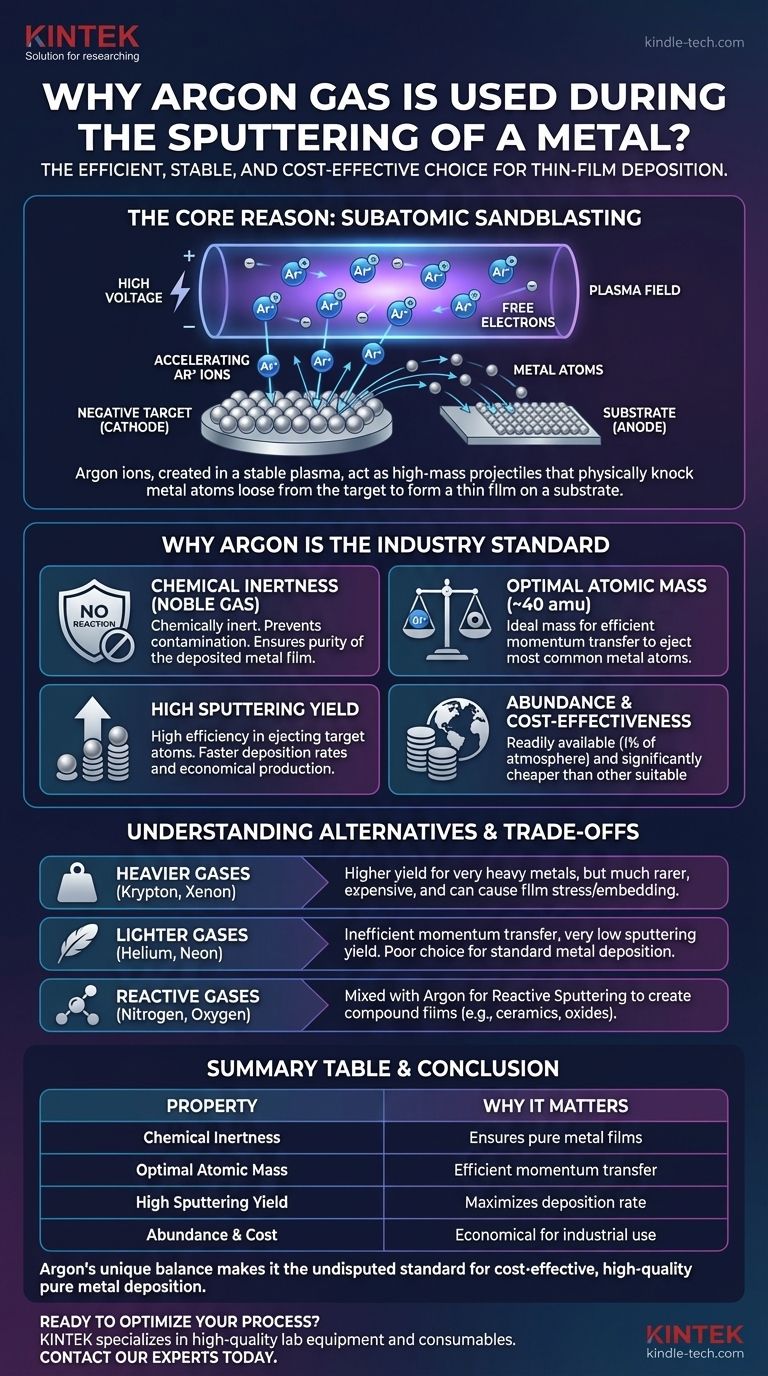
In short, argon is used in metal sputtering because it efficiently creates a stable plasma of non-reactive ions. These high-mass argon ions act like a subatomic sandblaster, accelerating into the metal target and physically knocking atoms loose, which then deposit as a thin film onto a substrate.
The core reason argon dominates sputtering is its ideal balance of properties: it is chemically inert, preventing contamination; its atomic mass is perfect for efficiently transferring momentum to eject metal atoms; and it is abundant and cost-effective.

The Fundamental Role of Gas in Sputtering
To understand why argon is the default choice, we must first understand why any gas is needed at all. The sputtering process happens inside a vacuum chamber and relies entirely on creating a controlled plasma environment.
Creating the Plasma
A sputtering chamber is first pumped down to a high vacuum to remove contaminants. Then, a small, controlled amount of a process gas—typically argon—is introduced.
A high voltage is applied between the substrate holder and the source material (the target). This electrical field energizes the gas, stripping electrons from the gas atoms and creating a glowing mixture of positive ions and free electrons known as plasma.
The Ion Bombardment Mechanism
The metal target is given a negative electrical charge (cathode). This causes the positively charged gas ions within the plasma to be forcefully accelerated toward the target.
They strike the target surface with significant kinetic energy, initiating the core sputtering action.
Ejecting Target Atoms
The impact of a high-energy ion transfers momentum to the atoms in the target's surface lattice. This is a purely physical process, much like a cue ball striking a rack of billiard balls.
If the momentum transfer is sufficient, it will knock out, or "sputter," atoms from the target. These ejected metal atoms travel through the low-pressure chamber and land on the substrate, building up layer by layer to form a thin film.
Why Argon Is the Industry Standard
While other gases can be used, argon possesses a unique combination of characteristics that make it the optimal choice for the vast majority of sputtering applications.
Chemical Inertness
Argon is a noble gas. It is chemically inert, meaning it will not react with the metal target, the growing film, or any components in the vacuum chamber.
This inertness is critical for physical vapor deposition (PVD), as it ensures the purity of the deposited film. The final material is composed only of the target material, not an unintended compound.
Optimal Atomic Mass
Effective sputtering is a game of momentum transfer. Argon, with an atomic mass of approximately 40 amu, is in a sweet spot.
It is heavy enough to efficiently eject atoms from most commonly sputtered metals (e.g., aluminum, copper, titanium, chromium). Lighter gases like helium (4 amu) have a very low sputtering yield because they tend to bounce off the heavier metal atoms with little momentum transfer.
High Sputtering Yield
Sputtering yield is the measure of how many target atoms are ejected per incident ion. Argon's combination of a good mass match and its ability to be readily ionized results in a high, efficient sputtering yield for most materials.
This translates directly to faster deposition rates, making manufacturing processes more economical and timely.
Abundance and Cost-Effectiveness
Argon is the third most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere (~1%). This makes it far more common and significantly less expensive to produce and purify than other suitable noble gases like krypton (Kr) or xenon (Xe).
Understanding the Trade-offs and Alternatives
While argon is the standard, other gases are used in specific situations where their unique properties are required. Understanding these alternatives highlights why argon is the default.
Heavier Gases: Krypton and Xenon
Krypton (~84 amu) and Xenon (~131 amu) are much heavier than argon. They can provide even higher sputtering yields, especially for very heavy target materials like gold or platinum.
However, they are orders of magnitude rarer and more expensive. They can also cause higher compressive stress in the film due to a more forceful "peening" effect and have a higher tendency to become embedded in the film.
Lighter Gases: Helium and Neon
Helium (He) and Neon (Ne) are generally poor choices for sputtering because their low mass results in inefficient momentum transfer and very low sputtering yields. They are almost never used for standard metal deposition.
Reactive Gases: Nitrogen and Oxygen
Sometimes, the goal is not to deposit a pure metal but a compound. In reactive sputtering, a reactive gas like nitrogen (N₂) or oxygen (O₂) is intentionally mixed with the argon.
The argon still performs the primary sputtering action, but the reactive gas combines with the sputtered metal atoms in-flight or on the substrate surface. This allows for the creation of ceramic films like titanium nitride (TiN) for hard coatings or silicon dioxide (SiO₂) for optics.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The choice of process gas is fundamental to controlling the outcome of a deposition. Your decision should be based on the desired film properties and economic realities.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, pure metal deposition: Argon is the undisputed standard choice due to its ideal balance of inertness, sputtering efficiency, and low cost.
- If your primary focus is maximizing the deposition rate of a very heavy element (like gold): Krypton or xenon can be considered, but you must account for the significantly higher gas cost and potential for film stress.
- If your primary focus is creating a ceramic compound film (e.g., an oxide or nitride): A precisely controlled mixture of argon and a reactive gas (like O₂ or N₂) is necessary for reactive sputtering.
Ultimately, understanding the role of the process gas is the first step toward mastering control over your thin-film's composition, quality, and performance.
Summary Table:
| Property | Why It Matters for Sputtering |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Prevents contamination, ensuring pure metal films. |
| Optimal Atomic Mass (~40 amu) | Efficiently transfers momentum to eject target atoms. |
| High Sputtering Yield | Maximizes deposition rate for cost-effective production. |
| Abundance & Cost | Readily available and economical for industrial use. |
Ready to optimize your thin-film deposition process? The right sputtering equipment and consumables are critical for achieving consistent, high-purity results. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for all your laboratory needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific application with reliable solutions and expert guidance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- How long can coating last? Maximize Durability with the Right System
- What are the uses of pyrolysis bio-oil? A Guide to Fuel, Chemical, and Power Applications
- How does the sputtering process work? A Guide to Thin Film Deposition
- What are the uses of centrifuge in everyday life? From Dairy to Detergents, See How Separation Powers Your World
- What temperature ranges are typically associated with ultra-low temperature freezers? Preserve Samples from -40°C to -86°C
- Can graphite withstand high-temperature? Maximizing Performance in Controlled Atmospheres
- How are biological samples typically stored in ULT freezers? A Guide to Systematic Organization
- How is filter press capacity calculated? Unlock Accurate Sizing for Your Specific Slurry



















