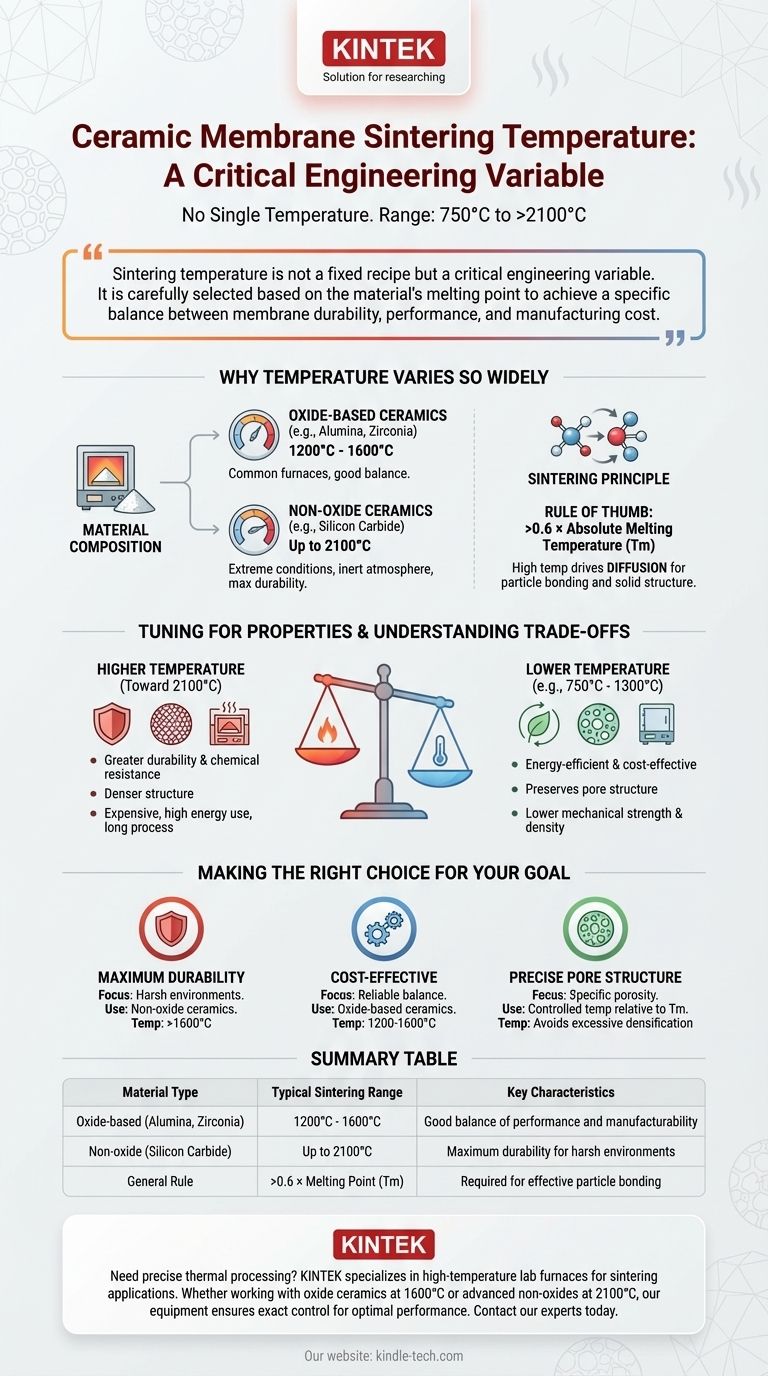
There is no single sintering temperature for ceramic membranes. The required temperature varies dramatically, typically falling within a broad range of 750°C to over 2100°C. This range is determined primarily by the specific ceramic material being used and the desired physical and chemical properties of the final membrane.
Sintering temperature is not a fixed recipe but a critical engineering variable. It is carefully selected based on the material's melting point to achieve a specific balance between membrane durability, performance, and manufacturing cost.

Why Sintering Temperature Varies So Widely
The significant temperature differences in ceramic membrane sintering are not arbitrary. They are dictated by fundamental material science and the intended application of the membrane.
The Critical Role of Material Composition
The most significant factor influencing sintering temperature is the type of ceramic powder used. Different materials require vastly different thermal energy to consolidate.
Oxide-based ceramics, like alumina or zirconia, are common and are typically sintered in furnaces at temperatures between 1200°C and 1600°C.
Non-oxide ceramics, such as silicon carbide, often require much more extreme conditions. To achieve maximum durability, these can be fired in a high-temperature furnace with an inert atmosphere at temperatures reaching up to 2100°C.
The Fundamental Principle of Sintering
As a rule of thumb, effective sintering requires a temperature greater than 0.6 times the material's absolute melting temperature (Tm). This principle explains why different materials need different heat treatments.
This high temperature provides the necessary thermal energy to drive diffusion. Atoms migrate across the surfaces of the powder particles, fusing them together, reducing surface area, and creating a solid, cohesive structure.
Tuning for Final Membrane Properties
Temperature directly controls the final characteristics of the membrane. Engineers manipulate the temperature to achieve a specific outcome.
Higher temperatures generally lead to a denser, stronger membrane with greater physical durability and chemical resistance. The process, however, can last for several days.
Lower temperatures might be used to preserve a specific pore structure or reduce energy consumption, but this can come at the cost of mechanical strength.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a sintering temperature involves a critical balance between achieving desired performance and managing practical constraints.
Higher Temperature: Durability vs. Cost
Pushing temperatures toward 2100°C creates exceptionally robust membranes suitable for harsh chemical environments.
However, this requires specialized, high-temperature furnaces, inert gas atmospheres, and immense energy consumption over several days, making it a very expensive process.
Lower Temperature: Efficiency vs. Performance
Operating in the lower range (e.g., 750°C to 1300°C) is far more energy-efficient and less costly.
The resulting membrane may have lower density and mechanical strength, making it unsuitable for high-pressure or chemically aggressive applications. The performance might be perfectly adequate for less demanding roles.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal sintering temperature is always tied to the end goal. Use the material and its properties as your guide.
- If your primary focus is maximum chemical and physical durability: You will need to work with high-performance, non-oxide ceramics sintered at very high temperatures, often exceeding 1600°C.
- If your primary focus is a standard, cost-effective membrane: Oxide-based ceramics sintered in the common 1200-1600°C range provide a reliable balance of performance and manufacturability.
- If your primary focus is preserving a highly specific pore structure: The temperature must be carefully controlled relative to the material's melting point to facilitate particle bonding without causing excessive densification or shrinkage.
Ultimately, the sintering temperature is the primary tool used to engineer a ceramic membrane for its specific purpose.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Typical Sintering Range | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Oxide-based (e.g., Alumina, Zirconia) | 1200°C - 1600°C | Good balance of performance and manufacturability |
| Non-oxide (e.g., Silicon Carbide) | Up to 2100°C | Maximum durability for harsh environments |
| General Rule | >0.6 × Melting Point (Tm) | Required for effective particle bonding |
Need precise thermal processing for your ceramic membranes? KINTEK specializes in high-temperature lab furnaces and consumables for sintering applications. Whether you're working with oxide ceramics at 1600°C or advanced non-oxides requiring 2100°C, our equipment ensures the exact temperature control and atmosphere conditions needed for optimal membrane performance. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific sintering requirements and achieve the perfect balance of durability, pore structure, and cost-efficiency for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is SiC melting point? Discover the Extreme Thermal Stability of Silicon Carbide
- What is the effect of heating rate on sintering? Achieve Uniform Density and Avoid Defects
- What are the effects of sintering temperature? Mastering the Balance Between Density and Microstructure
- Can ceramic withstand high heat? Understanding the Limits of Thermal Stability
- What are the 4 main classes of ceramic materials? A Guide to Their Functions and Applications
- What function do alumina ceramic plates serve as supports in the preparation of molecular sieve membranes?
- What is the role of polycrystalline alumina (Al2O3) substrates in YSZ thin film preparation? Enhance Film Integrity
- What is meant by ceramic powder? The Engineered Blueprint for Advanced Ceramics



















