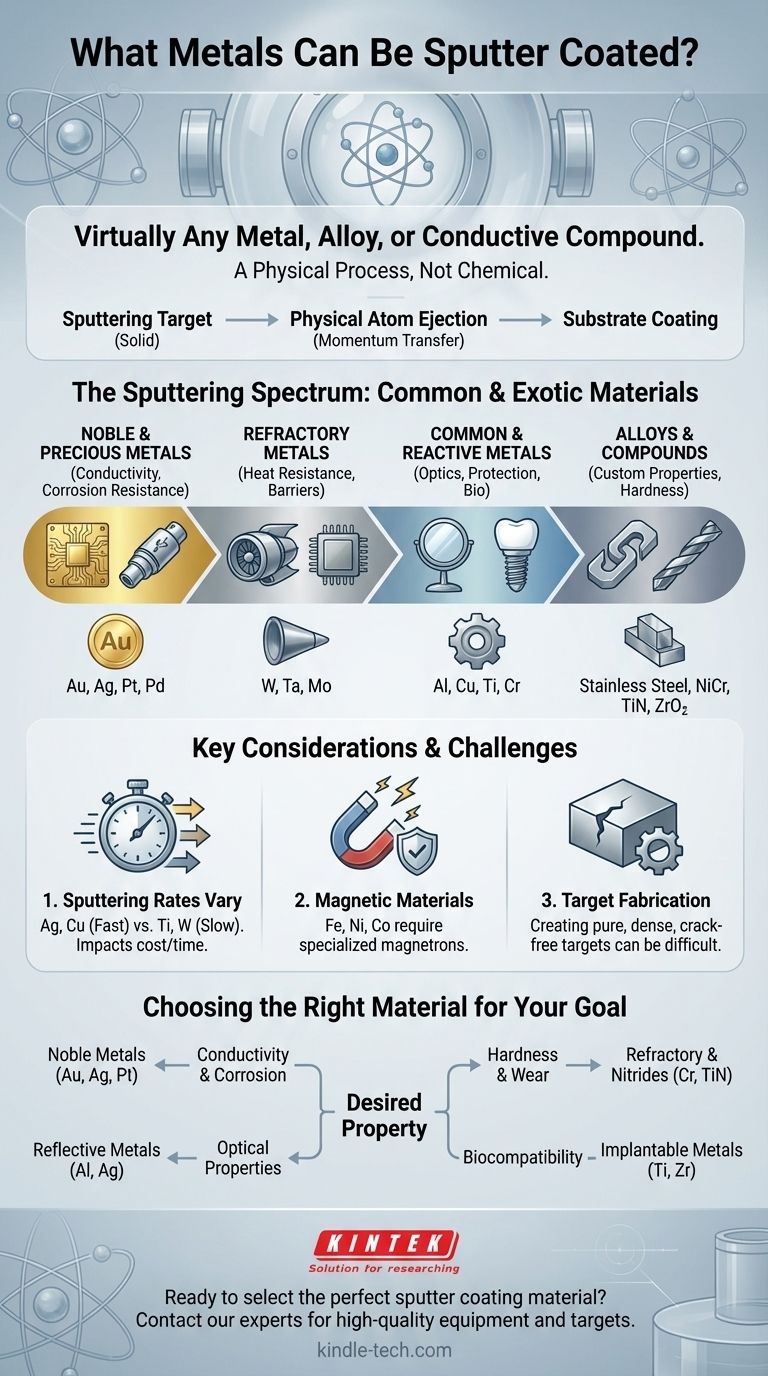
Virtually any metal, alloy, or even conductive compound can be used for sputter coating. The process is not limited to a select few materials like titanium or chromium; its versatility extends across nearly the entire periodic table. The primary physical limitation is not the element itself, but whether it can be fabricated into a solid source material, known as a "sputtering target."
The critical insight is that sputter coating is a physical process, not a chemical one. If a material can be formed into a solid target, it can be sputtered. This shifts the question from "what can be coated?" to "what properties do I need my coating to have?"

The Principle Behind Sputtering's Versatility
Sputter coating is fundamentally a momentum transfer process. It functions like an atomic-scale billiard game, where high-energy ions are accelerated to strike a source material (the target), knocking atoms loose which then deposit onto a substrate.
A Physical, Not Chemical, Process
Unlike processes that rely on melting, evaporation, or chemical reactions, sputtering is a mechanical action at the atomic level. This is why it works with materials that have extremely high melting points (like tungsten) or materials that would decompose before they evaporate.
The Importance of the Sputtering Target
The true limiting factor in sputtering is the target. This is a solid slab of the source material that must be engineered to be high-purity, dense, and uniform. If you can manufacture a stable target from a material, you can almost certainly sputter it.
From Pure Metals to Complex Compounds
The process is not restricted to pure elements. You can sputter:
- Pure Metals: Gold (Au), Aluminum (Al), Copper (Cu), Titanium (Ti), etc.
- Alloys: Stainless Steel, Nichrome (NiCr), and other custom metal mixtures.
- Compounds: By introducing a reactive gas like nitrogen or oxygen into the vacuum chamber, you can form compounds like Titanium Nitride (TiN) or Zirconium Oxide (ZrO₂), as mentioned in the references.
Common Examples Across the Spectrum
The range of sputter-able metals is vast and serves widely different industrial needs.
Noble and Precious Metals
Gold (Au), Silver (Ag), Platinum (Pt), and Palladium (Pd) are commonly sputtered. Their excellent conductivity and resistance to corrosion make them essential for coating electrical contacts and high-end electronics.
Refractory Metals
Metals with very high melting points, such as Tungsten (W), Tantalum (Ta), and Molybdenum (Mo), are easily deposited. They are used for applications requiring extreme heat resistance or as diffusion barriers in microchips.
Common and Reactive Metals
Workhorse metals like Aluminum (Al), Copper (Cu), Titanium (Ti), and Chromium (Cr) are among the most frequently sputtered materials. They are used for everything from creating reflective mirror coatings to providing hard, protective surfaces.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While nearly any metal can be sputtered, practical considerations and challenges exist.
Sputtering Rates Vary Significantly
Different materials have different sputter yields, meaning some eject atoms much more easily than others. Metals like silver and copper sputter very quickly, while materials like titanium or tungsten are much slower. This directly impacts manufacturing time and cost.
The Challenge of Magnetic Materials
Sputtering ferromagnetic materials like iron (Fe), nickel (Ni), and cobalt (Co) requires special consideration. Standard magnetron sputtering uses a powerful magnetic field, which can be shielded or trapped by these materials, making the process inefficient. Specialized magnetron designs are needed to handle them properly.
Target Fabrication Can Be the Main Hurdle
For exotic or brittle materials, manufacturing a high-quality, crack-free target can be the most difficult and expensive part of the entire process. This is often the primary practical barrier, not the physics of sputtering itself.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of metal should be driven entirely by the functional requirements of your final product.
- If your primary focus is conductivity and corrosion resistance: Noble metals like gold, platinum, or silver are the industry standard for high-performance electronics.
- If your primary focus is hardness and wear resistance: Refractory metals like chromium and titanium, often deposited with nitrogen to form nitrides, are excellent choices.
- If your primary focus is optical properties (like mirrors): Highly reflective metals such as aluminum or silver are the most common and cost-effective options.
- If your primary focus is biocompatibility: Medically-implantable metals like titanium and zirconium are frequently used for coatings on medical devices.
Ultimately, the versatility of sputter coating means your material choice is guided by the desired properties of the final film, not by the limitations of the process itself.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Common Examples | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Noble/Precious Metals | Gold (Au), Silver (Ag), Platinum (Pt) | High-end electronics, corrosion-resistant contacts |
| Refractory Metals | Tungsten (W), Tantalum (Ta), Molybdenum (Mo) | Heat-resistant coatings, diffusion barriers |
| Common/Reactive Metals | Aluminum (Al), Copper (Cu), Titanium (Ti) | Reflective coatings, protective surfaces, medical devices |
| Alloys & Compounds | Stainless Steel, Nichrome (NiCr), Titanium Nitride (TiN) | Custom material properties, enhanced hardness |
Ready to select the perfect sputter coating material for your specific application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including sputtering targets and coating systems. Our experts can help you navigate material choices based on your requirements for conductivity, hardness, optical properties, or biocompatibility.
Let us help you achieve superior coating results. Contact our team today to discuss your project needs and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why gold sputtering is used for SEM? Achieve Clear, High-Resolution Imaging of Non-Conductive Samples
- What is the purpose of the molding machine? Your Guide to Efficient Mass Production
- What is a pyrolysis fluidized bed reactor? Maximize Bio-Oil Yield with Superior Heat Transfer
- What is the future of synthetic diamonds? Reshaping the Market with Lab-Grown Technology
- How does a laboratory constant temperature drying oven assist in processing raw COF products? Master Material Activation
- What is the HIP process in ceramics? Achieve Full Density and Superior Mechanical Properties
- What are the advantages of using biomass? Achieve Renewable Energy & Waste-to-Power Solutions
- What is an example of fast pyrolysis? Converting Biomass to Bio-Oil in Under 2 Seconds



















