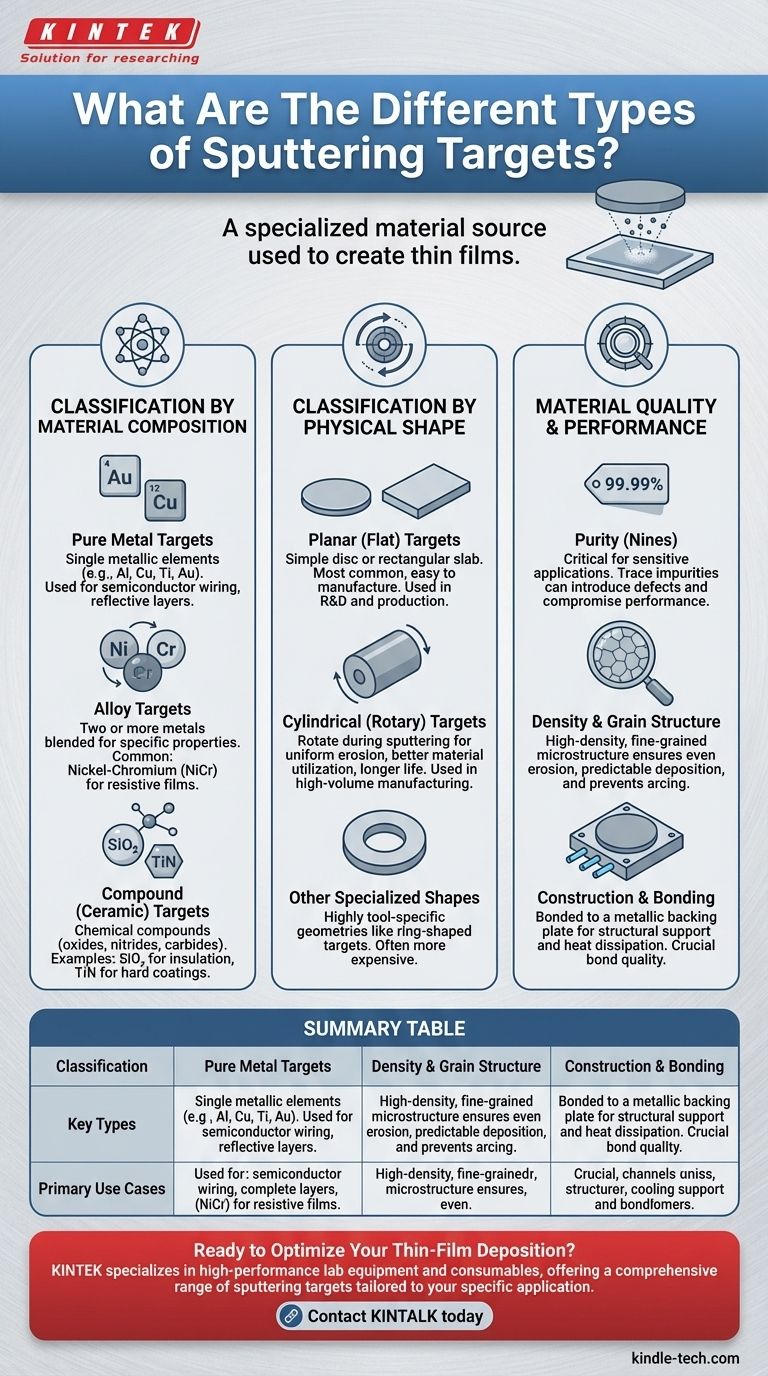
At its core, a sputtering target is a specialized material source used to create thin films. These targets are primarily categorized by their material composition (what they are made of) and their physical geometry (their shape), with material quality being a critical third dimension that dictates performance.
The "type" of sputtering target you need is not defined by a single characteristic. It is a specific combination of material composition, physical shape, and microstructural quality, all of which must be precisely matched to your deposition equipment and the desired properties of your final thin film.

Classification by Material Composition
The most fundamental way to classify a sputtering target is by the material it will deposit. This choice directly determines the chemical and physical properties of the resulting coating.
Pure Metal Targets
These are targets made from a single metallic element, such as aluminum (Al), copper (Cu), titanium (Ti), or gold (Au). They are widely used in applications ranging from semiconductor wiring to creating reflective layers.
Alloy Targets
Alloy targets are composed of two or more metals blended together to achieve specific properties that a pure metal cannot. A common example is nickel-chromium (NiCr), used for depositing resistive films in electronic components.
Compound (Ceramic) Targets
These targets are made from chemical compounds, often oxides, nitrides, or carbides. Examples include silicon dioxide (SiO₂) for insulating layers or titanium nitride (TiN) for hard, wear-resistant coatings. Sputtering these materials can be more complex than sputtering pure metals.
Classification by Physical Shape
The target's shape, or geometry, is determined by the design of the sputtering system (cathode) it will be installed in.
Planar (Flat) Targets
This is the most common and straightforward shape, resembling a simple disc or rectangular slab. Planar targets are generally easier and less expensive to manufacture and are used in a wide variety of R&D and production systems.
Cylindrical (Rotary) Targets
Used in large-scale, high-volume manufacturing, cylindrical targets rotate during the sputtering process. This rotation allows for more uniform erosion, leading to better material utilization, longer target life, and a more stable deposition process.
Other Specialized Shapes
While less common, some sputtering tools are designed for specific geometries like ring-shaped targets. These are highly tool-specific and are often more expensive due to the complexity of manufacturing.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Quality and Purity
Simply choosing a material and shape is not enough. The quality of the target material itself is arguably the most critical factor for achieving a high-performance thin film. Two targets of the same material and shape can produce dramatically different results.
The Critical Role of Purity
The purity of a target, often expressed in terms of "nines" (e.g., 99.99% or 4N), dictates the level of contaminants. In sensitive applications like semiconductor manufacturing, even trace impurities in the target can introduce defects and compromise the electrical performance of the final device.
Density and Grain Structure
A high-density target with a uniform, fine-grained microstructure is essential. Low-density targets with voids can cause process instability and arcing. A consistent grain size ensures the target erodes evenly, leading to a predictable and repeatable deposition rate.
Construction and Bonding
Sputtering targets are not just monolithic blocks of material. They are typically bonded to a metallic backing plate, which provides structural support and incorporates channels for water cooling to dissipate the intense heat generated during the process. The quality of this bond is crucial for thermal management and target integrity.
Selecting the Right Target for Your Application
Your choice must be driven by your end goal, balancing performance requirements against budget and equipment constraints.
- If your primary focus is research and development: High-purity planar targets offer the most flexibility and are ideal for experimenting with new materials and processes.
- If your primary focus is high-volume industrial production: Cylindrical (rotary) targets provide superior material utilization, longer campaigns, and better process stability, justifying their higher initial cost.
- If your primary focus is a decorative or protective coating: You may be able to use a target with a lower purity specification, reducing material costs without compromising the aesthetic or basic functional requirements of the film.
Understanding these distinct classifications empowers you to select the precise material source needed to control and optimize your thin-film deposition process.
Summary Table:
| Classification | Key Types | Primary Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Pure Metals (Al, Cu, Ti), Alloys (NiCr), Compounds (SiO₂, TiN) | Defines the chemical and physical properties of the deposited film. |
| Physical Shape | Planar (disc/rectangular), Cylindrical (rotary), Specialized (ring) | Determined by the sputtering system design for uniform erosion and material utilization. |
| Material Quality | High Purity (e.g., 99.99%), High Density, Fine Grain Structure | Critical for process stability, deposition rate, and final film performance in sensitive applications. |
Ready to Optimize Your Thin-Film Deposition?
Selecting the right sputtering target is a precise science that directly impacts your results. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, offering a comprehensive range of sputtering targets tailored to your specific application—from R&D to high-volume production.
Our expertise ensures you get the optimal combination of material composition, geometry, and microstructural quality for superior film properties, process stability, and cost-efficiency.
Contact KINTALK today to discuss your requirements and let our experts help you achieve flawless thin films.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Hollow Etching Flower Basket ITO FTO Developing Glue Removal
- Vacuum Cold Trap Direct Cold Trap Chiller
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is the difference between PECVD and sputter? Choose the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What is plasma activated chemical vapor deposition? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the drawbacks of PECVD? Understanding the Trade-offs of Low-Temperature Deposition




