In the world of cannabis concentrates, distillate represents the pinnacle of cannabinoid purity. It is a highly refined cannabis oil created not through a single extraction method, but through a multi-step process of initial extraction followed by fractional distillation. This process isolates specific cannabinoids, like THC or CBD, resulting in an exceptionally potent and versatile product that is nearly free of all other plant materials.
Distillation is not a primary extraction method itself, but rather an advanced refinement technique applied to crude cannabis oil. Its purpose is to separate compounds by their unique boiling points, systematically isolating cannabinoids to achieve the highest possible purity and potency.
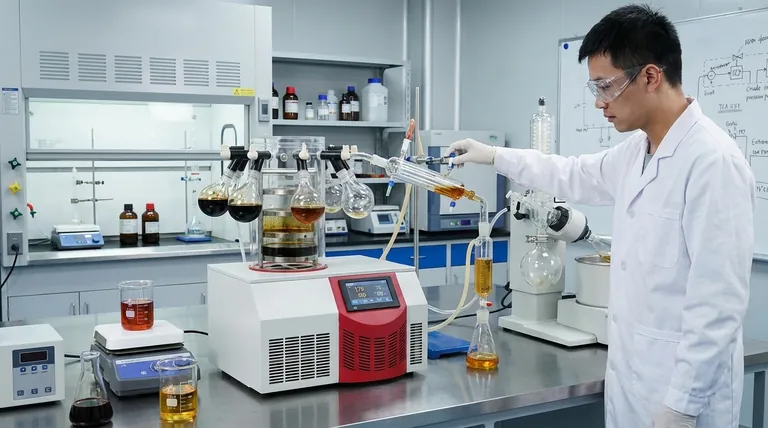

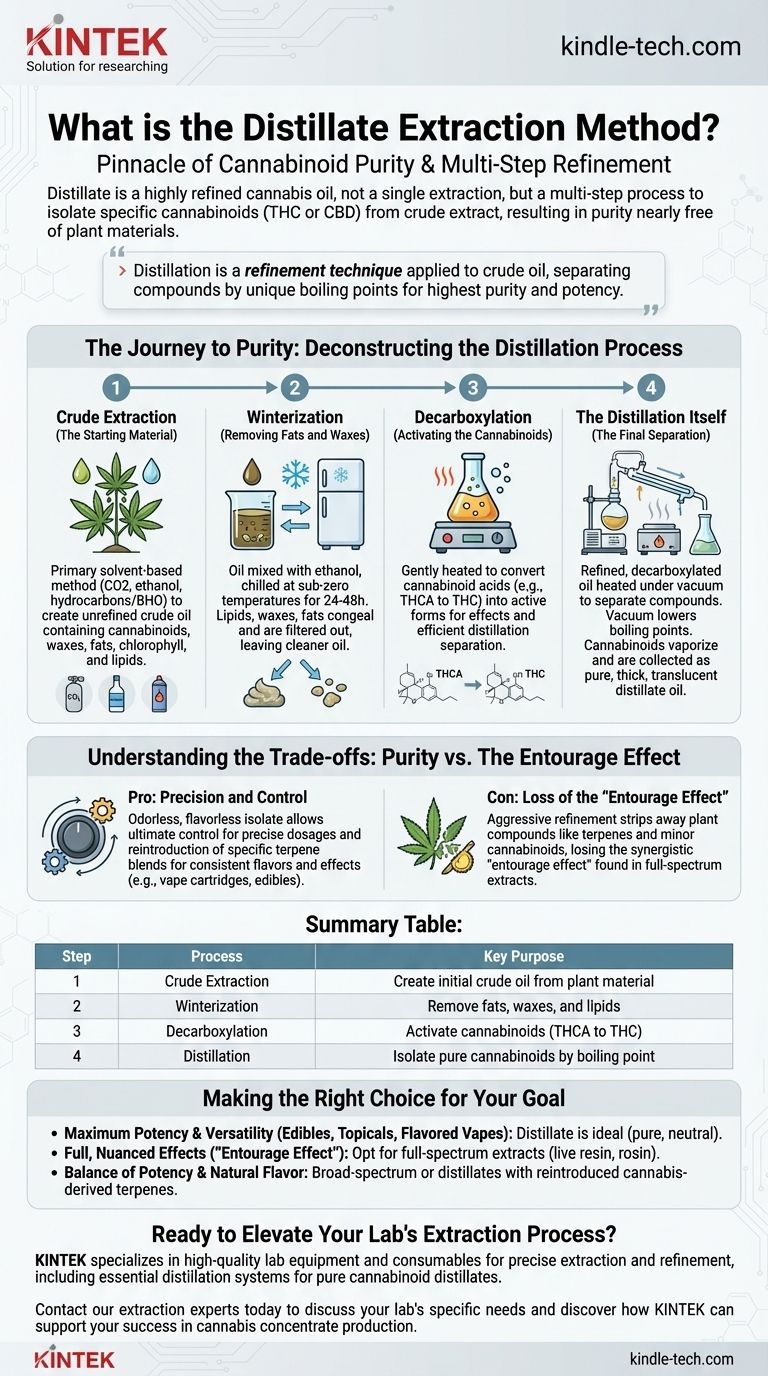
The Journey to Purity: Deconstructing the Distillation Process
Creating distillate is a meticulous, multi-stage journey. It begins with a crude extract and progressively refines it until only the target cannabinoids remain.
Step 1: Crude Extraction (The Starting Material)
Before distillation can begin, cannabinoids must be extracted from the raw plant material. This initial step uses a primary solvent-based method, such as CO2, ethanol, or a hydrocarbon like butane (BHO), to create a thick, unrefined crude oil. This oil contains cannabinoids, but also undesirable compounds like waxes, fats, chlorophyll, and lipids.
Step 2: Winterization (Removing Fats and Waxes)
The next step, winterization, targets the fats and waxes. The crude oil is mixed with ethanol and chilled at sub-zero temperatures for 24-48 hours. This extreme cold causes the lipids, waxes, and fats to congeal and separate from the solution. This solidified material is then removed through a filtration process, leaving behind a much cleaner, more fluid oil.
Step 3: Decarboxylation (Activating the Cannabinoids)
The oil is then gently heated in a process called decarboxylation. This crucial step removes a carboxyl acid group from cannabinoid acids (like THCA and CBDA), converting them into their "active" forms (THC and CBD). Activation not only makes the cannabinoids bioavailable for effects but also prepares them for efficient separation during distillation.
Step 4: The Distillation Itself (The Final Separation)
This is the core of the process. The refined, decarboxylated oil is placed into a short-path distillation system, which uses heat and vacuum pressure to separate compounds.
The vacuum is critical because it lowers the boiling points of cannabinoids, allowing them to be vaporized at temperatures low enough to prevent degradation. As the oil is slowly heated, compounds with lower boiling points (like residual terpenes) turn to vapor first and are collected separately. As the temperature rises further, the target cannabinoid (e.g., THC or CBD) vaporizes, travels through a condensing tube where it cools back into a liquid, and is collected in a separate flask as a pure, thick, translucent oil—the final distillate.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Purity vs. The Entourage Effect
While distillate's purity is its greatest strength, it also creates a fundamental trade-off that is critical to understand.
The Pro: Precision and Control
Because distillate is an odorless and flavorless isolate, it gives product manufacturers ultimate control. They can formulate products with exact, repeatable cannabinoid dosages. For vape cartridges, they can reintroduce specific terpene blends to create a wide variety of consistent flavors and effects, from "OG Kush" to "Blueberry."
The Con: Loss of the "Entourage Effect"
The aggressive refinement process that creates distillate strips away virtually all other plant compounds, including minor cannabinoids and, most notably, terpenes. Many believe these compounds work synergistically in what is known as the entourage effect, where the combined effect is greater than the sum of its parts. Full-spectrum extracts, like live resin, preserve these compounds, offering a more complex and nuanced experience that is closer to the original plant.
The Verdict: Purity is a Choice, Not a Mandate
Distillate is not inherently "better" or "worse" than a full-spectrum extract; it simply serves a different purpose. Its value lies in its consistency, potency, and neutrality, making it an ideal base for a vast range of commercial cannabis products. The choice between distillate and other concentrates depends entirely on the desired end-user experience.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When selecting a concentrate, your goal dictates the best option. Use this as your guide.
- If your primary focus is maximum potency and formulation versatility (for edibles, topicals, or flavored vapes): Distillate is the ideal choice due to its purity and neutral flavor profile.
- If your primary focus is experiencing the full, nuanced effects of the original plant (the "entourage effect"): You should opt for full-spectrum extracts like live resin or rosin, which preserve the natural terpene and cannabinoid profile.
- If your primary focus is a balance of high potency and natural flavor: Consider broad-spectrum products or distillates where cannabis-derived terpenes have been reintroduced.
Understanding that distillation is a tool for refinement allows you to select products based on your desired outcome, whether it's ultimate purity or a full-plant experience.
Summary Table:
| Step | Process | Key Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Crude Extraction | Use of CO2, ethanol, or hydrocarbons | Create initial crude oil from plant material |
| 2. Winterization | Mix with ethanol and chill | Remove fats, waxes, and lipids |
| 3. Decarboxylation | Gentle heating | Activate cannabinoids (THCA to THC) |
| 4. Distillation | Heat under vacuum pressure | Isolate pure cannabinoids by boiling point |
Ready to Elevate Your Lab's Extraction Process?
KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables needed for precise extraction and refinement, including the distillation systems essential for creating pure cannabinoid distillates. Our expertise ensures you have the reliable tools to achieve consistent, high-purity results.
Contact our extraction experts today to discuss your lab's specific needs and discover how KINTEK can support your success in cannabis concentrate production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- Why is a freeze dryer preferred for drying nickel nanoparticle precursors? Prevent Hard Agglomeration Now
- Why is a freeze dryer preferred over thermal drying for Fe-ZTA cermets? Ensure Pure, Homogeneous Slurry Processing
- What is the function of Freeze-thaw Equipment in Au-(PNiPAAm/PVA) hydrogel? Achieve High-Speed Photothermal Actuation
- Why is a freeze dryer preferred for reduced graphene oxide (Hh-RGO) powders? Preserve Nano-Structure and Performance
- What role does a laboratory freeze dryer play in the synthesis of graphene-based electrocatalysts? Preserve 3D Structures



















