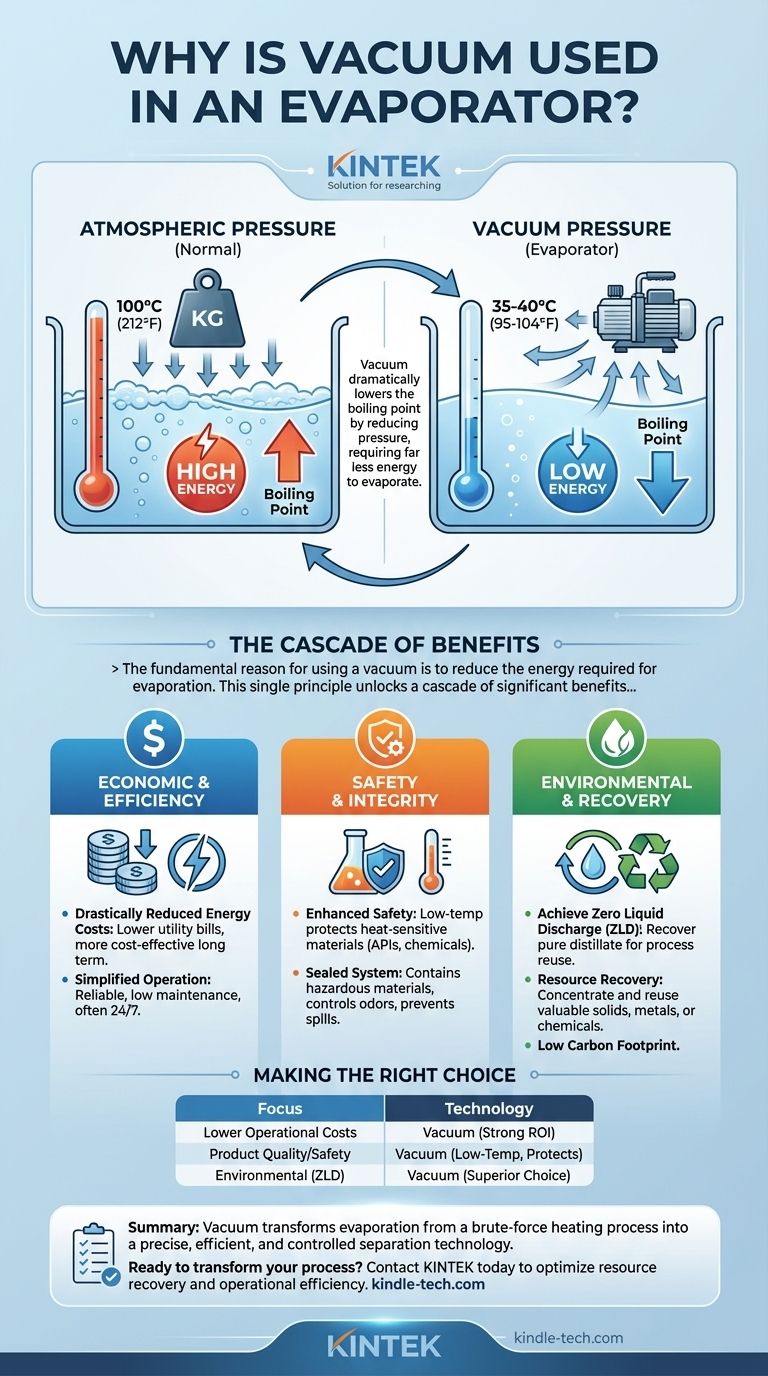
At its core, using a vacuum in an evaporator dramatically lowers the boiling point of the liquid being treated. By reducing the ambient pressure inside the evaporation chamber, water and other solvents can turn into vapor at much lower temperatures—often as low as 35-40°C (95-104°F)—instead of the 100°C (212°F) required at normal atmospheric pressure.
The fundamental reason for using a vacuum is to reduce the energy required for evaporation. This single principle unlocks a cascade of significant benefits, transforming the process into a highly efficient, safe, and cost-effective method for water treatment and resource recovery.

The Fundamental Principle: Lowering the Boiling Point
The primary function of the vacuum is to alter the physical conditions of the evaporation process, making it fundamentally more efficient. This is not a minor adjustment; it is the central mechanism that enables all other advantages.
How Vacuum Changes the Physics
Atmospheric pressure constantly pushes down on the surface of a liquid, making it harder for molecules to escape as vapor. A vacuum pump removes most of this air and pressure.
With this opposing force gone, liquid molecules require far less energy (heat) to break free and enter a gaseous state. This is why water can boil at room temperature if the vacuum is strong enough.
The Direct Impact on Energy Consumption
Heating a liquid to its boiling point is the most energy-intensive part of evaporation. By lowering that boiling point significantly, the total energy demand of the system plummets.
This direct reduction in energy use is the primary driver of the lower operational costs associated with vacuum evaporators.
Key Operational and Economic Advantages
Lowering the boiling point creates a ripple effect of benefits that extend to cost, safety, and operational simplicity.
Drastically Reduced Energy Costs
Because the system operates at lower temperatures, the energy required for heating is substantially less than in atmospheric evaporators. This translates directly into lower utility bills and a more cost-effective operation over the long term.
Enhanced Safety and Material Integrity
Operating at low temperatures is inherently safer, reducing risks for personnel. It also prevents the thermal degradation of heat-sensitive materials in the wastewater, such as Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) or certain chemicals.
Furthermore, the sealed vacuum system effectively contains hazardous materials, controls odors, and prevents spills, ensuring a cleaner and safer workspace.
Simplified and Reliable Operation
Modern vacuum evaporators are often designed for fully automatic, 24/7 operation. Their reliability and low maintenance requirements mean they can run for extended periods with minimal human intervention, reducing labor costs.
Increased Versatility
The low-temperature process allows vacuum evaporators to treat a wide range of difficult or hazardous waste streams with little to no pre-treatment. This makes them exceptionally versatile for industries dealing with complex wastewater challenges.
Understanding the Environmental and Recovery Benefits
Beyond operational efficiency, vacuum evaporation is a powerful tool for environmental stewardship and resource recovery.
Achieving Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD)
The vapor produced during evaporation is condensed back into a liquid, known as the distillate. This resulting water is typically very pure and can be recovered and recycled directly back into the facility's processes.
This capability helps facilities achieve Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) goals, a critical objective for water conservation and environmental compliance.
Recovering Valuable Components
When water is removed, the dissolved solids, chemicals, or metals are left behind in a concentrated form. In many cases, these materials are valuable and can be recovered for reuse. This includes precious metals, salts, or other raw materials that would otherwise be lost.
Minimizing Environmental Footprint
The combination of low energy consumption and the potential for ZLD gives vacuum evaporation a very low carbon footprint. By closing the loop on water and raw materials, it represents a highly sustainable approach to waste treatment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, vacuum evaporation is not a universal solution. It is essential to understand its limitations to make an informed decision.
Higher Initial Capital Cost
Vacuum evaporators, with their pumps, condensers, and control systems, typically have a higher upfront purchase price than simpler atmospheric evaporation systems. The economic benefit is realized through lower long-term operational costs.
System Complexity
While reliable, these are not zero-maintenance systems. The vacuum integrity is critical to performance, and troubleshooting issues like air leaks requires a degree of technical expertise.
Best Suited for Specific Challenges
For waste streams that are not heat-sensitive, where energy costs are negligible, or where the volumes are very small, a less complex atmospheric system might be more cost-effective. The primary value of vacuum is unlocked when dealing with energy costs, heat-sensitive materials, or ZLD requirements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right technology depends entirely on your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is minimizing long-term operational costs: A vacuum evaporator's energy savings will almost always provide a strong return on investment.
- If your primary focus is product quality or safety: The low-temperature operation is essential for protecting heat-sensitive materials and safely handling hazardous waste.
- If your primary focus is environmental compliance and sustainability: The ability to achieve Zero Liquid Discharge and recover resources makes this technology a superior choice.
Ultimately, using a vacuum transforms evaporation from a brute-force heating process into a precise, efficient, and controlled separation technology.
Summary Table:
| Key Benefit | How Vacuum Enables It |
|---|---|
| Lower Energy Costs | Reduces boiling point, requiring less heat for evaporation. |
| Enhanced Safety | Low-temperature operation prevents thermal degradation of materials. |
| Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) | Allows for high-purity water recovery and recycling. |
| Resource Recovery | Concentrates valuable solids, metals, or chemicals for reuse. |
Ready to transform your evaporation process with efficiency and sustainability?
KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment, including vacuum evaporation systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of modern labs. Our solutions help you significantly reduce energy consumption, safely handle heat-sensitive materials, and achieve your environmental goals like Zero Liquid Discharge.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss how a KINTEK vacuum evaporator can provide a cost-effective, safe, and sustainable solution for your specific application. Let our experts help you optimize your resource recovery and operational efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of the compression chamber in a vacuum pump? The Heart of Vacuum Generation
- What can I use a vacuum pump for? Powering Industrial Processes from Packaging to Automation
- What types of gases can a water circulating vacuum pump handle? Safely Manage Flammable, Condensable & Dirty Gases
- What are the advantages of a water circulating vacuum pump? Superior Durability for Demanding Lab Environments
- How does the impeller rotation affect the gas flow in a water circulating vacuum pump? A Guide to the Liquid Ring Principle



















