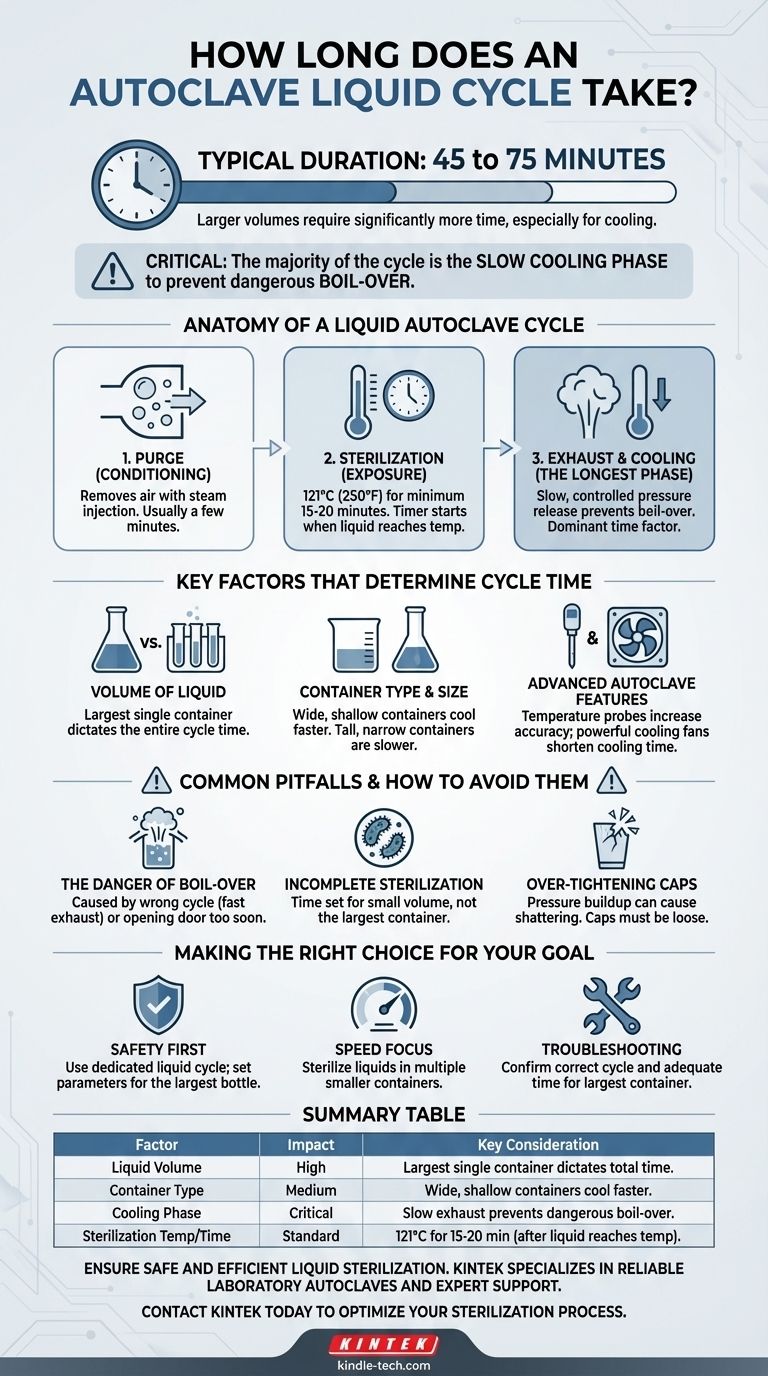
A standard liquid autoclave cycle typically takes between 45 and 75 minutes from start to finish. The exact duration depends heavily on the volume of the liquid being sterilized, as larger volumes require significantly more time to heat up and, more importantly, to cool down safely.
The critical factor to understand is that the majority of a liquid cycle's duration is dedicated to the slow, controlled cooling phase. This prevents the superheated liquid from boiling over violently when the chamber pressure is released, which is the primary safety risk and cause of lost samples.
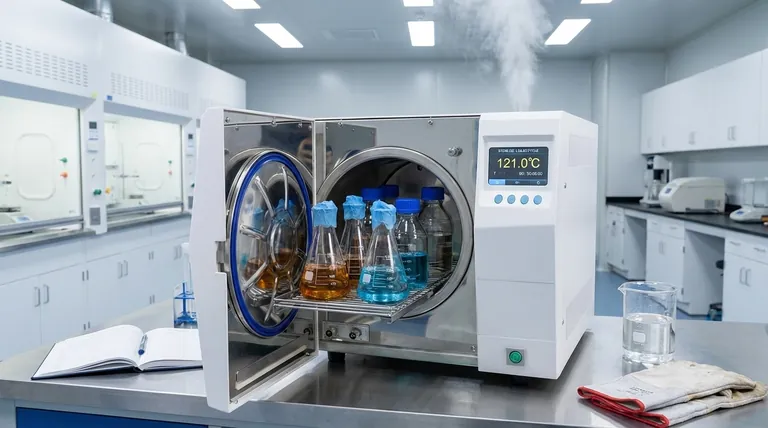

The Anatomy of a Liquid Autoclave Cycle
To understand the time commitment, you must first understand that an autoclave cycle isn't a single event. It's a sequence of distinct phases, each with a specific purpose.
Phase 1: Purge (Conditioning)
This initial phase removes air from the autoclave chamber by injecting steam. Effective air removal is critical because trapped air pockets can prevent steam from directly contacting and sterilizing the load. This phase is relatively quick, usually lasting a few minutes.
Phase 2: Sterilization (Exposure)
This is the core of the process. The chamber is held at a specific temperature and pressure for a set duration to achieve sterilization. The most common standard is 121°C (250°F) for a minimum of 15-20 minutes.
However, this timer only begins once the chamber reaches the target temperature. Larger liquid volumes take much longer to heat, so the actual exposure time for the liquid itself might require a longer programmed cycle.
Phase 3: Exhaust and Cooling (The Longest Phase)
This is the most time-consuming and critical phase for liquids. The chamber's pressure must be released very slowly.
If pressure were dropped rapidly (a "fast exhaust" cycle for glassware), the boiling point of the water in your media would instantly drop below its current temperature. This causes a phenomenon called boil-over, where the liquid erupts from its container, leading to loss of media, contamination, and a significant safety hazard. The slow, controlled pressure release allows the liquid to cool gradually, keeping it below its boiling point as the pressure drops.
Key Factors That Determine Cycle Time
Not all liquid loads are the same. The time your specific cycle takes will vary based on several key factors.
Volume of the Liquid
This is the single most significant factor. A 4-liter flask will take substantially longer to heat to 121°C and even longer to cool safely compared to a rack of 100mL test tubes. The cycle time must be set according to the largest single container in the load.
Container Type and Size
The shape and material of your container matter. A tall, narrow-necked Erlenmeyer flask will heat and cool more slowly than a wide-mouthed, shallow beaker containing the same volume. Loosely sealed caps are essential to allow for pressure equalization without letting contaminants in.
Advanced Autoclave Features
Modern autoclaves often have features that affect cycle time. Some use an internal temperature probe placed directly in a reference liquid container. This ensures the cycle timer doesn't start until the liquid itself reaches 121°C, adding accuracy but potentially extending the heating phase.
Conversely, some units have powerful cooling fans that circulate air around the chamber after the sterilization phase, significantly shortening the cooling time.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Understanding the process is key to avoiding common and costly mistakes.
The Danger of Boil-Over
This is the most common failure in liquid autoclaving. It is almost always caused by using the wrong cycle (e.g., a "gravity" or "solids" cycle with a fast exhaust) or by opening the door before the liquid has cooled sufficiently, even if the chamber pressure reads zero.
Incomplete Sterilization
If you set your cycle time based on a small volume but are sterilizing a large flask, the core of that liquid may never reach the required temperature for the necessary duration. This creates a false sense of sterility and can ruin experiments.
Over-tightening Caps
While it may seem intuitive to seal containers tightly, this is extremely dangerous. As the liquid heats, it will create immense pressure inside the container with no way to escape, leading to the risk of the container shattering. Caps must always be left loose.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure safety and success, select your approach based on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is safety and guaranteed sterility: Always use a dedicated liquid cycle and set the time and volume parameters based on the largest single bottle in your load.
- If your primary focus is speed: Sterilize liquids in multiple smaller containers instead of one large one, as this will dramatically reduce the necessary heating and cooling time.
- If you are troubleshooting a failed cycle: First, confirm you are using the correct "liquid" or "slow exhaust" program, and then ensure your sterilization time is adequate for the volume of your largest container.
Ultimately, a patient and methodical approach to liquid sterilization prevents lost samples, ensures reliable results, and maintains a safe laboratory environment.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Cycle Time | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Liquid Volume | High | Largest single container dictates total cycle time. |
| Container Type | Medium | Wide, shallow containers cool faster than tall, narrow ones. |
| Cooling Phase | Critical | Slow exhaust prevents dangerous boil-over; this is the longest phase. |
| Sterilization Temp/Time | Standard | Typically 121°C for 15-20 minutes (after liquid reaches temperature). |
Ensure safe and efficient liquid sterilization in your lab.
Autoclaving liquids requires precision to prevent dangerous boil-overs and guarantee sterility. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable laboratory autoclaves and expert support tailored to your specific needs, whether you're processing media, solutions, or other sensitive liquids.
Let our experts help you optimize your sterilization process for safety and speed. Contact KINTEK today to find the perfect autoclave solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function and principle of autoclaving? Master Lab Sterilization with High-Pressure Steam
- What is the normal temperature of an autoclave? Achieve Sterile Confidence with Precise Control
- What is the necessity of using an autoclave for pre-treating culture media? Ensure Accurate Ag2O/TiO2 Testing
- How do you use an autoclave in a microbiology lab? Master Sterilization for Lab Safety & Accuracy
- What types of items and materials can be processed in a laboratory autoclave? Essential Guide for Lab Safety



















