At its core, the rotary vacuum evaporator process is a method of gentle distillation used to separate a liquid solvent from a sample. By combining rotation, controlled heat, and a vacuum, it allows the solvent to evaporate at a much lower temperature than its normal boiling point, thereby preserving the delicate, heat-sensitive components of the original sample.
The essential insight is that high heat is destructive. A rotary evaporator, often called a "rotovap," bypasses the need for high temperatures by using a vacuum to lower the solvent's boiling point, enabling efficient separation without damaging the product you want to keep.

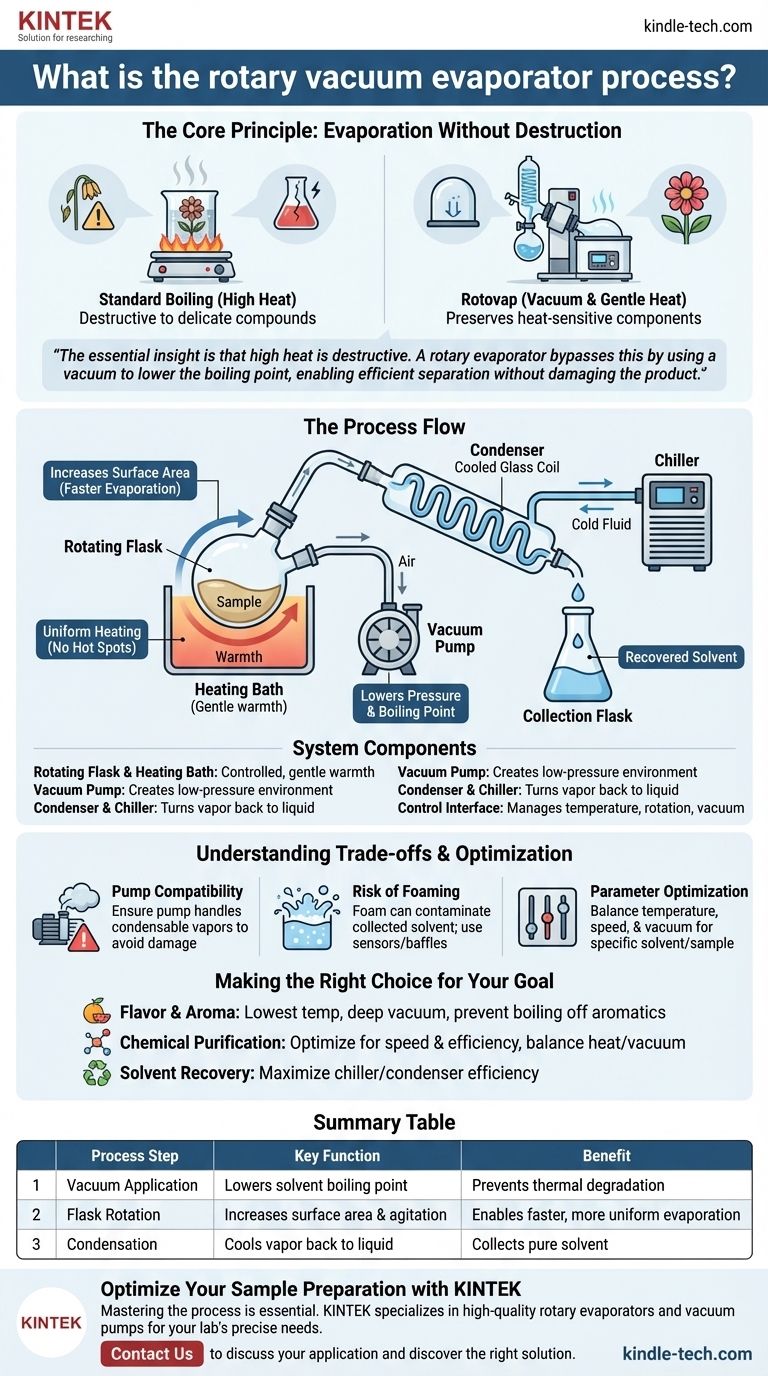
The Core Principle: Evaporation Without Destruction
Standard boiling is often a brute-force method. Applying high heat to a mixture can be effective for separating components, but it frequently destroys the very compounds, such as flavors and aromas, that you wish to preserve. The rotovap process was designed to solve this exact problem.
The Role of the Vacuum
The defining feature of this process is the vacuum. A vacuum pump removes air from the system, drastically lowering the internal pressure.
Boiling point is not a fixed number; it is dependent on the surrounding pressure. By creating a vacuum, the temperature at which a solvent will boil and turn to vapor is significantly reduced. This allows for evaporation at gentle, lukewarm temperatures, protecting the sample from thermal degradation.
The Importance of Rotation
The sample is held in a round flask that is continuously rotated. This rotation serves two critical functions.
First, it dramatically increases the surface area of the liquid, spreading it in a thin film along the inner wall of the flask. This larger surface area allows for much faster and more efficient evaporation.
Second, it provides constant agitation, ensuring the sample is heated evenly by the warming bath and preventing localized hot spots that could damage the product.
The Function of the Condenser
Once the solvent evaporates into a vapor, it needs to be removed and collected. The vapor travels into a cooled glass coil known as a condenser.
A chiller, typically containing a fluid like ethylene glycol, runs through the condenser to keep it extremely cold. When the warm solvent vapor hits the cold surface, it rapidly condenses back into a liquid, which then drips into a separate collection flask. This completes the separation process.
A Breakdown of the System's Components
Understanding the process is easier when you know the function of each part of the system.
The Rotating Flask and Heating Bath
The sample begins in a rotating flask, often called the "pot." This flask is partially submerged in a heating bath, which is usually filled with water and precisely temperature-controlled to provide gentle, consistent warmth.
The Vacuum Pump
This is the engine of the process. Rotary vane vacuum pumps are common, creating the low-pressure environment inside the system. A reliable pump is crucial for maintaining the deep vacuum needed to lower the boiling point effectively.
The Condenser and Chiller
This is the recovery unit. The condenser's cold coils are the destination for the solvent vapor. The chiller is an external refrigeration unit that continuously pumps cold fluid through the condenser to ensure it remains effective at turning vapor back into liquid.
The Control Interface
Modern systems use a central interface to manage the key variables. This allows an operator to set and monitor the rotation speed, heating bath temperature, and the precise level of vacuum to optimize the process for a specific solvent and sample.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
While highly effective, the rotovap process is not without its complexities. Achieving optimal results requires careful management of its variables.
Pump and Vapor Compatibility
The vacuum pump must be able to handle the condensable vapors of the solvent being removed. If the pump is not designed for this, the vapors can condense inside it, damaging the pump and reducing its ability to hold a vacuum.
The Risk of Foaming
Some samples have a tendency to foam or bubble vigorously under vacuum. This can cause the sample to be carried out of the rotating flask and into the condenser, contaminating the collected solvent and resulting in product loss. Accessories like foam sensors can help mitigate this.
Parameter Optimization
This is not a "one-size-fits-all" process. The ideal temperature, rotation speed, and vacuum level depend entirely on the specific solvent being removed and the nature of the sample. Finding the right balance is key to maximizing efficiency while protecting the final product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To apply this process effectively, you must first clarify your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is flavor and aroma concentration: Use the lowest possible temperature and a deep vacuum to gently remove water or alcohol without boiling off the volatile aromatic compounds.
- If your primary focus is chemical purification: Optimize for speed and efficiency by finding the ideal balance of heat and vacuum that removes the solvent quickly without degrading your target chemical compound.
- If your primary focus is solvent recovery: Ensure your chiller and condenser are operating at maximum efficiency to capture and reclaim as much of the evaporated solvent as possible.
Ultimately, mastering the rotary evaporator process is about using pressure as a tool to achieve gentle and precise separation.
Summary Table:
| Process Step | Key Function | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Application | Lowers solvent boiling point | Prevents thermal degradation of samples |
| Flask Rotation | Increases surface area & agitation | Enables faster, more uniform evaporation |
| Condensation | Cools vapor back to liquid | Collects pure solvent for recovery or disposal |
Optimize Your Sample Preparation with KINTEK
Mastering the rotary evaporator process is essential for efficiently concentrating flavors, purifying compounds, or recovering solvents without damaging your valuable samples. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including reliable rotary evaporators and vacuum pumps, designed to meet the precise needs of your laboratory.
Let our experts help you select the perfect system to enhance your workflow and protect your heat-sensitive materials. Contact us today to discuss your application and discover the right solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Benchtop Water Circulating Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Ceramic Evaporation Boat Set Alumina Crucible for Laboratory Use
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- How does the impeller rotation affect the gas flow in a water circulating vacuum pump? A Guide to the Liquid Ring Principle
- What are the failures in a hydraulic system? Prevent Costly Downtime with Expert Diagnosis
- What determines the vacuum degree achievable by a water circulating vacuum pump? Unlock the Physics of Its Limits
- What are the preventive maintenance of hydraulic systems? Extend Equipment Life and Maximize Uptime
- What types of gases can a water circulating vacuum pump handle? Safely Manage Flammable, Condensable & Dirty Gases



















