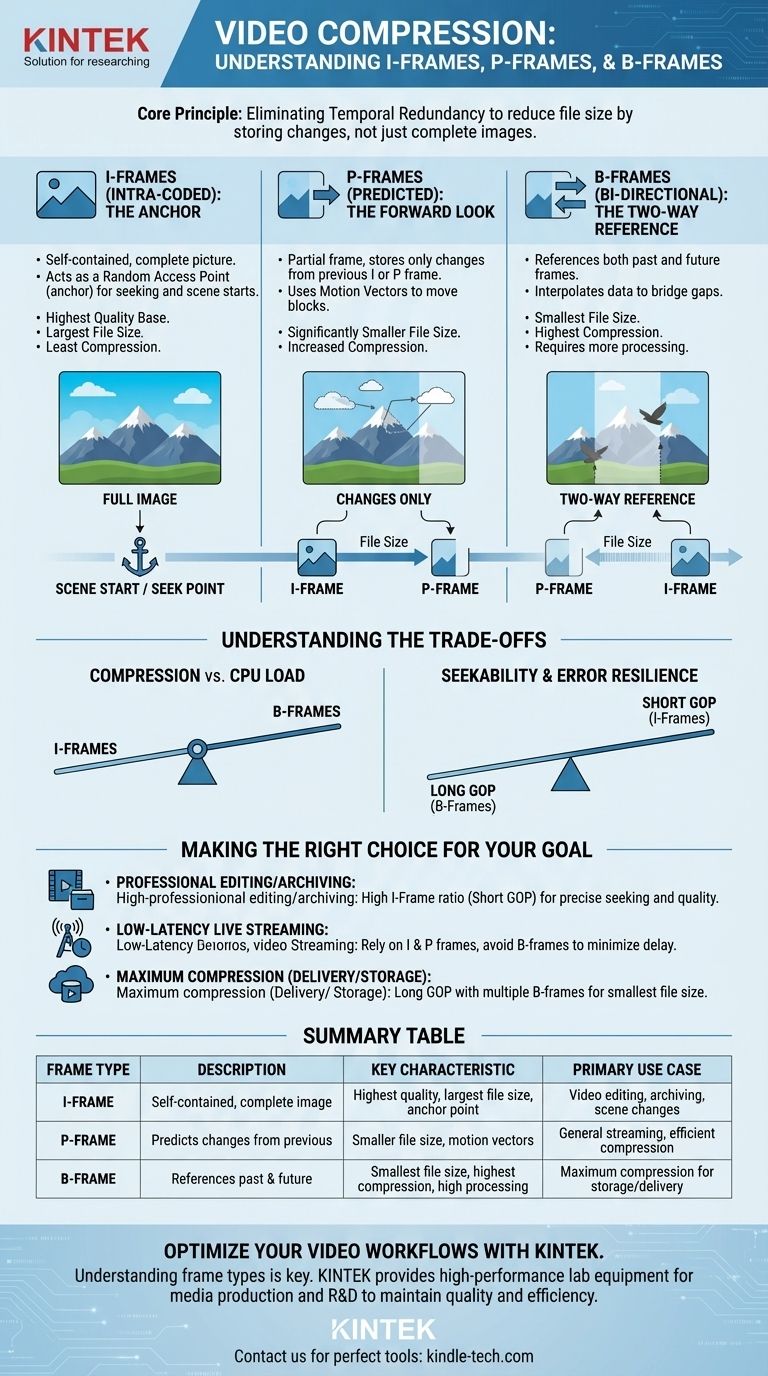
In modern video compression, there are three fundamental types of frames, or pictures: I-frames, P-frames, and B-frames. An I-frame is a complete, self-contained image, while P-frames and B-frames are partial frames that only store the changes from other frames, which is how compression is achieved. P-frames predict forward from a previous frame, and B-frames predict in both directions from past and future frames.
The core principle behind these frame types is the elimination of temporal redundancy. By storing one complete image (I-frame) and then only describing what moves or changes in subsequent frames (P and B-frames), a video codec can drastically reduce file size without a perceptible loss in quality.
The Foundation: I-Frames (Intra-coded)
The Self-Contained Image
An I-frame, or Intra-coded frame, is a complete picture. You can think of it as a standard JPEG or BMP image embedded within the video stream.
It contains all the necessary data to be displayed on its own and does not rely on information from any other frame.
The Anchor of the Video Stream
Because they are self-contained, I-frames serve as random access points, or anchors, within a video file. When you seek to a new point in a video, the player looks for the nearest preceding I-frame to begin decoding.
They are also used at the start of new scenes or after significant visual changes.
Size and Quality
I-frames use the least amount of compression compared to other frame types. As a result, they are the largest in file size but provide the highest quality base from which other frames are built.
The Forward Look: P-Frames (Predicted)
Storing Only the Changes
A P-frame, or Predicted frame, is a partial frame that increases compression efficiency. It works by only encoding the differences between itself and the I-frame or P-frame that came before it.
How Prediction Works
Instead of storing a whole new image, a P-frame essentially contains instructions like, "Take the block of pixels from this location in the previous frame and move it here." This instruction is called a motion vector.
It also stores data for any new image information that wasn't present in the reference frame.
The Efficiency Gain
Because P-frames only store changes and motion vectors, they are significantly smaller in file size than I-frames, forming a critical part of the compression strategy.
The Two-Way Reference: B-Frames (Bi-directional)
The Most Efficient Frame
A B-frame, or Bi-directional predicted frame, offers the highest level of compression. It takes the prediction concept a step further by referencing data from both a preceding frame and a subsequent frame.
Interpolating the Gaps
By looking both backward and forward, a B-frame can be incredibly efficient. For example, if an object is temporarily covered and then reappears, a B-frame can effectively interpolate its position using data from both before and after the obstruction.
The Highest Level of Compression
This two-way referencing makes B-frames the smallest and most efficient frame type, allowing for the greatest reduction in video file size.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Compression vs. CPU Load
There is a direct trade-off between compression efficiency and computational cost. I-frames are the easiest to decode, while B-frames are the most demanding because the decoder must hold past and future frames in memory to reconstruct the image.
This is why very low-latency streaming applications sometimes avoid B-frames to reduce decoding delay.
Seekability and Error Resilience
A long sequence of P and B-frames between I-frames is called a Group of Pictures (GOP). A long GOP results in a smaller file size but can make seeking less precise.
Furthermore, an error in an I-frame or P-frame can corrupt the display of all subsequent frames that depend on it until the next I-frame appears.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding these frame types allows you to make informed decisions when encoding video.
- If your primary focus is professional editing or archiving: Use a higher ratio of I-frames (a short GOP) to ensure precise frame-accurate seeking and minimize quality loss.
- If your primary focus is low-latency live streaming: Rely primarily on I-frames and P-frames, often avoiding B-frames entirely to minimize the processing delay on the viewer's end.
- If your primary focus is maximum compression for delivery or storage: Employ longer GOPs with multiple B-frames between I and P-frames to achieve the smallest possible file size.
Ultimately, mastering the interplay between I, P, and B-frames gives you direct control over the critical balance between video quality, file size, and playback performance.
Summary Table:
| Frame Type | Description | Key Characteristic | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| I-Frame | Self-contained, complete image | Highest quality, largest file size, serves as a random access point | Video editing, archiving, scene changes |
| P-Frame | Predicts changes from previous frames | Smaller file size, uses motion vectors for compression | General streaming, efficient compression |
| B-Frame | References both past and future frames | Smallest file size, highest compression, but requires more processing | Maximum compression for storage or delivery |
Optimize your video workflows with the right equipment. Understanding frame types is just the start—achieving consistent results requires reliable lab technology. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables tailored for media production, research, and development. Whether you're encoding, analyzing, or archiving video, our solutions help you maintain quality and efficiency. Contact us today to find the perfect tools for your laboratory's needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Planetary Ball Mill Cabinet Planetary Ball Milling Machine
- Shortpass Filters for Optical Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between a ball mill and a planetary mill? Choose the Right Grinding Tool for Your Lab
- What is the difference between a ball mill and a planetary ball mill? Unlock the Right Grinding Technology for Your Lab
- What is the working principle of planetary ball mill? Unlock High-Energy Grinding for Nanoscale Results
- What is the primary function of a high-energy planetary ball mill? Powering Sulfide Solid-State Electrolyte Synthesis
- What are the parameters of a planetary ball mill? Master Speed, Time, and Media for Perfect Grinding

