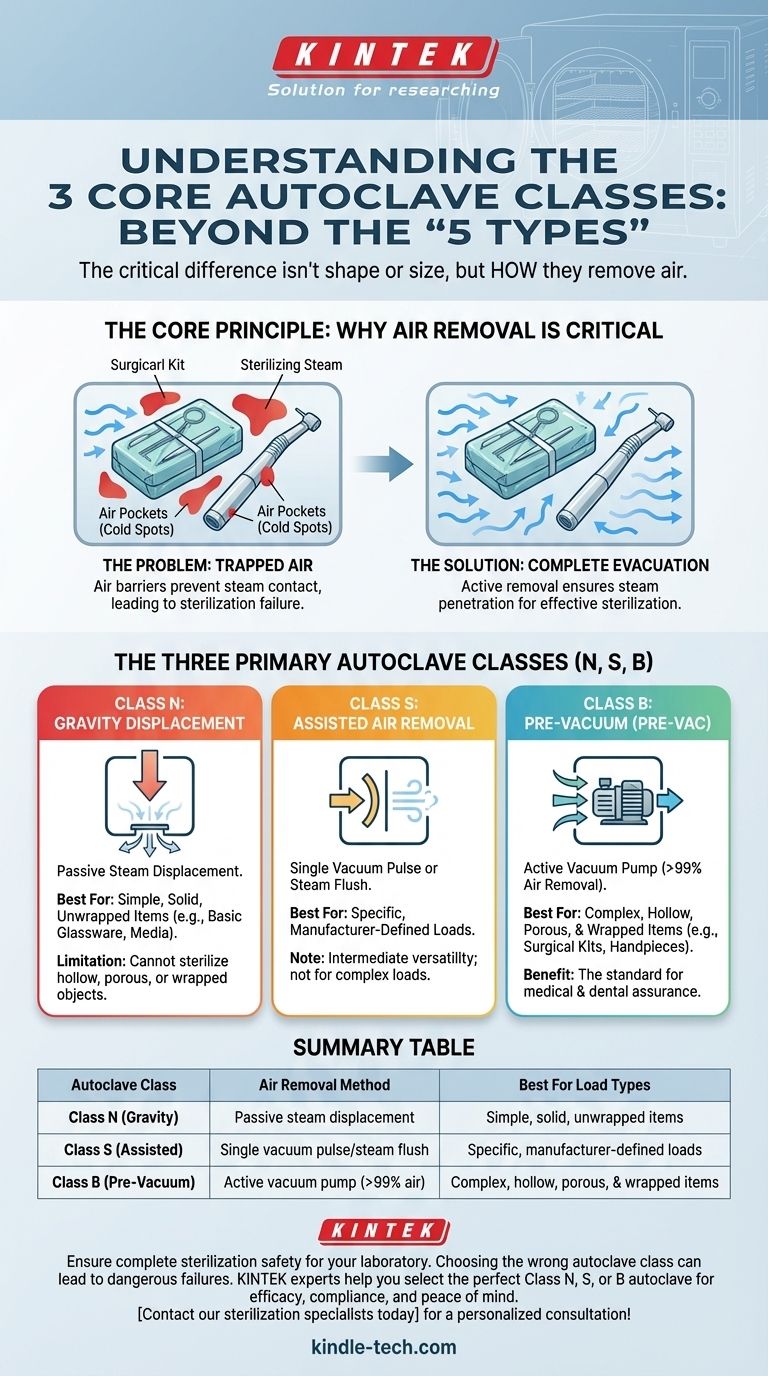
While the question asks for five types of autoclaves, the most critical and universally recognized classification system in professional and medical settings is based on three classes: N, S, and B. These classes are defined by the method used to remove air before sterilization, which directly determines what types of materials they can safely process.
The crucial difference between autoclave types isn't their size or shape, but how they remove air from the chamber. This single factor determines whether an autoclave can sterilize simple solid objects or complex hollow and porous loads, making it the most important consideration for ensuring safety and efficacy.
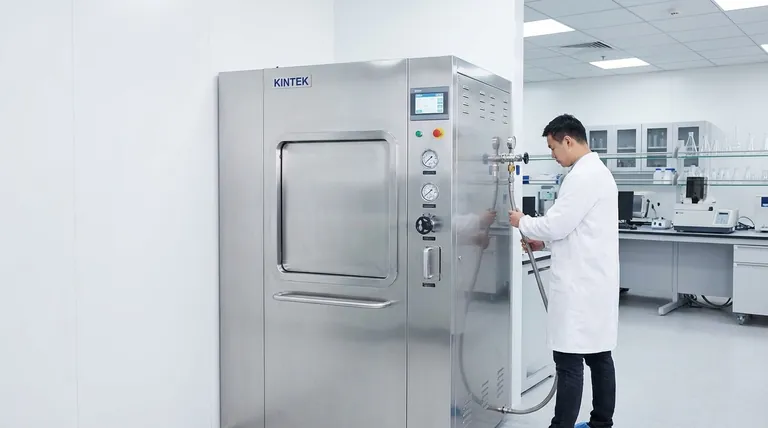

The Core Principle: Why Air Removal Is Critical
Before sterilization can begin, all air must be removed from the autoclave chamber and from within the items being sterilized.
The Problem with Trapped Air
Air pockets trapped within a load (like in a dental handpiece, a wrapped surgical kit, or a textile pack) act as an insulating barrier.
These "cold spots" prevent the sterilizing steam from making direct contact with all surfaces, leading to a critical sterilization failure.
The Solution: Active vs. Passive Removal
The different classes of autoclaves are defined by how they solve this air removal problem. Less sophisticated models do it passively, while more advanced models use active, mechanical systems for complete air evacuation.
The Three Primary Autoclave Classes
Understanding these three classes provides a definitive framework for choosing the correct equipment for any sterilization task.
Class N: Gravity Displacement
This is the most basic type of autoclave. It operates on a simple principle where incoming steam, being lighter than air, displaces the heavier air, pushing it out through a drain vent.
It is often called a gravity displacement autoclave. Think of it like a sophisticated pressure cooker.
Because this method is passive, it is only effective for sterilizing simple, solid, unwrapped items like basic laboratory glassware or certain media. It cannot reliably sterilize hollow, porous, or wrapped objects.
Class S: Assisted Air Removal
Class S autoclaves are an intermediate category designed for specific loads as defined by the manufacturer. They are more capable than Class N but not as versatile as Class B.
They often use a single vacuum pulse or an overpressure steam flush to actively assist in air removal before the sterilization cycle begins.
This class is less common and is best suited for applications where a specific, known load type proves difficult for a Class N unit but does not require the full capability of a Class B unit.
Class B: Pre-Vacuum (Pre-Vac)
This is the most advanced and versatile class of autoclave. It is also known as a pre-vacuum or negative pressure displacement sterilizer.
Before introducing steam, a Class B autoclave uses a powerful vacuum pump to actively and forcibly remove over 99% of the air from the chamber and the load. It typically performs this in a series of vacuum and pressure pulses.
This active air removal ensures there are no trapped air pockets, allowing steam to penetrate deep into complex, hollow instruments, porous materials, and multiple wrapped surgical kits. Class B autoclaves are the standard for medical, dental, and veterinary clinics.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these classes involves balancing capability against cost and complexity.
Cost vs. Capability
Class N autoclaves are the simplest and most affordable, but their application is highly restricted.
Class B autoclaves are the most expensive due to their vacuum pump and complex control systems, but they offer universal sterilization capability.
Class S units fall in between, offering a solution for specific loads at a price point typically lower than a Class B machine.
The Load Type Is Non-Negotiable
The most critical factor is the type of load you need to sterilize. Using an inadequate autoclave class for a complex load is not a compromise—it is a failure of the sterilization process.
For example, attempting to sterilize a hollow dental tool in a Class N autoclave poses a significant risk of cross-contamination because trapped air will prevent sterilization of the internal surfaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your decision must be guided entirely by the items you need to sterilize.
- If your primary focus is simple, solid, unwrapped items (e.g., basic lab glassware, petri dishes): A Class N autoclave is a sufficient and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is complex, hollow, or porous items (e.g., dental handpieces, wrapped surgical kits, textiles): A Class B autoclave is the only safe and appropriate choice to guarantee sterilization.
- If your primary focus is a specific named product (e.g., a certain type of instrument) that fails in a Class N: A Class S unit, if specified by the manufacturer for that item, may be a suitable option.
Ultimately, selecting the right autoclave is about matching the air removal method to the complexity of your load to ensure absolute sterilization assurance.
Summary Table:
| Autoclave Class | Air Removal Method | Best For Load Types |
|---|---|---|
| Class N (Gravity) | Passive steam displacement | Simple, solid, unwrapped items (e.g., glassware) |
| Class S (Assisted) | Single vacuum pulse or steam flush | Specific, manufacturer-defined loads |
| Class B (Pre-Vacuum) | Active vacuum pump (removes >99% air) | Complex, hollow, porous, & wrapped items (e.g., surgical kits) |
Ensure complete sterilization safety for your laboratory. Choosing the wrong autoclave class for your specific loads—whether simple glassware or complex hollow instruments—can lead to dangerous sterilization failures. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts will help you select the perfect Class N, S, or B autoclave to guarantee efficacy, compliance, and peace of mind. Contact our sterilization specialists today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- Why use PPL-Lined Autoclaves for Vanadium Dioxide Nanorods? Achieve Pure Crystallization at 280°C
- Why is chemical sterilization sometimes used as an alternative to autoclaving? To Safely Sterilize Heat-Sensitive Equipment
- How do you autoclave lab equipment? A Step-by-Step Guide to Sterile Results
- What medical equipment can be autoclaved? Ensure Sterile, Safe, and Durable Instruments
- What core conditions must a high-pressure autoclave meet for supercritical water corrosion? Master 27 MPa & 600°C Tests
- How is temperature controlled in autoclave? Master the Link Between Pressure and Sterilization
- What instruments are sterilized in an autoclave the temperature must be maintained at what? The Essential Guide to Effective Sterilization
- Why is autoclaving the most effective? Harness the Power of Pressurized Steam for Absolute Sterility



















