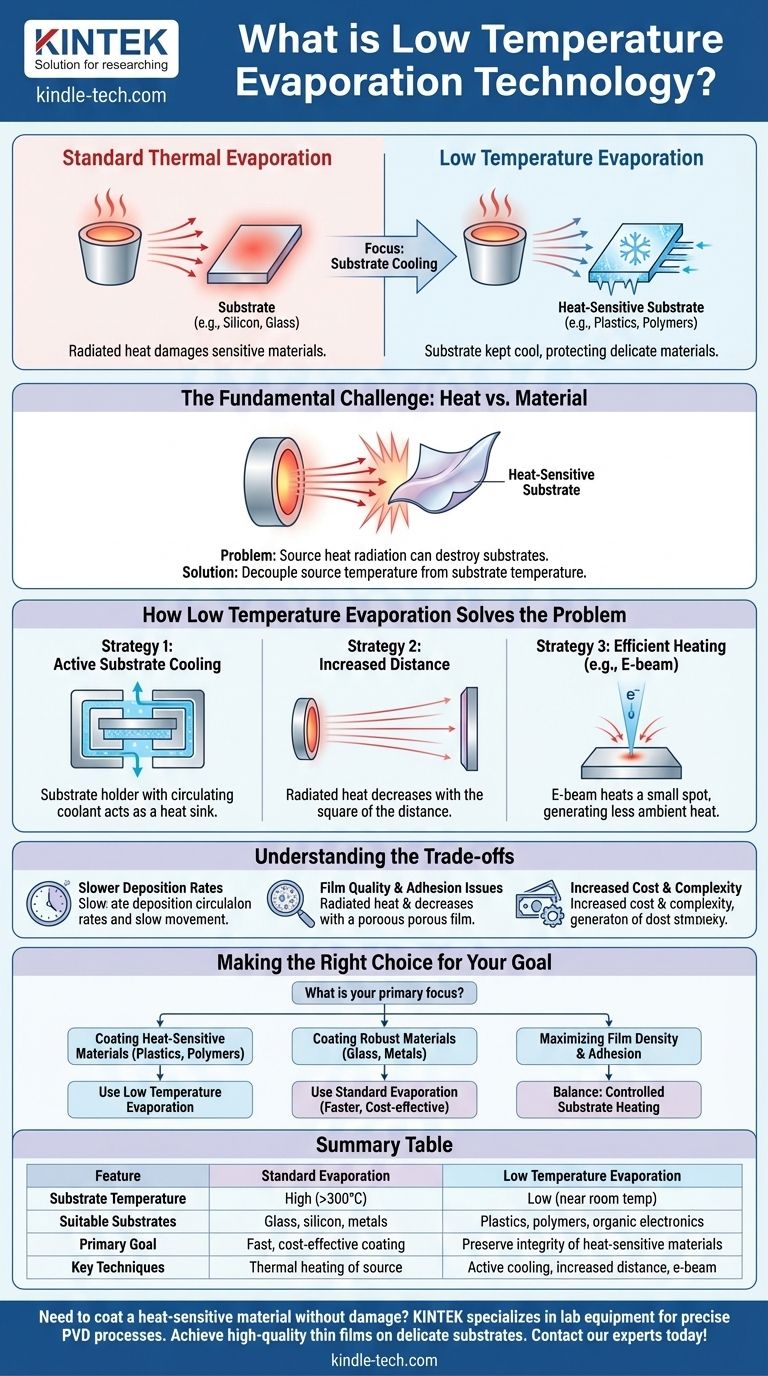
At its core, low temperature evaporation is a category of physical vapor deposition (PVD) processes engineered to deposit a thin film onto a surface while keeping the substrate's temperature minimal. Unlike standard thermal evaporation where radiated heat from the source can easily damage sensitive materials, these techniques focus on minimizing heat transfer to the object being coated. This allows for the successful coating of materials like plastics, polymers, and organic electronics that cannot withstand high temperatures.
The central challenge of evaporation is that you must heat a source material until it turns to vapor, but this process radiates significant heat that can destroy the very substrate you're trying to coat. Low temperature evaporation solves this by focusing on keeping the substrate cool, not by making the source cold.

The Fundamental Challenge: Heat vs. Material
To understand the value of low temperature evaporation, we must first understand the inherent conflict in the standard process.
How Standard Evaporation Works
In any PVD evaporation process, a source material (like aluminum or gold) is placed in a high-vacuum chamber. This material is then heated until its atoms or molecules gain enough energy to enter a gaseous phase. These vaporized particles travel in a straight line through the vacuum until they condense on the cooler substrate, forming a thin film.
The Problem of Radiated Heat
The source material must reach a very high temperature to create sufficient vapor pressure for an efficient coating process. This intensely hot source acts like a radiator, broadcasting thermal energy throughout the chamber. A substrate placed in the line of sight of this source will absorb this energy and heat up, often to several hundred degrees Celsius. This is not a problem for robust substrates like silicon wafers or glass, but it is catastrophic for heat-sensitive materials.
How Low Temperature Evaporation Solves the Problem
Low temperature evaporation is not a single technology but rather a collection of strategies designed to manage this heat transfer. The goal is always the same: keep the substrate temperature low while the source remains hot enough to evaporate.
It's About the Substrate, Not the Source
This is the most critical concept to grasp. You cannot perform evaporation with a "cold" source. The innovation lies in decoupling the source temperature from the substrate temperature.
Strategy 1: Active Substrate Cooling
The most direct method is to actively remove heat from the substrate as it is being deposited. This is typically done using a specialized substrate holder, or "chuck," that has channels for a coolant like chilled water to circulate through. This acts as a heat sink, pulling thermal energy away from the substrate and preventing it from overheating.
Strategy 2: Increasing Source-to-Substrate Distance
Radiated heat intensity decreases with the square of the distance. By simply moving the substrate further away from the evaporation source, the amount of thermal energy it absorbs is significantly reduced. This is a simple but effective way to lower the substrate's equilibrium temperature during deposition.
Strategy 3: More Efficient Heating Methods
Instead of heating a large crucible full of source material (a "boat"), techniques like electron-beam (e-beam) evaporation use a high-energy beam of electrons to heat a very small spot on the source material. This is far more energy-efficient and generates less ambient radiant heat, contributing to a lower overall substrate temperature.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Employing these strategies introduces new considerations and is not always the best approach for every application.
Slower Deposition Rates
Increasing the distance between the source and substrate doesn't just reduce heat; it also reduces the amount of material arriving at the substrate per second. This directly translates to slower deposition rates and longer process times.
Film Quality and Adhesion
Sometimes, a moderately elevated substrate temperature is beneficial. It can give the deposited atoms more surface mobility, allowing them to arrange into a denser, more ordered, and better-adhering film. Aggressively cooling the substrate can sometimes result in a more porous film with lower adhesion, a trade-off that must be managed.
Increased Cost and Complexity
Simple thermal evaporators are the least expensive PVD systems. Adding active cooling systems, larger chambers to accommodate longer throw distances, or sophisticated e-beam sources all add significant cost, complexity, and maintenance requirements to the system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use low temperature evaporation techniques depends entirely on the nature of your substrate and the desired properties of your film.
- If your primary focus is coating heat-sensitive materials (like plastics, polymers, or organic electronics): Low temperature evaporation is non-negotiable and essential to prevent substrate damage.
- If your primary focus is coating robust materials (like glass, silicon, or metals): Standard evaporation is often faster and more cost-effective, as the moderate heat exposure is not a concern and can even improve film quality.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum film density and adhesion: You may need to find a balance, potentially applying minimal, controlled heating to the substrate rather than aggressive cooling.
Ultimately, controlling substrate temperature is a critical variable that transforms evaporation from a brute-force process into a precise tool tailored to your material's needs.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Standard Evaporation | Low Temperature Evaporation |
|---|---|---|
| Substrate Temperature | High (can be >300°C) | Low (often near room temperature) |
| Suitable Substrates | Glass, silicon, metals | Plastics, polymers, organic electronics |
| Primary Goal | Fast, cost-effective coating | Preserve integrity of heat-sensitive materials |
| Key Techniques | Thermal heating of source | Active cooling, increased distance, e-beam |
Need to coat a heat-sensitive material without damage? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for precise PVD processes. Our expertise in low temperature evaporation technology can help you achieve high-quality thin films on plastics, polymers, and other delicate substrates. Let's discuss your application and find the right solution for your laboratory. Contact our experts today!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
People Also Ask
- What is plasma CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for Sensitive Materials
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Coating Solution for Sensitive Materials
- What are the advantages of plasma enhanced CVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















