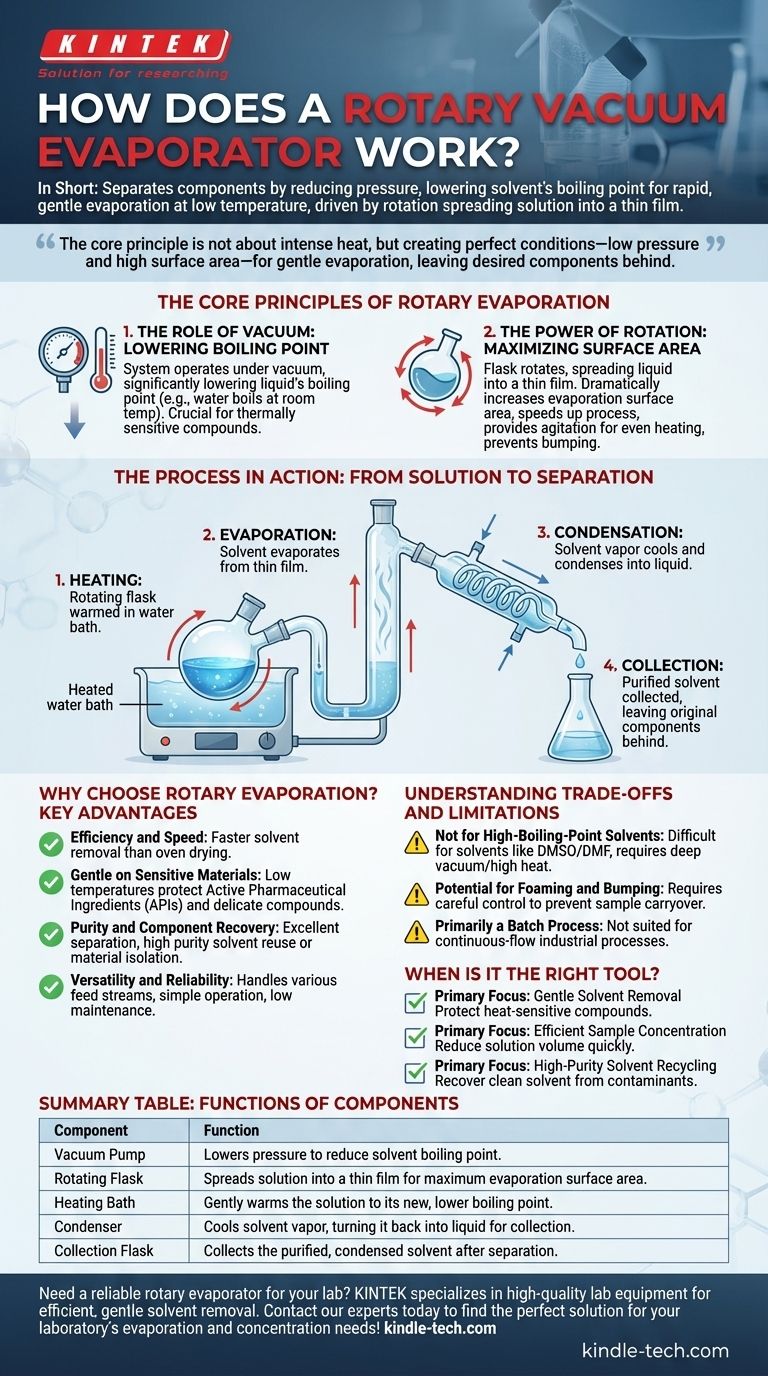
In short, a rotary vacuum evaporator separates components of a solution by reducing the pressure inside the system, which lowers the solvent's boiling point. This allows for rapid and gentle evaporation at a low temperature, driven by the rotation of the flask which continuously spreads the solution into a thin film.
The core principle is not about boiling with intense heat, but about creating the perfect conditions—low pressure and high surface area—for a solvent to evaporate gently and efficiently, leaving the desired components behind.

The Core Principles of Rotary Evaporation
A rotary evaporator, often called a "rotovap," is a standard piece of equipment in chemistry and biochemistry labs. Its function is based on a few elegant principles working in concert.
The Role of Vacuum: Lowering the Boiling Point
The entire system operates under a vacuum. By reducing the ambient pressure, the boiling point of the liquid is significantly lowered.
For example, water boils at 100°C (212°F) at standard atmospheric pressure, but under a strong vacuum, it can boil at room temperature. This is crucial for thermally sensitive compounds that would degrade or be destroyed by high heat.
The Power of Rotation: Maximizing Surface Area
The flask containing the solution is continuously rotated. This rotation spreads the liquid into a thin film on the inner surface of the flask.
This dramatically increases the surface area available for evaporation, making the process much faster and more efficient than simple heating. The rotation also provides agitation, ensuring even heating and preventing violent "bumping" of the boiling liquid.
The Process in Action: From Solution to Separation
- Heating: The rotating flask is lowered into a heated water bath, which gently warms the solution to the new, lower boiling point.
- Evaporation: As the flask rotates, the solvent evaporates from the thin film of liquid.
- Condensation: The solvent vapor travels into a condenser coil, which is cooled by circulating water or another coolant. This causes the vapor to condense back into a pure liquid.
- Collection: The purified, condensed solvent drips down into a separate collection flask, leaving the original non-volatile components (contaminants, purified compounds, etc.) behind in the rotating flask.
Why Choose Rotary Evaporation? Key Advantages
This method isn't just effective; its specific advantages make it indispensable for many applications, from wastewater treatment to pharmaceutical development.
Efficiency and Speed
By combining a vacuum with a large surface area, rotovaps remove solvents much faster than other methods like oven drying or simple distillation. This drastically reduces processing time.
Gentle on Sensitive Materials
The ability to operate at low temperatures is the rotovap's most critical feature. It is the standard method for isolating Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) or other delicate organic compounds that would be damaged by aggressive heating.
Purity and Component Recovery
The process provides an excellent separation between volatile solvents and non-volatile solutes. This allows for the recovery of highly pure solvent for reuse or the isolation of valuable materials, such as precious metals or a synthesized chemical product.
Versatility and Reliability
Vacuum evaporation can handle a wide range of feed streams with little pre-treatment. The mechanics are straightforward, leading to systems that are simple to operate and have low maintenance requirements.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, the rotary evaporator is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Not for High-Boiling-Point Solvents
While a vacuum lowers the boiling point, solvents with extremely high boiling points (e.g., DMSO or DMF) can still require high bath temperatures and a very deep vacuum, which can be challenging to achieve.
Potential for Foaming and Bumping
Certain solutions have a tendency to foam or "bump" (boil violently) under vacuum, which can carry the sample over into the collection flask and ruin the separation. This requires careful control of the rotation speed and vacuum depth.
Primarily a Batch Process
Rotary evaporators are designed for processing one batch at a time. They are not suited for continuous-flow industrial processes where a constant stream of material needs to be handled.
When is a Rotary Evaporator the Right Tool?
Choosing the right tool depends entirely on your goal. A rotovap excels in specific scenarios where precision and care are paramount.
- If your primary focus is gentle solvent removal: Use a rotovap to protect heat-sensitive compounds when isolating a product from a reaction mixture.
- If your primary focus is efficient sample concentration: It is the ideal choice for quickly reducing the volume of a solution to concentrate a non-volatile solute before further analysis.
- If your primary focus is high-purity solvent recycling: Select this method when you need to recover a clean, pure solvent from a solution containing non-volatile contaminants.
Ultimately, the rotary evaporator is an indispensable tool for precise, gentle, and efficient separation in any modern laboratory.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Vacuum Pump | Lowers pressure to reduce solvent boiling point. |
| Rotating Flask | Spreads solution into a thin film for maximum evaporation surface area. |
| Heating Bath | Gently warms the solution to its new, lower boiling point. |
| Condenser | Cools solvent vapor, turning it back into liquid for collection. |
| Collection Flask | Collects the purified, condensed solvent after separation. |
Need a reliable rotary evaporator for your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including rotary evaporators designed for efficient, gentle solvent removal—protecting your sensitive samples and boosting productivity. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory's evaporation and concentration needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Benchtop Water Circulating Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
- Ceramic Evaporation Boat Set Alumina Crucible for Laboratory Use
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- Why is a hydrogen and water vapor (H2/H2O) gas manifold system necessary for LBE corrosion control? Precision Analysis
- Is it economically viable to recycle plastic? The Harsh Economic Reality of Plastic Recycling
- What is the instrument used in IR spectroscopy analysis? The Definitive Guide to FTIR Spectrometers
- Why do we need magnetic field in magnetron sputtering? Boost Deposition Rates & Film Quality
- What are the two types of XRF systems? EDXRF vs. WDXRF for Accurate Material Analysis
- What are the advantages of physical vapor deposition? Achieve High-Purity, Durable Thin Films
- What is the moisture content of pyrolysis oil? Unlock the Key to Fuel Quality and Stability
- What is sinter metal? A Guide to Cost-Effective, Complex Metal Parts



















