Introduction to Rotary Evaporator Chillers
Rotary evaporator chillers are an essential part of laboratory equipment used for efficient separation of solvents from samples by evaporation. They work by cooling the solvent vapor, which condenses and is collected separately from the sample. This process requires a chiller to provide the necessary cooling power. Chillers are available in different sizes and types, with varying cooling capacities, to match the requirements of different rotary evaporator models. Without a chiller, the evaporator would not be able to function effectively, making it an important component in the laboratory setting.
Table of Contents
Operating Principle of Rotary Evaporators
Rotary evaporators are essential laboratory equipment used to separate solvents from a mixture through evaporation. The operating principle behind rotary evaporators is based on the fact that different liquids have different boiling points and can be separated by evaporating them at different temperatures. The following are the steps involved in the operating principle of rotary evaporators:
Step 1: Sample Preparation
The first step in operating a rotary evaporator is to prepare the sample. The sample is placed in the sample flask, which is then attached to the rotary evaporator.
Step 2: Applying Heat
Heat is then applied to the sample flask using a water bath or heating mantle. The heat causes the solvent to evaporate, leaving the solute behind.
Step 3: Condensation
The evaporated solvent then condenses in a separate flask cooled by a chiller. The chiller reduces the pressure in the system and helps to prevent the solvent from boiling.
Step 4: Separation
The operating principle of rotary evaporators is based on the principle of separation. Different liquids have different boiling points, and they can be separated by evaporating them at different temperatures. The rotary evaporator's rotating flask creates a thin film of process media on the inner wall, ensuring uniform heating across the entire mass and less possibility of bumping. This results in the separation of the solvents, which can then be collected in a separate flask.
Step 5: Purification and Concentration
Rotary evaporator chillers are a useful tool in the purification and concentration of compounds. The evaporator works efficiently to separate solvents and leave behind pure compounds. Rotary evaporators are especially suitable for the concentration and purification of biological products that are easily decomposed and denatured at high temperature.
In conclusion, the operating principles of rotary evaporators involve sample preparation, applying heat, condensation, separation, and purification. Understanding the basic principles of how rotary evaporator chillers work and the different components involved in their operation is crucial to achieving optimal results in laboratory applications. It is also important to take proper operating procedures and safety measures into consideration when using this equipment to avoid accidents and ensure accurate results.
Components of a Rotary Evaporator
A rotary evaporator is a laboratory instrument used to separate solvents from a mixture, and it consists of several components that work together to achieve this. Here are the main components of a rotary evaporator:
Heating Bath
The heating bath is a heated bath that encloses the main rotary flask and is used to indirectly heat the contents of the process. The bath is usually equipped with electric heaters that can be ATEX-compliant or weather-proof, depending on the application area’s Hazardous Zone Classification. As a safety feature, the bath is appropriately insulated so that the outside surface is not too hot to touch.
Rotary Flask
The rotary flask is the main component where the process fluid is initially charged and is made of Borosilicate Glass 3.3 raw material. The flask’s construction is of prime importance for the smooth rotation along the central axis. Our advanced manufacturing techniques ensure that the evaporating flask is rotating perfectly along the central axis, thereby ensuring that the entire surface area comes in contact for the same time with the heating media in the bath.
Mechanical Seal
The mechanical seal, along with the motor unit connected to the flask, is responsible for smooth and leakproof rotation of the flask at a constant speed.
RTD
An RTD is placed just above the vapor tube to measure the vapor temperature before it goes into the condenser. The RTD is inserted inside the vapor tube in a glass thermowell. This ensures that the contact parts are strictly Borosilicate Glass 3.3 and PTFE only and the metal tip of PT-100 sensor does not come in direct contact with the process vapor.
Condenser
A Shell & Coil type condenser of suitable heat transfer area is chosen so that there is no pressure build-up due to excessive un-condensed vapors. The condenser is preferably placed in vertical orientation for efficient condensation. Different configurations with single and double condensers are available depending on the application. As a standard, a single condenser is provided.
Vacuum Pump
The vacuum pump is used to create a vacuum inside the rotary evaporator, which helps to lower the boiling point of the liquid and facilitate the evaporation process.
Collection Flask
The collection flask is the container that collects the condensed liquid after it passes through the condenser. It is typically connected to the condenser via a glass tube.
Vacuum Controller
The vacuum controller is used to regulate the vacuum inside the rotary evaporator. It is equipped with a gauge that displays the pressure inside the system.
In conclusion, understanding the components of a rotary evaporator is crucial to its proper use and maintenance. By knowing the function of each component, researchers and scientists can effectively use this tool for their laboratory experiments.
Importance of Chillers in Rotary Evaporators
A rotary evaporator is a laboratory equipment used in heating and evaporating solvents from samples. The process requires the use of a chiller to cool the condenser and prevent the solvent from evaporating into the atmosphere. Chillers play a critical role by providing the cooling needed to maintain a consistent temperature, ensuring accurate, repeatable results.
Factors to consider when selecting a chiller
The type of chiller used will depend on the specific requirements of the laboratory and the type of solvents used in the evaporation process. Factors such as cooling capacity, temperature range, and ease of use must be considered when selecting a chiller.
Cooling capacity and appropriate chiller
To calculate the necessary cooling capacity and the appropriate chiller, you’ll need to consider three factors related to a particular solvent: vapor temperature, desired evaporation rate, and condenser temperature. The lower the desired condenser temperature, the more cooling capacity you’ll need from your recirculating chiller.
Indicators when you don't have enough cooling capacity
If the chiller temperature increases from the setpoint during operation, this indicates that the cooling load exceeds the recirculating chiller’s cooling capacity. Inadequate cooling could result in solvent vapor exiting the rotary evaporator into the vacuum pump, potentially damaging the pump in the process.
Using one recirculating chiller for multiple rotary evaporators
A single chiller can operate multiple rotary evaporators. In this case, a few rotary evaporators are daisy-chained together, and a single chiller cools down the circulating water. Note: you’ll need to be sure you have sufficient cooling capacity for each solvent and process if you’re using different solvents or have different condenser temperatures, vapor temperatures, or desired evaporation rates.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the proper use of a chiller in a rotary evaporator is essential for achieving accurate, repeatable results and maintaining the integrity of the sample, making it a crucial component of any laboratory setup. By selecting the appropriate chiller based on the specific requirements of the laboratory and the type of solvents used in the evaporation process, the cooling capacity can be optimized for the desired condenser temperature, ensuring efficient and effective results.
Types of Rotary Evaporator Chillers
There are different types of rotary evaporator chillers available in the market designed for specific laboratory applications. The most common types include water-cooled, air-cooled, and recirculating chillers.
Water-Cooled Chillers
Water-cooled chillers are the most efficient type of rotary evaporator chillers. They can handle high volumes of solvent and are ideal for laboratories that require precise temperature control. Water-cooled chillers use water as a coolant and require a separate water source. They are typically more costly than other types of rotary evaporator chillers but are worth the investment for laboratories that require high efficiency and accuracy.
Air-Cooled Chillers
Air-cooled chillers are ideal for smaller laboratories that do not require high volumes of solvent. They are less expensive than water-cooled chillers and do not require any additional water source. However, air-cooled chillers are less efficient than water-cooled chillers and may not provide precise temperature control.
Recirculating Chillers
Recirculating chillers are versatile and can be used with a variety of solvents. They are an excellent option for laboratories that require flexibility in their solvent distillation processes. Recirculating chillers can be used with either water or air as a coolant, depending on the laboratory's specific needs. They are typically less expensive than water-cooled chillers and offer more flexibility than air-cooled chillers.
It is crucial to choose the right type of rotary evaporator chiller depending on your specific laboratory needs. Additionally, it is important to consider the chiller's cooling capacity, temperature range, and flow rate when selecting one for your lab. By choosing the right type of rotary evaporator chiller, you can ensure efficient and accurate results in your solvent distillation processes.
Advantages of Using Rotary Evaporator Chillers
Rotary evaporator chillers are an essential piece of equipment in laboratories, used to remove solvents from liquid mixtures through evaporation. Here are some of the advantages of using rotary evaporator chillers:
1. Lower Boiling Temperatures
The use of a vacuum system in conjunction with a rotary evaporator chiller reduces the pressure of the system. This means that the separation of solvents and other compounds can be achieved at lower temperatures than usual. Lower water bath temperatures ensure that the apparatus stays in good shape for longer as they are exposed to lower temperatures.
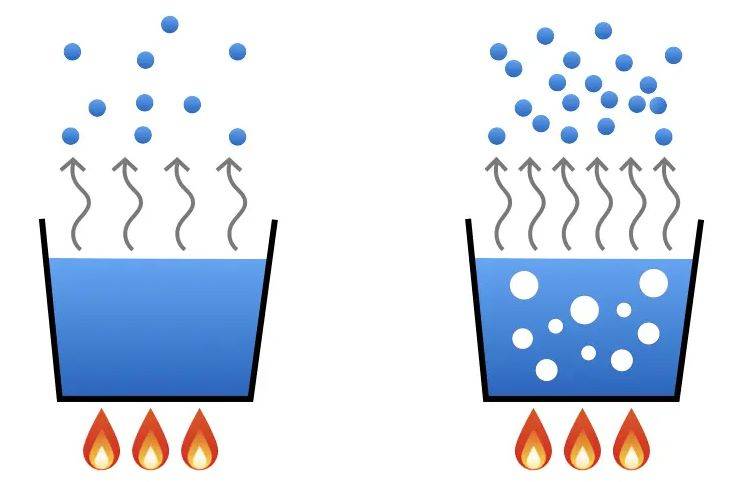
2. Faster Evaporation of Solvent
The process of separation in rotary evaporator chillers involves two main forces: the centripetal force and friction. This allows the mixture to form a film on the inner surface of the flask, creating a larger surface area for heating.
The distillation speeds of the rotary evaporator chiller are electronically controlled to enable the rotation of the flask at a constant speed. Under the low pressure caused by the vacuum pump, the distillation speed is increased significantly due to the large surface area of the mixture.
3. Fewer Operations
A rotary evaporator chiller consists of a built-in lifting and falling motor, allowing the automatic raising of the rotary bottle to a position just above the water bath for the rotation process. This means that a technician is less involved in the holding of the apparatus, which makes work easier for them. The motor is electrically powered, making it an efficient and reliable apparatus for most chemistry labs.
4. Rotary Evaporator Chillers Suppress Bumping
Due to the forces that contribute to the evaporation process (centripetal force and friction), bumping is often suppressed. This allows for quick and gentle evaporation of mixtures, and therefore allows even the inexperienced users to utilize these apparatus.
5. Reduction of Heat-Sensitive Compounds
Rotary evaporator chillers help reduce the loss of heat-sensitive compounds, which could be destroyed during the process. Using a chiller during the evaporation process is beneficial because it allows the solvent vapor produced during the evaporation process to cool, allowing it to condense and be collected in a separate flask. This results in a more concentrated and pure sample, making it easier to analyze.
In conclusion, using rotary evaporator chillers has many advantages, including lower boiling temperatures, faster evaporation of solvent, fewer operations, and bumping suppression. These benefits make rotary evaporator chillers a useful tool in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, chemical, and food processing.

Conclusion
Rotary evaporator chillers are essential equipment in various laboratory applications. They help to maintain precise temperature control during the evaporation process, ensuring high-quality results. In this guide, we have discussed the operating principle and components of a rotary evaporator, the importance of chillers in the process, and the different types of rotary evaporator chillers available in the market. When choosing the right rotary evaporator chiller for your laboratory needs, consider factors such as the sample size, type, and volume, among others. Investing in a high-quality rotary evaporator chiller can deliver numerous benefits, including increased efficiency and productivity.
Related Products
- 50L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- Laboratory Rotary Vane Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- 5L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- 30L Chiller Water Bath Cooling Circulator Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath
Related Articles
- Don't Let Overheating Ruin Your Experiment Use a Chiller for Your Rotavap
- Choosing the Right Cooling Circulation System for a Rotary Evaporator
- Why Tap Water Chilling Is Not Enough for Your Rotavap
- Why a Chiller is a Must-Have for Your Rotavap
- Preparation and Finishing Work for Using a Low-Temperature Thermostatic Reaction Bath