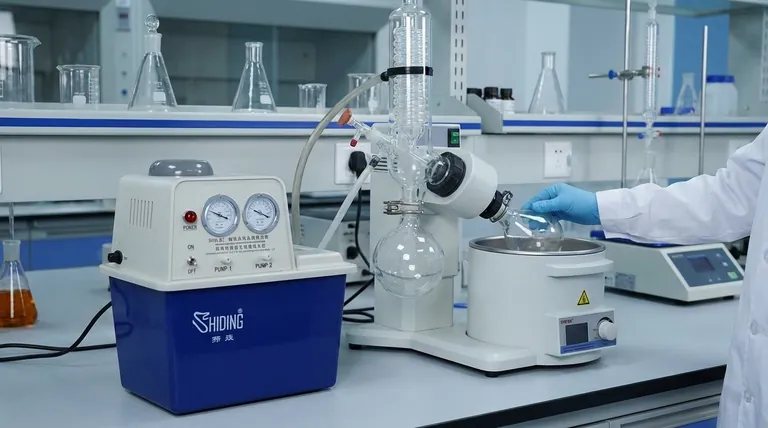
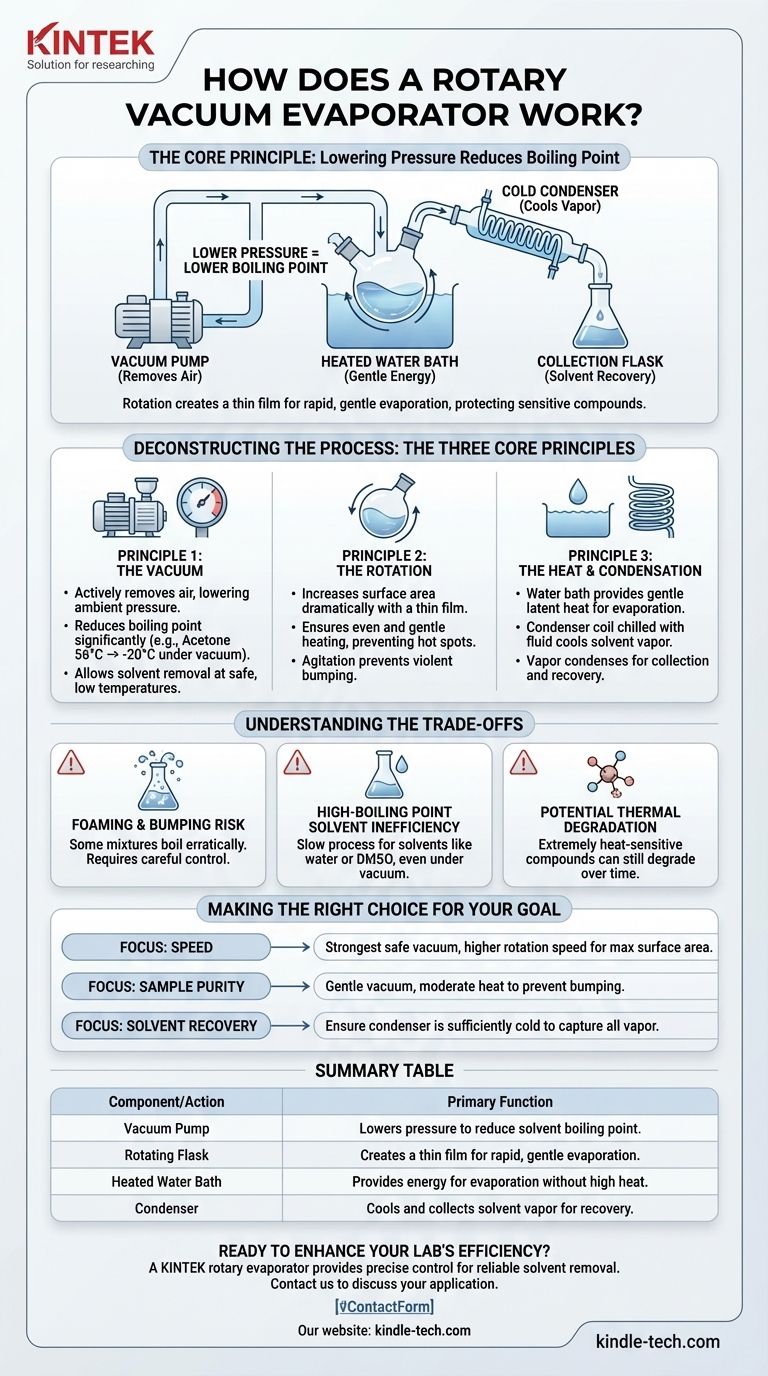
At its core, a rotary evaporator separates chemicals by exploiting a simple physical principle: lowering pressure reduces a liquid's boiling point. It uses a vacuum to evaporate a solvent at a much lower temperature than normal, protecting sensitive compounds while speeding up the process. This is achieved by rotating a flask in a heated water bath under vacuum, which continuously creates a thin film of liquid with a large surface area for rapid and gentle evaporation.
The true function of a rotary evaporator isn't just to boil off a solvent. It is a precision instrument designed to gently remove a volatile solvent from a non-volatile sample by lowering the boiling point through a vacuum, preventing thermal degradation of the target compound.

Deconstructing the Process: The Three Core Principles
A rotary evaporator, or "rotovap," integrates three key actions to achieve efficient and controlled distillation. Understanding how these actions work together is crucial to using the instrument effectively.
Principle 1: The Vacuum
The most critical element is the vacuum. A pump, often a rotary vane type, actively removes air from the system.
This reduction in ambient pressure directly lowers the temperature at which the solvent will boil. For example, acetone boils at 56°C at standard atmospheric pressure but boils at -20°C under a strong vacuum.
This allows you to remove the solvent without exposing your valuable sample to potentially damaging high temperatures.
Principle 2: The Rotation
The rotation of the sample flask serves three distinct purposes.
First, it dramatically increases the surface area of the liquid. The constant spinning spreads the solvent into a thin film on the inner wall of the flask, which massively accelerates the rate of evaporation.
Second, it ensures even and gentle heating as the flask rotates through the water bath. This prevents localized hot spots that could degrade the sample.
Third, the agitation prevents violent boiling, known as "bumping," which can cause you to lose your sample as it splashes up into the collection apparatus.
Principle 3: The Heat and Condensation
While the vacuum does most of the work, a gentle heat source (usually a water bath) is needed to provide the energy for the phase change from liquid to gas. This energy is called the latent heat of vaporization.
Once the solvent evaporates, the gas travels into a glass condenser coil. This coil is chilled with circulating cold fluid (like water or an antifreeze mixture).
The cold surface forces the solvent vapor to condense back into a liquid, which is then collected in a separate flask. This allows for the recovery and potential reuse of the solvent.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the rotovap is not a universal solution. Its effectiveness is dependent on the properties of the solvent and the sample.
Risk of Foaming and Bumping
Some mixtures have a tendency to foam or boil erratically under vacuum. This can cause the sample to be carried along with the solvent vapor, leading to product loss and contamination of the glassware. Careful control of the vacuum and rotation speed is required to manage this.
Inefficiency with High-Boiling Point Solvents
The technique is most effective for removing volatile solvents with low boiling points (like ethanol, ethyl acetate, or dichloromethane). For high-boiling point solvents such as water or DMSO, the process can be extremely slow, even under a deep vacuum.
Potential for Thermal Degradation
Although the process is designed to be gentle, extremely heat-sensitive compounds can still degrade over time, even in a warm water bath. The goal is always to use the lowest possible temperature that allows for efficient evaporation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Effectively using a rotovap means adjusting its parameters to match your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is speed: Use the strongest vacuum your solvent and equipment can safely handle and a slightly higher rotation speed to maximize the surface area film.
- If your primary focus is sample purity: Use a gentle vacuum and moderate heat to prevent any bumping that could carry your sample into the collection flask.
- If your primary focus is solvent recovery: Ensure your condenser is sufficiently cold to capture all the vapor, especially when working with very volatile low-boiling solvents.
By mastering these principles, you transform the rotary evaporator from a machine into a precise and powerful tool for chemical separation.
Summary Table:
| Component/Action | Primary Function |
|---|---|
| Vacuum Pump | Lowers pressure to reduce solvent boiling point. |
| Rotating Flask | Creates a thin film for rapid, gentle evaporation. |
| Heated Water Bath | Provides energy for evaporation without high heat. |
| Condenser | Cools and collects solvent vapor for recovery. |
Ready to enhance your lab's efficiency and protect your sensitive samples?
A KINTEK rotary evaporator provides the precise control and gentle processing you need for reliable solvent removal and compound purification. Our rotovaps are engineered for durability and performance, serving the exacting needs of research and quality control laboratories.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss your application and find the perfect solution for your lab. Let KINTEK be your partner in precision.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Benchtop Water Circulating Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Ceramic Evaporation Boat Set Alumina Crucible for Laboratory Use
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- How does the impeller rotation affect the gas flow in a water circulating vacuum pump? A Guide to the Liquid Ring Principle
- How is a circulating water vacuum pump utilized for hydrogen production residues? Optimize Your Solid-Liquid Separation
- What types of gases can a water circulating vacuum pump handle? Safely Manage Flammable, Condensable & Dirty Gases
- What factors affect evaporation and condensation? Master the Science of Water's Phase Changes
- Why must a laboratory vacuum pump be used to evacuate a PM-HIP capsule before it is sealed? Ensure Material Integrity



















