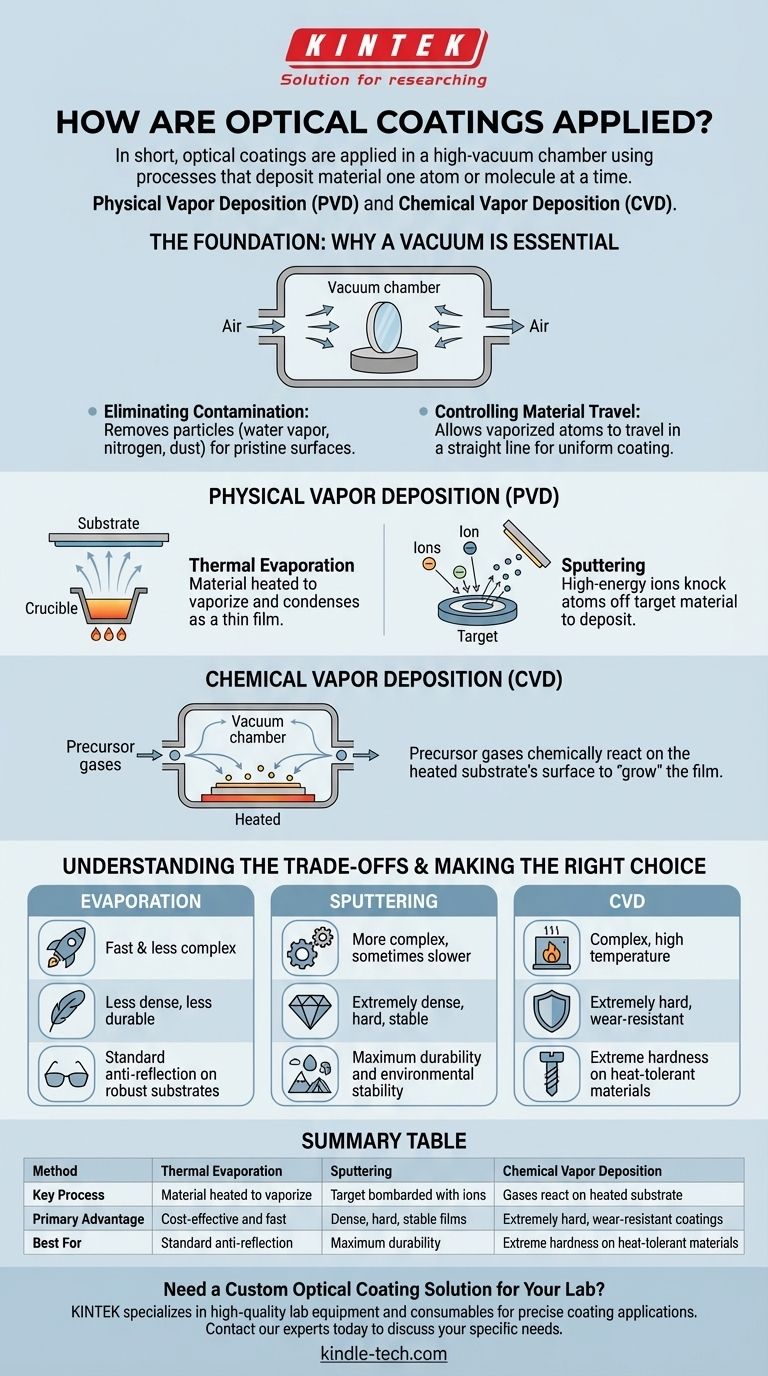
In short, optical coatings are applied in a high-vacuum chamber using processes that deposit material one atom or molecule at a time. The two dominant families of methods are Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). This atomic-level control is what allows for the creation of incredibly thin, precise layers that manipulate light.
The core principle is not to "paint" a surface, but to build a new one. All modern optical coating methods rely on a highly controlled vacuum environment to deposit ultra-thin films of material, allowing for precise control over the coating's structure, density, and optical properties.
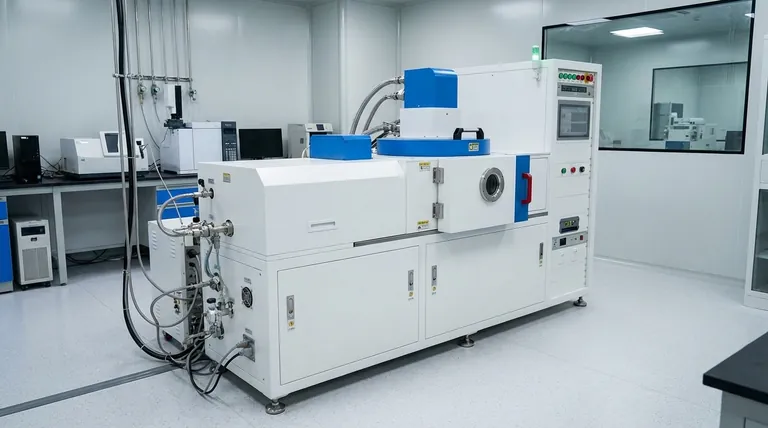

The Foundation: Why a Vacuum is Essential
Before any coating is applied, the optical component (the substrate) is placed inside a sealed vacuum chamber. The air is then pumped out to create an environment with extremely low pressure. This step is non-negotiable for two critical reasons.
Eliminating Contamination
The normal atmosphere is filled with particles like water vapor, nitrogen, and dust. These particles would contaminate the coating, creating imperfections that would degrade or destroy its optical performance. A vacuum ensures a pristine environment.
Controlling Material Travel
In a vacuum, there are very few air molecules for the coating material to collide with. This allows the vaporized atoms to travel in a straight line from their source directly to the optical surface, ensuring a uniform and predictable coating.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD): The "Physical" Approach
PVD encompasses a group of methods where a material is converted into a vapor through purely physical means and then condenses onto the substrate. This is the most common category for precision optical coatings.
Thermal Evaporation
This is a foundational PVD technique. The coating material, held in a small crucible or "boat," is heated until it evaporates. The resulting vapor rises through the vacuum and condenses on the cooler optical components, forming a thin film.
Sputtering
In sputtering, a solid block of the coating material, known as the "target," is bombarded with high-energy ions (typically from an inert gas like argon). This energetic collision acts like a subatomic sandblaster, knocking individual atoms off the target. These ejected atoms then travel and deposit onto the substrate.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): The "Chemical" Approach
Unlike PVD, Chemical Vapor Deposition involves a chemical reaction on the surface of the optic itself.
How CVD Works
In CVD, one or more volatile precursor gases are introduced into the chamber. These gases react or decompose on the heated substrate's surface to produce the desired solid coating. This process essentially "grows" the film chemically rather than just physically depositing it.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice of method is driven by the required performance, cost, and the type of optical material being coated. Each process has distinct advantages and disadvantages.
Evaporation: Speed vs. Density
Thermal evaporation is often faster and less complex than other methods, making it cost-effective for many applications. However, the resulting films can sometimes be less dense and durable, making them more susceptible to environmental shifts.
Sputtering: Density vs. Complexity
Sputtering produces coatings that are extremely dense, hard, and stable. This makes them ideal for applications requiring high durability. The trade-off is often a more complex and sometimes slower deposition process.
CVD: Durability vs. High Temperature
CVD can produce some of the hardest and most wear-resistant coatings available. However, the process typically requires very high substrate temperatures, which can damage many sensitive optical materials like plastics or certain types of glass.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct coating process is critical to achieving the desired outcome for your optical system.
- If your primary focus is standard anti-reflection on robust substrates: Thermal evaporation often provides the best balance of performance and cost.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and environmental stability: Sputtering is the superior choice for its dense, stable film structure.
- If your primary focus is extreme hardness on a heat-tolerant material: CVD is the go-to method for creating highly resilient, wear-resistant surfaces.
Understanding these fundamental processes empowers you to specify and source coatings that meet the precise demands of your application.
Summary Table:
| Method | Key Process | Primary Advantage | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal Evaporation | Material is heated to vaporize in a vacuum | Cost-effective and fast | Standard anti-reflection on robust substrates |
| Sputtering | Target material is bombarded with ions to eject atoms | Produces dense, hard, and stable films | Maximum durability and environmental stability |
| Chemical Vapor Deposition | Gases react on a heated substrate surface | Creates extremely hard, wear-resistant coatings | Extreme hardness on heat-tolerant materials |
Need a Custom Optical Coating Solution for Your Lab?
Selecting the right deposition method is critical for your optical system's performance. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for precise coating applications. Our expertise ensures you achieve the durability, precision, and stability your research demands.
Let us help you enhance your optical components. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and discover the ideal coating solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of plasma enhanced CVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is the plasma CVD process? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma activated chemical vapor deposition? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for Sensitive Materials
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings



















