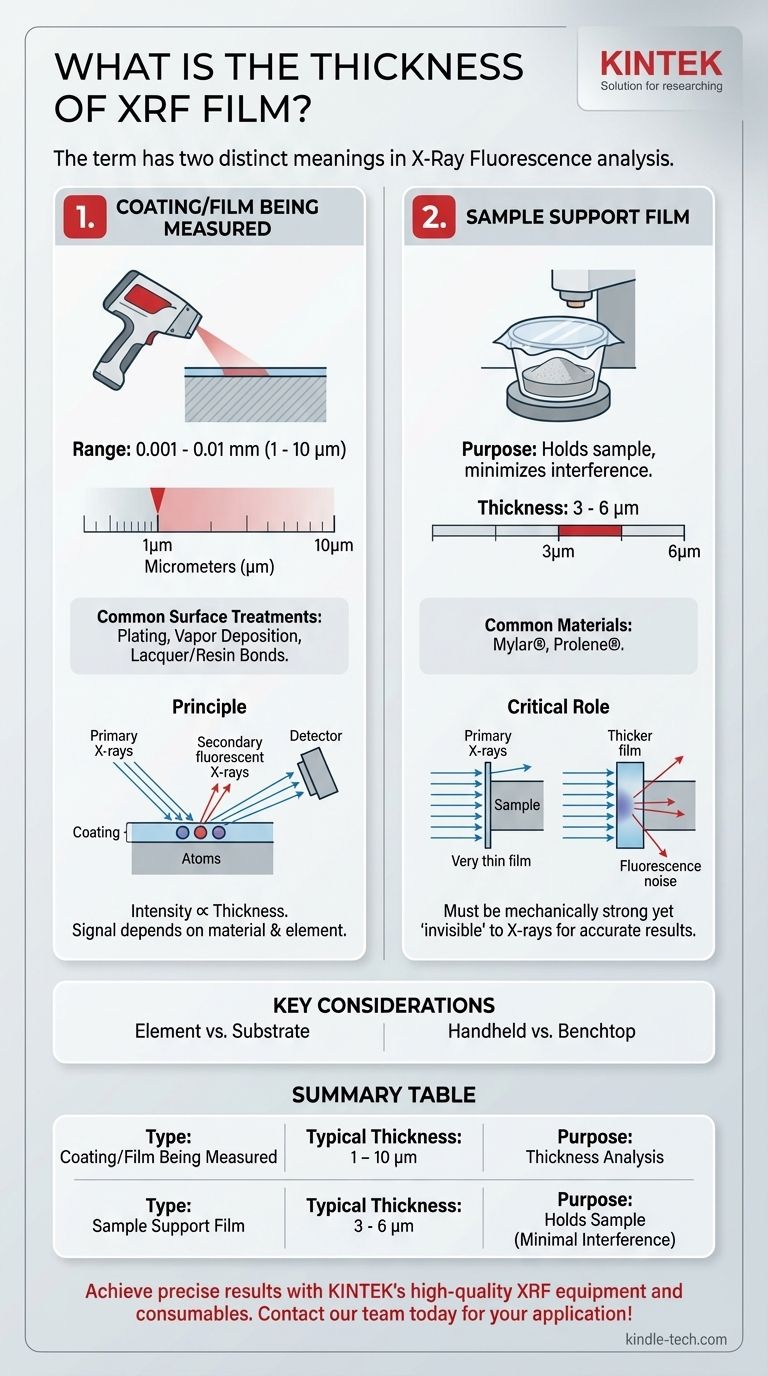
The measurable thickness of a film or coating using X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) typically ranges from 0.001 to 0.01 millimeters (mm). This range, equivalent to 1 to 10 micrometers (µm), is well-suited for analyzing common surface treatments like plating, vapor deposition, and various lacquer or resin bonds.
The term "XRF film" has two common meanings. It can refer to the thin coating being measured by the device, or it can refer to the thin polymer film used to hold a sample during analysis. Understanding which one applies to your situation is critical for accurate results.

Measuring Coating Thickness with XRF
X-Ray Fluorescence is a non-destructive analytical technique that is highly effective for determining the thickness and composition of thin layers of material.
The Principle of Measurement
An XRF instrument directs primary X-rays at a sample, causing atoms within the coating to become excited and emit secondary, "fluorescent" X-rays. The instrument's detector measures the intensity of these secondary X-rays.
Because the intensity of the signal is directly proportional to the number of atoms present, the analyzer can calculate the thickness of the coating material.
Typical Measurement Range
Handheld XRF analyzers can reliably measure thicknesses from 1 to 10 µm (0.001 to 0.01 mm). This capability covers a wide array of industrial and commercial finishing processes.
Dependence on Material
The effective measurement range is not universal; it depends heavily on the element being measured. The energy of the fluorescent X-rays and the density of the material both influence the depth from which a signal can be detected.
Understanding XRF Sample Support Films
In many XRF applications, especially with powders or liquids, a thin film is used to contain the sample in a sample cup. This is a fundamentally different context for the term "XRF film."
The Role of a Support Film
The purpose of this film is to hold the sample in place while being as "invisible" to the X-rays as possible. It must be mechanically strong enough to not break but thin enough to minimize any interference with the analysis.
Common Materials and Thicknesses
These support films are typically made of polymers like Mylar® or Prolene®. Their thickness is usually between 3 to 6 micrometers. This is extremely thin, ensuring maximum transparency to the X-rays and preventing contamination of the results.
Why Thinness is Critical
If the support film were too thick, it could absorb some of the primary or fluorescent X-rays, weakening the signal from the actual sample. The film material itself could also fluoresce, adding noise and leading to an inaccurate measurement.
Key Trade-offs and Considerations
Achieving an accurate thickness measurement requires understanding the limitations and variables involved in the process.
The Element vs. The Substrate
The material being measured is the primary factor. However, the substrate—the material underneath the coating—also matters. If the substrate contains elements that could interfere with the coating's signal, specialized calibrations may be required.
Handheld vs. Benchtop Instruments
The reference specifically notes the capabilities of handheld XRF. While incredibly versatile, these devices may have different sensitivities and limits compared to larger, more powerful benchtop XRF systems found in dedicated laboratories.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure accuracy, it's essential to apply these principles to your specific analytical task.
- If your primary focus is measuring a surface coating: Confirm that your expected thickness falls within the instrument's effective range (typically 1-10 µm) and that it is properly calibrated for the specific element you are analyzing.
- If your primary focus is selecting a sample support film: Choose the thinnest film (e.g., 3-6 µm Mylar® or Prolene®) that provides the necessary strength to reliably contain your sample without tearing.
Distinguishing between the film being measured and the film used for analysis is the foundation of precise and reliable XRF results.
Summary Table:
| Type of XRF Film | Typical Thickness | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Coating/Film Being Measured | 0.001 - 0.01 mm (1 - 10 µm) | Thickness analysis of platings, deposits, etc. |
| Sample Support Film | 3 - 6 µm | Holds powder/liquid samples for analysis with minimal interference |
Achieve precise and reliable thickness measurements with the right equipment. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including XRF analyzers and thin polymer support films. Our experts can help you select the perfect tools for your specific coating analysis or sample preparation needs, ensuring accurate results and enhanced lab efficiency. Contact our team today to discuss your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable XRD Sample Holders for Diverse Research Applications
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the factors that affect melting and boiling point? Unlock the Science of Phase Transitions
- How can corrosion of the sample holder be prevented when using corrosive chemicals? Protect Your Lab's Integrity
- What is the minimum sample required for XRD analysis? Optimize Your Material Analysis
- Why is an airtight sample holder with a beryllium window required for XRD of sulfide solid electrolytes?
- What are the specific storage requirements for a sample holder? Protect Your Lab's Critical Assets










