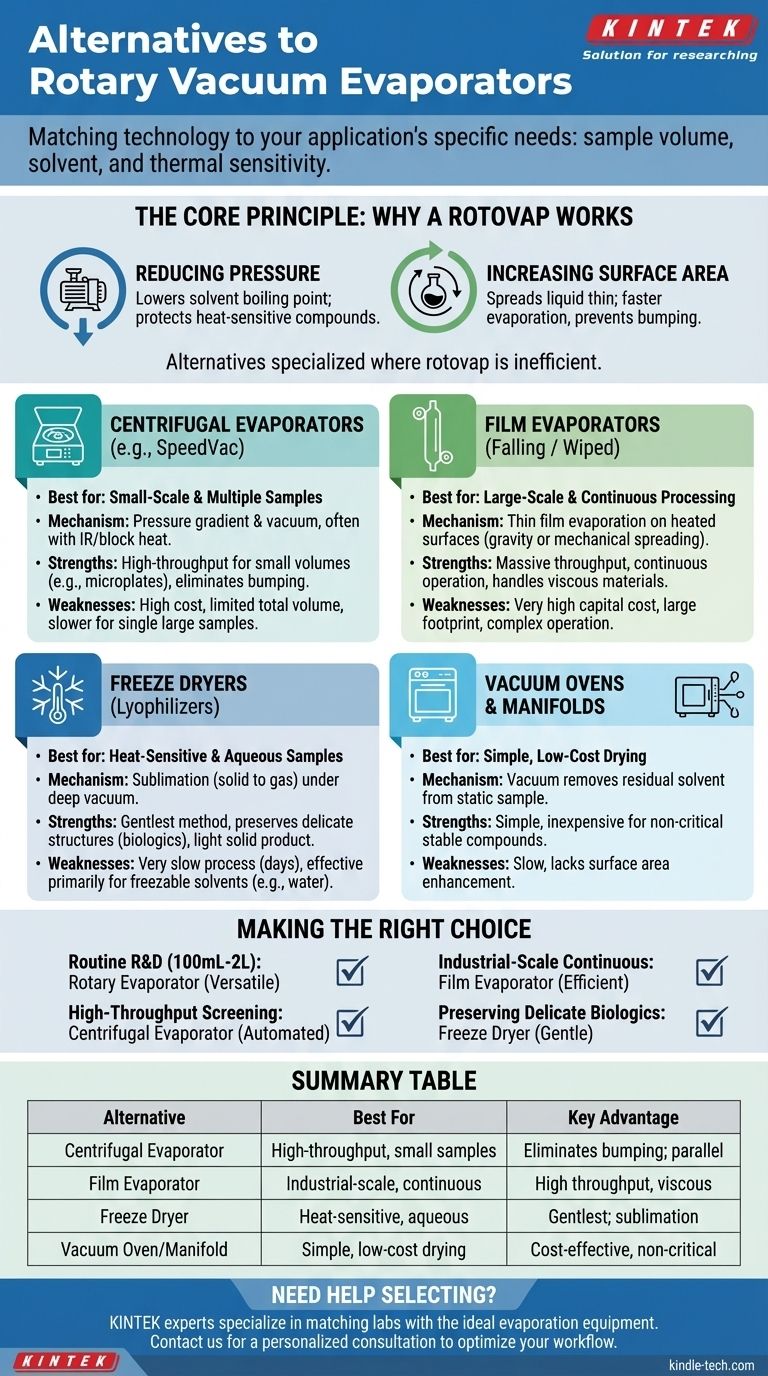
While the rotary evaporator is a laboratory staple, several powerful alternatives exist, each optimized for different needs. The most common alternatives are centrifugal evaporators (like a SpeedVac), falling or wiped film evaporators for industrial scale, and freeze dryers (lyophilizers) for extremely sensitive materials. The best choice depends entirely on your sample volume, solvent type, and processing goals.
The search for a rotary evaporator alternative is not about finding a "better" machine, but about correctly matching the evaporation technology to your specific application. The decision hinges on three factors: sample volume (scale), solvent properties, and the thermal sensitivity of your compound.
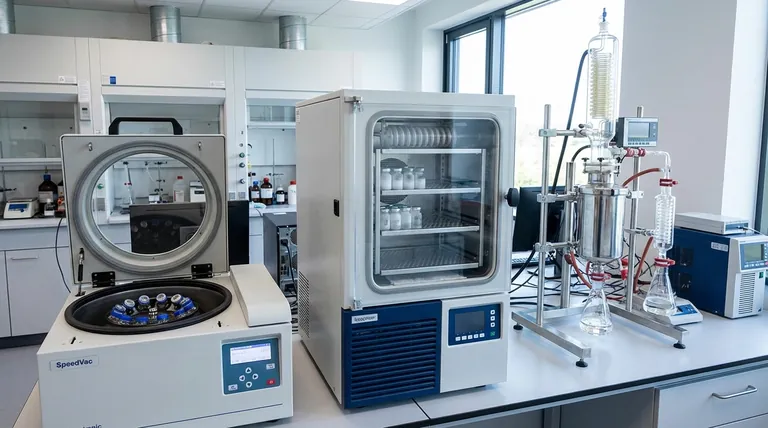

The Core Principle: Why a Rotovap Works
To understand the alternatives, we must first recognize what a rotary evaporator (rotovap) does so well. It efficiently removes a solvent from a solute by manipulating two key physical principles.
Reducing Pressure
A vacuum pump lowers the pressure inside the system. This directly reduces the solvent's boiling point, allowing for evaporation at a much lower temperature than would be required at atmospheric pressure. This is crucial for protecting heat-sensitive compounds.
Increasing Surface Area
The rotation of the flask continuously spreads the sample liquid into a thin film on the inner wall. This dramatically increases the surface area available for evaporation, making the process much faster and more efficient than static evaporation. It also provides gentle agitation that prevents violent bumping.
Key Alternatives, Categorized by Application
No single device replaces the rotovap in all scenarios. Instead, alternatives are specialized to excel where a rotovap may be inefficient or impractical.
For Small-Scale & Multiple Samples: Centrifugal Evaporators
A centrifugal evaporator (often known by the brand name SpeedVac or Genevac) is the go-to alternative for labs handling many small samples in parallel, such as in microplates or vials.
It uses a centrifuge to create a pressure gradient within the sample tubes, preventing bumping and solvent boiling over. Simultaneously, a vacuum pump removes the evaporated solvent, and infrared lamps or block heaters provide controlled energy for evaporation.
For Large-Scale & Continuous Processing: Film Evaporators
When you need to move beyond bench-scale batch processing, film evaporators are the industrial solution. They are designed for high-throughput, continuous operation.
Falling Film Evaporators introduce the liquid at the top of a long, heated tube. Gravity causes it to flow down the walls as a thin film, evaporating as it goes.
Wiped Film Evaporators (or Thin Film Evaporators) use mechanical blades or rollers to actively spread the liquid into an exceptionally thin, turbulent film against a heated surface. This is ideal for very viscous or heat-sensitive materials that require minimal residence time.
For Heat-Sensitive & Aqueous Samples: Freeze Dryers (Lyophilizers)
A freeze dryer doesn't evaporate a liquid but instead removes a frozen solvent through sublimation (transitioning directly from solid to gas). This is the gentlest method of solvent removal available.
The process involves freezing the sample and then applying a deep vacuum. This allows the frozen solvent (typically water) to turn directly into vapor, which is then collected on a cold condenser. It is the standard for preserving delicate biologicals like proteins, pharmaceuticals, and microorganisms.
For Simple, Low-Cost Drying: Vacuum Ovens & Manifolds
For the simplest applications, such as drying a stable compound in a flask, you don't always need a complex apparatus. A flask attached to a vacuum manifold (like a Schlenk line) or placed in a vacuum oven can effectively remove residual solvent. This process is slow and lacks the surface area enhancement of a rotovap, but it is simple and inexpensive for non-critical applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs of Each Method
Choosing the right tool requires an objective look at the benefits and drawbacks of each.
Rotary Evaporator: The Versatile Workhorse
- Strengths: Highly versatile for various solvents and volumes (50 mL to 5 L), provides excellent visual feedback, and is relatively cost-effective. It is the jack-of-all-trades for an R&D lab.
- Weaknesses: A manual, batch-based process. Glassware is fragile, and it is inefficient for very high-boiling point solvents or processing many small samples at once.
Centrifugal Evaporator: The Parallel Processor
- Strengths: Unmatched for high-throughput processing of small-volume samples (e.g., 96-well plates). Eliminates bumping risk.
- Weaknesses: High initial cost, generally limited to smaller total volumes per run, and can be slower than a rotovap for a single, large-volume sample.
Film Evaporators: The Industrial Scaler
- Strengths: Designed for massive throughput and continuous operation, making them ideal for pilot plants and manufacturing. Highly efficient for viscous or challenging materials.
- Weaknesses: Extremely high capital cost, large footprint, and significant operational complexity. Not suitable for small-scale, variable R&D work.
Freeze Dryer: The Gentle Guardian
- Strengths: The gentlest method available, preserving the structure of delicate molecules. Produces a light, fluffy solid that is easily redissolved.
- Weaknesses: A very slow process (can take days), primarily effective for freezable solvents (like water or t-butanol), and represents a significant capital investment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your evaporation method based on the primary goal of your work.
- If your primary focus is routine R&D with varied batch sizes (100 mL to 2 L): The rotary evaporator remains the most flexible and cost-effective choice for its versatility.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput screening of many small samples: A centrifugal evaporator is the superior tool for automated, parallel processing.
- If your primary focus is industrial-scale production with continuous flow: A falling or wiped film evaporator is the necessary solution for handling large volumes efficiently.
- If your primary focus is preserving delicate biologics or removing water at the lowest possible temperature: A freeze dryer (lyophilizer) is the only method that guarantees sample integrity through sublimation.
Ultimately, selecting the right tool requires a clear understanding of your sample, your solvent, and your desired scale.
Summary Table:
| Alternative | Best For | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Centrifugal Evaporator | High-throughput, small-volume samples | Eliminates bumping; parallel processing |
| Film Evaporator | Industrial-scale, continuous flow | High throughput for viscous materials |
| Freeze Dryer | Extremely heat-sensitive, aqueous samples | Gentlest method via sublimation |
| Vacuum Oven/Manifold | Simple, low-cost drying of stable compounds | Cost-effective for non-critical applications |
Need Help Selecting the Right Evaporation Equipment?
Choosing the wrong evaporation technology can lead to inefficient processes, damaged samples, or unnecessary costs. The expert team at KINTEK specializes in matching laboratories with the ideal equipment for their specific needs—whether you're scaling up production, handling delicate biologics, or require high-throughput screening.
We provide a comprehensive range of lab equipment and consumables, including rotary evaporators, centrifugal evaporators, and freeze dryers. Our specialists will work with you to understand your application, sample volume, and solvent properties to recommend the most effective and cost-efficient solution.
Let KINTEK help you optimize your lab's workflow. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation and discover the right evaporation technology for your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Ceramic Evaporation Boat Set Alumina Crucible for Laboratory Use
- Small Lab Rubber Calendering Machine
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
People Also Ask
- What is the importance of high-purity ceramic crucibles in carbide melting experiments? Ensure High-Temperature Accuracy
- How is deposition time calculated? Mastering the Clock for Strategic Legal Advantage
- What is thermal evaporation technique thin film deposition? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective PVD
- What is the meaning of thermal evaporation? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective Thin Film Coating
- What are the technical considerations for using an alumina crucible for silicone oil? Expert Vapor Deposition Guide



















