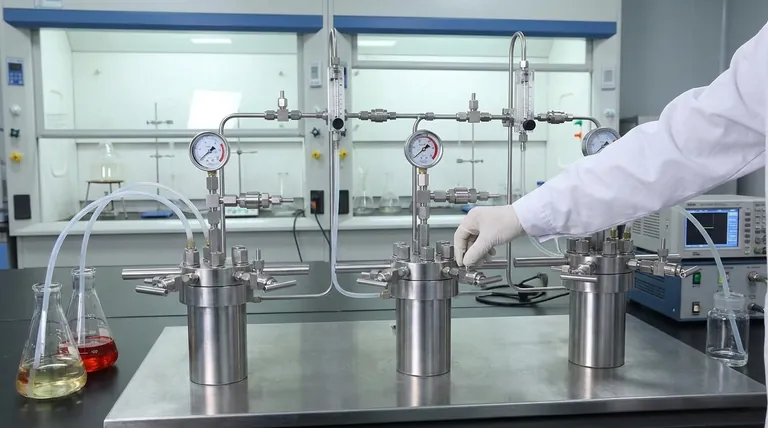
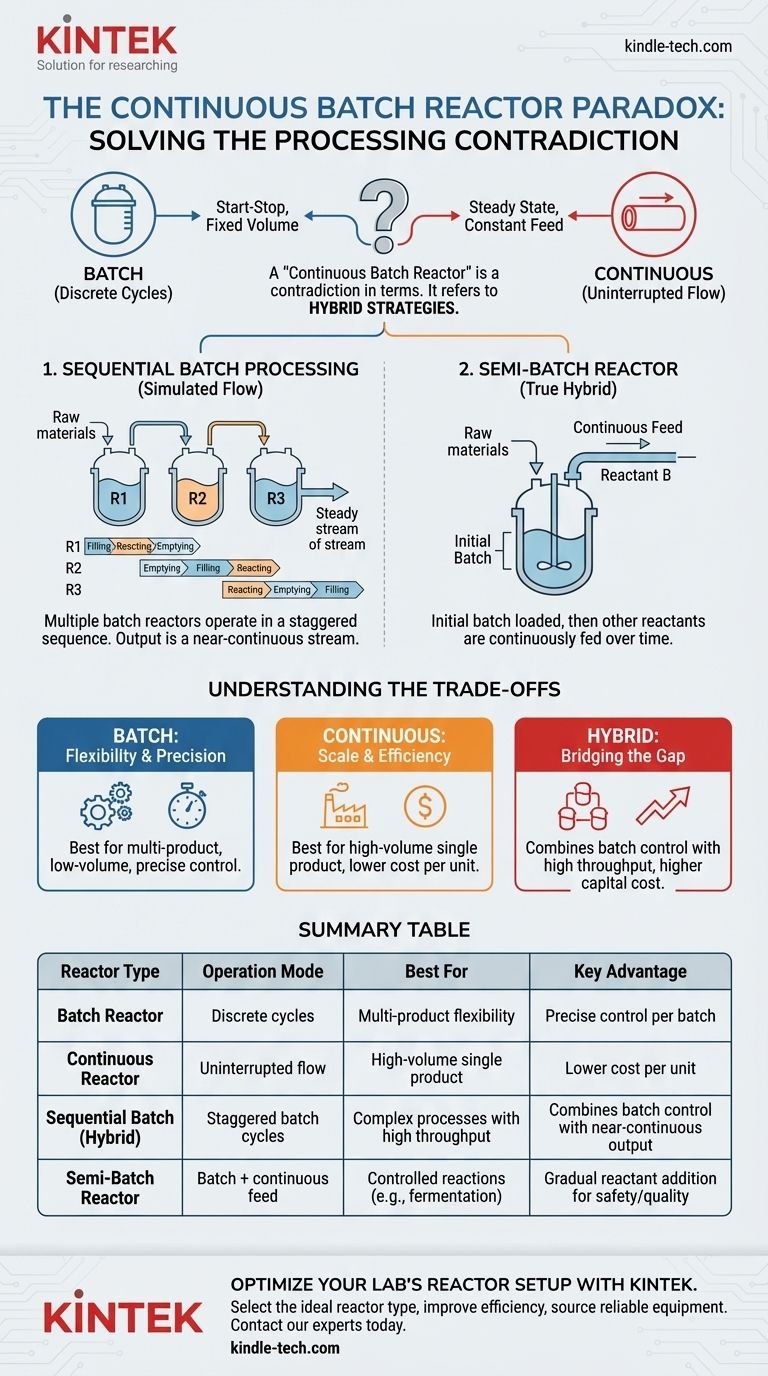
Strictly speaking, a "continuous batch reactor" is a contradiction in terms. In process engineering, "batch" and "continuous" describe two fundamentally different modes of operation. A batch process handles a fixed volume of material in a discrete cycle, while a continuous process involves a constant, uninterrupted flow of material. The term you've encountered likely refers to a hybrid operational strategy, not a single type of reactor.
The term "continuous batch reactor" is not a standard classification but usually describes one of two systems: a series of batch reactors operating in a staggered sequence to simulate a continuous output, or a semi-batch reactor where one material is added continuously to a fixed batch.

Understanding the Core Processing Modes
To understand the paradox, we must first define the two fundamental processing types clearly. Each serves a distinct purpose and carries its own set of advantages and limitations.
The Batch Reactor: A Self-Contained Process
A batch reactor is a closed system where a finite amount of raw material (a "batch") is loaded all at once. The materials undergo a process—such as mixing, heating, or reacting—for a set period. Once the process is complete, the entire finished batch is unloaded.
Think of it like baking a cake. You put all the ingredients in a bowl (the reactor), mix and bake them for a specific time, and then take the finished cake out. The vessel is then cleaned and ready for the next batch.
The Continuous Reactor: An Uninterrupted Flow
A continuous reactor operates with an uninterrupted flow. Raw materials are constantly fed into the reactor, and the finished product is simultaneously and continuously withdrawn. The process inside the reactor reaches a steady state, where conditions like temperature and concentration remain constant over time.
This is analogous to a manufacturing assembly line. Components are always entering one end, being worked on at various stations, and finished products are always emerging from the other end without stopping the line.
The Fundamental Contradiction
The two modes are opposites. Batch is defined by its start-and-stop cycles (discrete), while continuous is defined by its non-stop operation (flow). A single reactor cannot physically operate in both modes simultaneously.
Resolving the "Continuous Batch" Paradox
The term you've encountered arises from clever engineering solutions designed to get the benefits of both worlds. It almost always describes a system, not a single piece of hardware.
The Most Likely Reality: Sequential Batch Processing
This is the most common interpretation. A system is created using multiple batch reactors that run in a staggered sequence. While one reactor is in the middle of its processing cycle, another is being emptied and cleaned, and a third is being filled.
By carefully timing these cycles, the output from the overall system becomes a near-continuous stream of product. This gives the illusion of a "continuous batch" operation. It allows for the precise control of a batch process while achieving the high throughput of a continuous one.
The Alternative: The Semi-Batch Reactor
A semi-batch reactor is a true hybrid. In this setup, the reactor is initially loaded with some of the reactants (the batch component). Then, other reactants are fed into the reactor continuously over the course of the reaction.
A common example is in fermentation, where a culture of microorganisms is placed in the reactor (the batch), and a nutrient solution is fed in slowly and continuously to control the growth rate.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a processing strategy is a critical decision based on balancing cost, flexibility, and scale.
Why Choose Batch? Flexibility and Precision
True batch processing is ideal for manufacturing multiple different products in the same equipment, as it can be thoroughly cleaned between runs. It also offers exceptional control over reaction conditions and is well-suited for low-volume or high-value products.
Why Choose Continuous? Scale and Efficiency
Continuous processing is the backbone of large-scale commodity production (e.g., fuel, plastics, fertilizers). Its primary advantages are lower operational costs per unit of product and highly consistent product quality once a steady state is achieved.
The Hybrid Advantage: Bridging the Gap
A sequential batch system attempts to secure the best of both. It can handle complex, multi-step reactions that are difficult to manage in a true continuous flow, but it arranges them to produce a steady, high-volume output. The main trade-off is higher capital investment (multiple reactors) and greater operational complexity.
Selecting the Right Process for Your Goal
The choice between these systems depends entirely on your specific production needs and business objectives.
- If your primary focus is flexibility and producing multiple products: A true batch reactor system is your most effective and straightforward choice.
- If your primary focus is maximizing output for a single, high-demand product: A true continuous reactor is the most economically efficient solution at scale.
- If your primary focus is achieving high throughput for a complex process requiring precise cycle control: A sequential batch or semi-batch system is likely the "continuous batch" concept you are looking for.
By understanding the distinct principles of batch and continuous operation, you can design or select the process that perfectly aligns with your technical and commercial goals.
Summary Table:
| Reactor Type | Operation Mode | Best For | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Batch Reactor | Discrete cycles | Multi-product flexibility | Precise control per batch |
| Continuous Reactor | Uninterrupted flow | High-volume single product | Lower cost per unit |
| Sequential Batch (Hybrid) | Staggered batch cycles | Complex processes with high throughput | Combines batch control with near-continuous output |
| Semi-Batch Reactor | Batch + continuous feed | Controlled reactions (e.g., fermentation) | Gradual reactant addition for safety/quality |
Optimize Your Lab's Reactor Setup with KINTEK
Whether you're scaling up a batch process, designing a continuous flow system, or exploring hybrid solutions like sequential batch reactors, having the right equipment is crucial. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab reactors, fermenters, and supporting consumables tailored to your research and production needs.
We help you:
- Select the ideal reactor type for your specific process
- Improve efficiency and consistency in your lab operations
- Source reliable equipment for flexible or high-throughput applications
Ready to enhance your reaction processes? Contact our experts today to discuss your requirements and discover how KINTEK's solutions can drive your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a high-pressure reactor demonstrate its value in accelerated aging? Predict Catalyst Durability Fast
- Why are high-pressure autoclaves essential for preparing bio-based polyamide curing agents from dimeric acid?
- What is the role of high-pressure reactors in the study of alloy oxidation? Essential Tools for Supercritical Research
- What is the purpose of using a high-temperature hydrothermal reactor? Enhance Iodine@Activated Carbon Cathode Synthesis
- What roles do autoclaves play in MFI zeolite synthesis? Master Hydrothermal Crystalline Growth



















