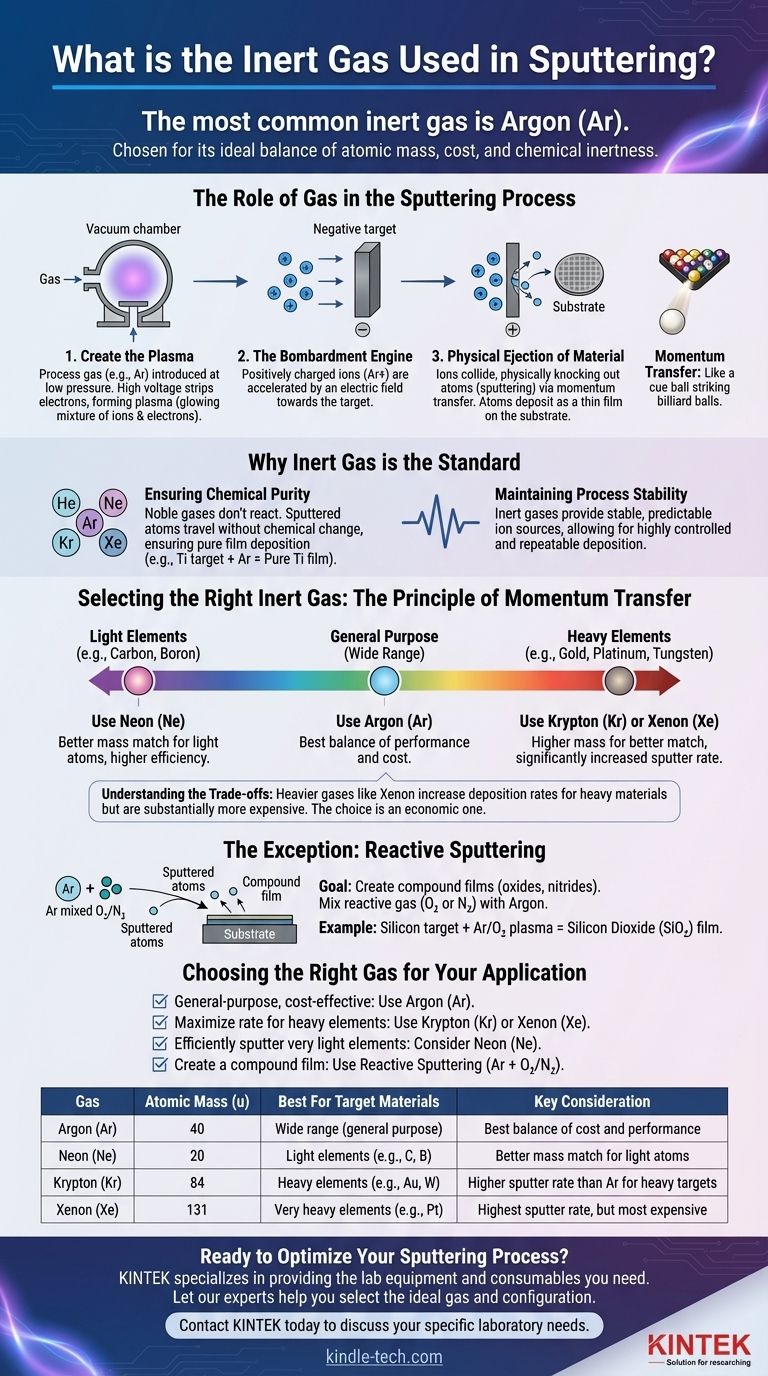
The most common inert gas used in sputtering is Argon (Ar). It is chosen for its ideal balance of atomic mass, cost, and chemical inertness. Argon atoms are ionized to form a plasma, and these ions are then accelerated to bombard a target material, physically ejecting atoms that deposit as a thin film onto a substrate.
The choice of gas in sputtering is a critical decision that dictates the efficiency and chemical nature of the deposition process. While Argon is the universal standard due to its cost-effectiveness, the optimal gas is selected based on a physical principle: matching the atomic mass of the gas to the target material for the most efficient momentum transfer.

The Role of Gas in the Sputtering Process
Creating the Plasma
The sputtering process begins in a vacuum chamber. A process gas, typically an inert gas, is introduced at very low pressure.
A high voltage is then applied, which strips electrons from the gas atoms. This creates a state of matter called plasma, a glowing mixture of positively charged gas ions and free electrons.
The Bombardment Engine
The positively charged ions within the plasma (e.g., Ar+) are powerfully accelerated by an electric field toward the target, which is the source material for the film and holds a negative charge.
Physical Ejection of Material
These high-energy ions collide with the target surface with immense force. The collision is a purely physical process based on momentum transfer, much like a cue ball striking a rack of billiard balls.
This impact physically knocks out, or "sputters," atoms from the target material. These sputtered atoms travel through the chamber and deposit onto a substrate (such as a silicon wafer or glass slide), gradually building up a thin film.
Why Inert Gas is the Standard
Ensuring Chemical Purity
The primary reason for using an inert gas is its non-reactive nature. Noble gases like Argon, Neon, Krypton, and Xenon do not readily form chemical bonds.
This ensures that the sputtered atoms from the target travel to the substrate without reacting with the process gas. If you sputter a pure titanium target with Argon, you deposit a pure titanium film.
Maintaining Process Stability
Inert gases provide a stable and predictable source of ions. They do not decompose or participate in unwanted side-reactions within the plasma, which allows for a highly controlled and repeatable deposition process.
Selecting the Right Inert Gas
Argon: The Workhorse of Sputtering
Argon is the default choice for a vast majority of sputtering applications. It is relatively inexpensive, readily available, and has an atomic mass that provides good sputtering efficiency for a wide range of common materials.
The Principle of Momentum Transfer
For the most efficient sputtering process, the atomic weight of the sputtering gas should be as close as possible to the atomic weight of the target material. Maximum energy transfer occurs when the colliding particles have similar masses.
Neon for Lighter Elements
When sputtering very light elements (e.g., Carbon, Boron), the lighter Neon (Ne) gas provides a better mass match than Argon. This results in more efficient energy transfer and a better sputtering yield for those specific targets.
Krypton and Xenon for Heavier Elements
Conversely, when sputtering heavy target materials (e.g., Gold, Platinum, Tungsten), heavier inert gases like Krypton (Kr) or Xenon (Xe) are used. Their higher mass provides a much better match, leading to a significantly increased sputtering rate.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Cost vs. Sputter Rate
While Xenon can dramatically increase the deposition rate for heavy materials, it is substantially more expensive than Argon. The decision becomes an economic one: the benefit of increased process speed and throughput must be weighed against the higher operational cost of the gas.
The Exception: Reactive Sputtering
In some cases, the goal is not to deposit a pure film but a compound film. This is achieved through reactive sputtering.
In this technique, a reactive gas like Oxygen (O₂) or Nitrogen (N₂) is intentionally mixed with the Argon. The sputtered target atoms react with this gas on their way to the substrate, forming an oxide or nitride film. For example, sputtering a silicon target in an Argon/Oxygen plasma creates a silicon dioxide (SiO₂) film.
Choosing the Right Gas for Your Application
Selecting the correct gas is fundamental to achieving your deposition goal. Your choice depends directly on the material you are sputtering and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose, cost-effective sputtering: Use Argon, as it provides the best balance of performance and cost for a wide array of materials.
- If your primary focus is maximizing the deposition rate of heavy elements (e.g., Gold, Platinum): Use a heavier gas like Krypton or Xenon, but be prepared for the higher cost.
- If your primary focus is sputtering very light elements efficiently: Consider Neon for a better mass match and more efficient momentum transfer.
- If your primary focus is creating a compound film (e.g., an oxide or nitride): You must use reactive sputtering by adding a gas like Oxygen or Nitrogen to your Argon plasma.
Ultimately, the gas you choose directly controls both the physical efficiency and the chemical outcome of your thin-film deposition process.
Summary Table:
| Gas | Atomic Mass (u) | Best For Target Materials | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Argon (Ar) | 40 | Wide range (general purpose) | Best balance of cost and performance |
| Neon (Ne) | 20 | Light elements (e.g., Carbon, Boron) | Better mass match for light atoms |
| Krypton (Kr) | 84 | Heavy elements (e.g., Gold, Tungsten) | Higher sputter rate than Ar for heavy targets |
| Xenon (Xe) | 131 | Very heavy elements (e.g., Platinum) | Highest sputter rate, but most expensive |
Ready to Optimize Your Sputtering Process?
The right inert gas is critical for achieving high-quality, efficient thin-film deposition. KINTEK specializes in providing the lab equipment and consumables you need to perfect your sputtering applications, from high-purity gas delivery systems to precision targets.
Let our experts help you select the ideal gas and configuration to maximize your deposition rate and film quality. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and discover how we can enhance your research and production outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Vacuum Cold Trap Direct Cold Trap Chiller
- Laboratory High Pressure Horizontal Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Conductive Boron Nitride Crucible BN Crucible
People Also Ask
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What is plasma CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for Sensitive Materials
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications










