The degradation of THC distillate is not a single event, but a process that accelerates significantly with heat, light, and oxygen. While slow degradation occurs even at room temperature, the rate increases dramatically as temperatures rise, with meaningful breakdown happening during prolonged heating above 250°F (121°C) and rapid destruction occurring at temperatures well above its boiling point, especially nearing combustion.
The key to preserving THC is understanding that degradation is a function of temperature, time, and exposure. Your goal is not to avoid a single "magic number," but to control the environment—cool, dark, and airtight—to minimize the rate of breakdown.

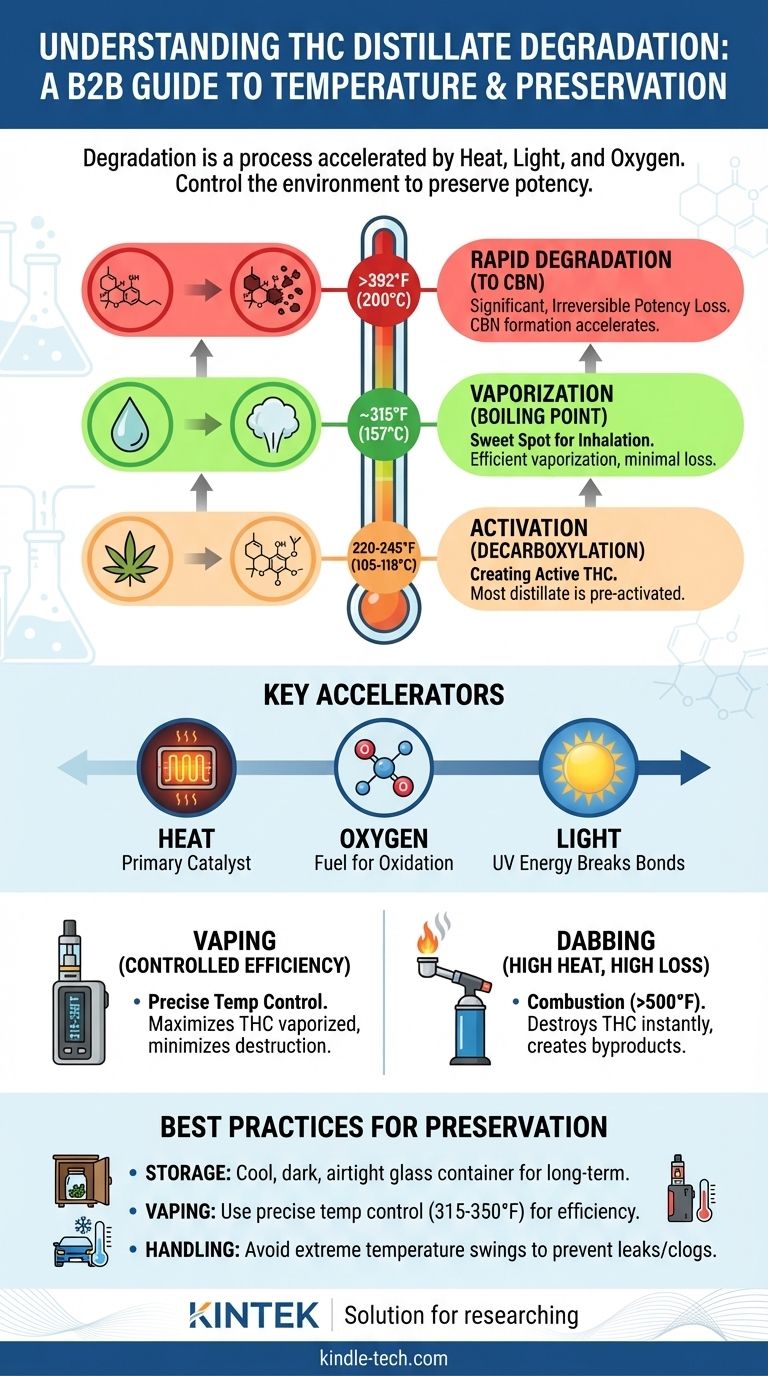
Activation, Vaporization, and Degradation: Three Critical Temperatures
Many users confuse the temperatures for activating, vaporizing, and degrading THC. Understanding the difference is fundamental to using distillate effectively, whether for storage, edibles, or inhalation.
Activation (Decarboxylation): Creating THC
Before it can produce its primary effects, the raw cannabinoid in cannabis, THCA, must be converted into Delta-9-THC. This process is called decarboxylation.
This conversion is a form of controlled "degradation" that is actually desirable. It typically occurs between 220-245°F (105-118°C) over 30-60 minutes. Most commercial distillate is already decarboxylated, or "active."
Vaporization: The Sweet Spot for Inhalation
To be inhaled, THC must be heated to its boiling point, turning the liquid into a vapor. The boiling point of Delta-9-THC is approximately 315°F (157°C).
This is the target temperature for vaporizers and e-rigs. The goal is to heat the distillate just enough to release the THC molecule without burning it or instantly breaking it down.
Degradation: Losing Potency to CBN
True degradation occurs when THC breaks down into other cannabinoids, primarily Cannabinol (CBN), which has a much milder, more sedative effect. This is an irreversible loss of potency.
This process happens slowly over time but is drastically accelerated by heat. While any heat contributes, significant degradation begins with prolonged exposure to temperatures above its vaporization point. At temperatures exceeding 392°F (200°C), THC begins to break down much more rapidly into both CBN and other unwanted byproducts.
The Key Factors That Accelerate Degradation
Temperature is the main catalyst, but it doesn't act alone. Two other environmental factors are critical to control.
Heat: The Primary Catalyst
Heat provides the energy needed to drive the chemical reaction that converts THC to CBN. The higher the temperature, the faster your distillate will lose potency. This is why leaving a vape pen in a hot car is so detrimental to the quality of the oil.
Oxygen: The Fuel for Oxidation
Degradation is an oxidation process. The THC molecule reacts with oxygen in the air, causing it to change its chemical structure. Storing distillate in an airtight container is one of the most effective ways to slow this process.
Light: Breaking Bonds with UV Energy
Light, especially UV light from the sun, provides energy that breaks the chemical bonds in the THC molecule. This makes it highly unstable and speeds up its conversion to CBN, even without significant heat. This is why cannabis products are almost always packaged in opaque or dark-colored containers.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Vaping vs. Combustion
How you consume your distillate directly impacts how much THC is preserved versus destroyed.
The Goal of Vaping: Controlled Efficiency
Vaping devices with precise temperature control are designed for efficiency. By heating the distillate to its boiling point (~315°F / 157°C) but staying well below the point of rapid degradation, you maximize the amount of THC vaporized and minimize what gets destroyed.
The Reality of Dabbing: High Heat, High Loss
Traditional dabbing with a torch-heated nail often involves temperatures far exceeding 500°F (260°C). While this produces a rapid and intense effect, it also causes combustion.
Combustion instantly destroys a significant percentage of the THC and creates unwanted byproducts like benzene. You are trading efficiency and purity for speed and intensity.
Best Practices for Preserving Your Distillate
Your handling strategy should align with your intended use.
- If your primary focus is long-term storage: Store your distillate in a small, airtight glass container in a cool, dark place like a cupboard or drawer to minimize exposure to heat, air, and light.
- If your primary focus is consumption via vaping: Use a device with precise temperature control and set it between 315-350°F (157-177°C) to achieve efficient vaporization with minimal degradation.
- If your primary focus is preventing clogs or leaks: Avoid exposing your vape cartridge or device to extreme temperature swings, such as leaving it in a hot car or a freezing environment, as this affects viscosity and can damage the hardware.
By managing temperature, light, and air, you gain complete control over the integrity and potency of your THC distillate.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Process | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|---|
| 220-245°F (105-118°C) | Activation (Decarboxylation) | Converts THCA to active THC. Most distillate is already activated. |
| ~315°F (157°C) | Vaporization (Boiling Point) | Ideal target temperature for efficient inhalation with minimal loss. |
| >392°F (200°C) | Rapid Degradation (to CBN) | Significant, irreversible loss of potency occurs quickly. |
Ready to achieve precise temperature control for your cannabis products? KINTEK specializes in the lab equipment and consumables that research and production facilities rely on for consistent, high-quality results. From precise heating elements to analytical tools, our solutions help you preserve potency and ensure purity. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Hollow Etching Flower Basket ITO FTO Developing Glue Removal
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Culture Dish and Evaporation Dish
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Automatic Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Hollow Cleaning Basket and Rack Carrier
People Also Ask
- How should a PTFE cleaning basket be stored when not in use? Maximize Lifespan & Prevent Contamination
- What should be monitored during the cleaning process when using a PTFE cleaning basket? Ensure Reliable Results & Prevent Damage
- What technical advantages does a PTFE-based flow reaction platform offer? Speed Up Lignin Depolymerization by 95%
- How can mechanical damage to an all-PTFE electrolytic cell be prevented? Protect Your Laboratory Hardware
- What is the procedure for using a PTFE cleaning basket? A 3-Step Guide for Flawless Results













