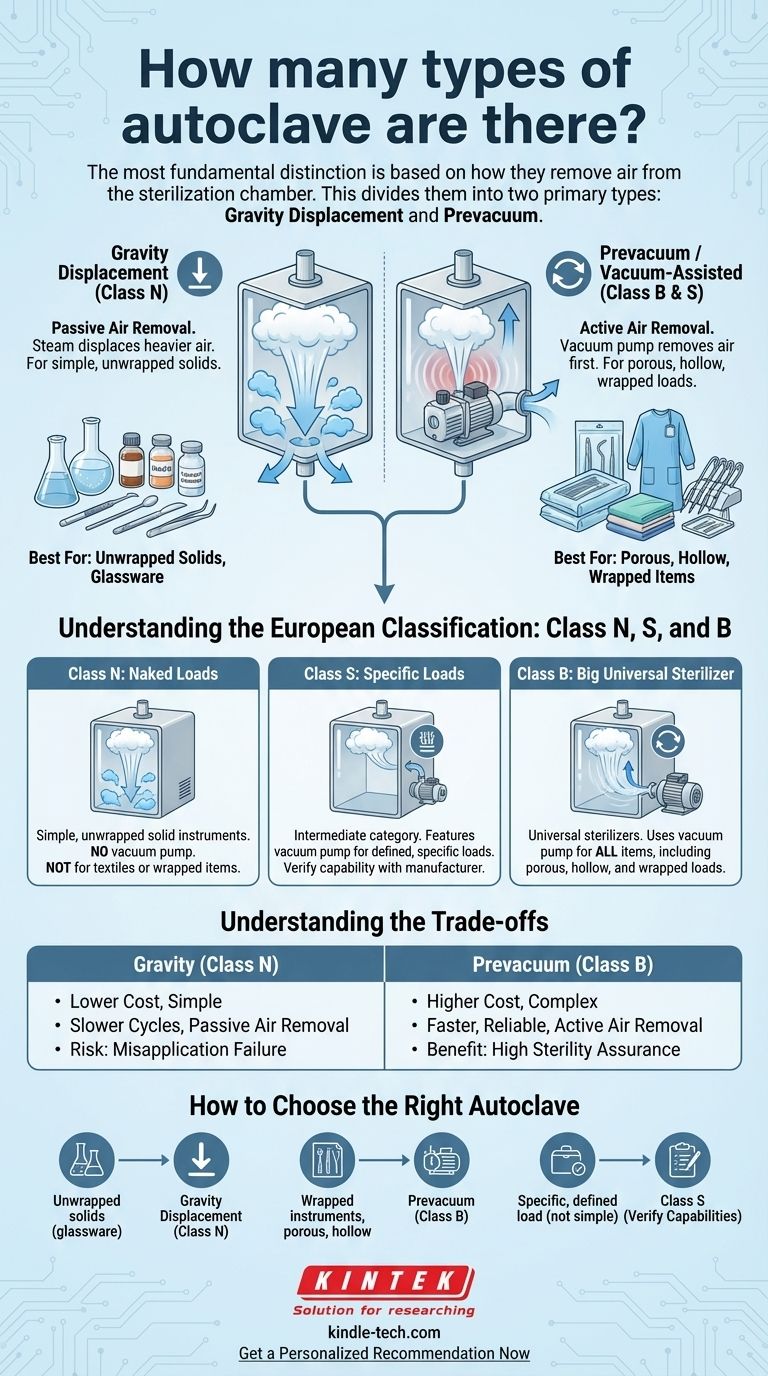
While there are several ways to classify autoclaves, the most fundamental distinction is based on how they remove air from the sterilization chamber. This single principle divides them into two primary types: Gravity Displacement autoclaves and Prevacuum (or vacuum-assisted) autoclaves. Other classifications, such as the European Class N, S, and B standards or categories based on size, are built upon this core difference.
The crucial takeaway is not the number of autoclave types, but the method they use to solve the core problem of sterilization: removing air. Trapped air prevents steam from reaching every surface, leading to failed sterilization. Your choice of autoclave must match the complexity of the items you need to sterilize.

The Core Principle: Air Removal Defines the Autoclave
The effectiveness of steam sterilization depends on direct contact between saturated steam and every surface of the load. Air is the enemy of this process, acting as an insulator and creating cold spots where microorganisms can survive. The primary difference between autoclave types is how they remove this air.
Gravity Displacement (Class N)
In a gravity displacement autoclave, steam is introduced into the chamber, typically from the top or sides. Because steam is less dense than the cool air already inside, it fills the chamber from the top down, forcing the heavier air out through a temperature-sensitive drain vent at the bottom.
This method is simple and cost-effective, much like how pouring a lighter liquid (like oil) on a heavier one (like water) will cause the heavier liquid to be displaced downwards.
These autoclaves are best suited for sterilizing simple, non-porous, and unwrapped items, such as laboratory glassware, media solutions, and basic metal instruments.
Prevacuum / Vacuum-Assisted (Class B & S)
Prevacuum autoclaves use a vacuum pump to actively remove air from the chamber before the steam is introduced. This process typically involves a series of vacuum pulses and steam injections to ensure all air is removed, even from within complex and porous materials.
By creating a near-perfect vacuum, steam can instantly penetrate deep into the most challenging loads.
This advanced method is essential for sterilizing porous items (gowns, textiles), hollow instruments (tubes, dental handpieces), and wrapped instrument packs common in medical and dental settings.
Understanding the European Classification: Class N, S, and B
This widely used standard directly relates to an autoclave's air removal capability and the types of loads it can safely sterilize.
Class N: For "Naked" Loads
Class N autoclaves correspond to the gravity displacement method. They are designed exclusively for sterilizing simple, "naked," or unwrapped solid instruments. They do not have a vacuum pump and cannot be used for textiles, porous items, or wrapped tools.
Class B: The "Big" Universal Sterilizer
Class B autoclaves are prevacuum systems. The "B" signifies their ability to handle the "biggest" range of load types, making them universal sterilizers. They use a vacuum pump for active air removal, making them suitable for all items, including porous, hollow, and wrapped loads.
Class S: For "Specific" Loads
Class S autoclaves are an intermediate category. They feature a vacuum pump but may not meet the stringent performance tests of a Class B unit. They are designed to sterilize "specific" loads as defined by the manufacturer and validated by the user. You must ensure a Class S unit is rated for your particular instruments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing an autoclave involves balancing capability against cost and complexity. There is no single "best" type, only the right tool for the job.
Cost vs. Capability
Gravity (Class N) autoclaves are significantly less expensive upfront. However, their limited application means they are unsuitable for clinical settings where instruments are wrapped.
Prevacuum (Class B) autoclaves have a higher initial cost due to the vacuum pump and more complex controls. This cost is justified by their versatility and the higher level of sterility assurance they provide for complex loads.
Cycle Time and Reliability
Gravity cycles are generally slower because the passive air removal process takes more time. They are also more prone to failure if the load is improperly arranged, trapping air pockets.
Prevacuum cycles are much faster and more reliable. Active air removal ensures consistent and rapid steam penetration, leading to shorter overall cycle times and greater confidence in the outcome.
The Critical Risk of Misapplication
The most significant pitfall is using a gravity (Class N) autoclave for a load that requires a prevacuum (Class B) cycle. Attempting to sterilize a wrapped or hollow instrument in a Class N unit will almost certainly result in sterilization failure, creating a major safety risk.
How to Choose the Right Autoclave
Your decision should be guided entirely by the types of materials you intend to sterilize.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing simple, unwrapped solid items (e.g., glassware, basic lab tools): A Gravity Displacement (Class N) autoclave is a cost-effective and suitable choice.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing wrapped instruments, porous materials (textiles), or hollow items (e.g., medical or dental tools): A Prevacuum (Class B) autoclave is essential to guarantee complete steam penetration and sterility.
- If your primary focus is a specific, defined load that is not a simple solid (e.g., certain types of wrapped instruments but no textiles): A Class S autoclave may be an option, but you must verify its specified capabilities match your exact load type.
Understanding that autoclave type is defined by its air removal method empowers you to select the correct tool for ensuring absolute sterility.
Summary Table:
| Autoclave Type | Air Removal Method | Best For Load Types | European Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gravity Displacement | Passive (steam displaces air) | Simple, unwrapped solids (glassware, media) | Class N |
| Prevacuum | Active (vacuum pump) | Porous, hollow, wrapped items (textiles, instruments) | Class B |
| Class S | Active (vacuum pump, limited) | Specific loads as defined by manufacturer | Class S |
Ensure Sterility and Safety with the Right Autoclave from KINTEK
Choosing the correct autoclave is critical for effective sterilization and lab safety. Whether you need a cost-effective Gravity Displacement model for simple glassware or a high-performance Prevacuum system for complex medical instruments, KINTEK has the solution.
As your trusted lab equipment partner, we provide:
- Expert Guidance: Help you select the perfect autoclave type (Gravity, Class B, or Class S) for your specific sterilization needs.
- Reliable Performance: Durable autoclaves that deliver consistent, validated results cycle after cycle.
- Full Support: Installation, validation, and maintenance services to keep your lab running smoothly.
Don't risk sterilization failure. Contact our experts today to discuss your requirements and find the ideal autoclave for your laboratory.
Get a Personalized Recommendation Now
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory High Pressure Horizontal Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- What is the size of the autoclave? Choose the Right Capacity for Your Lab
- What is the life expectancy of an autoclave machine? Maximize Your Investment with Proper Care
- What is the purpose of treating polyester fabric in an autoclave? Ensure Reliable Results in Lab Experiments
- What role does an autoclave play in remediation experiments? Ensure Precision by Eliminating Biological Noise
- What is the pressure bar for autoclave sterilization? Master the Critical Link Between Pressure and Temperature



















