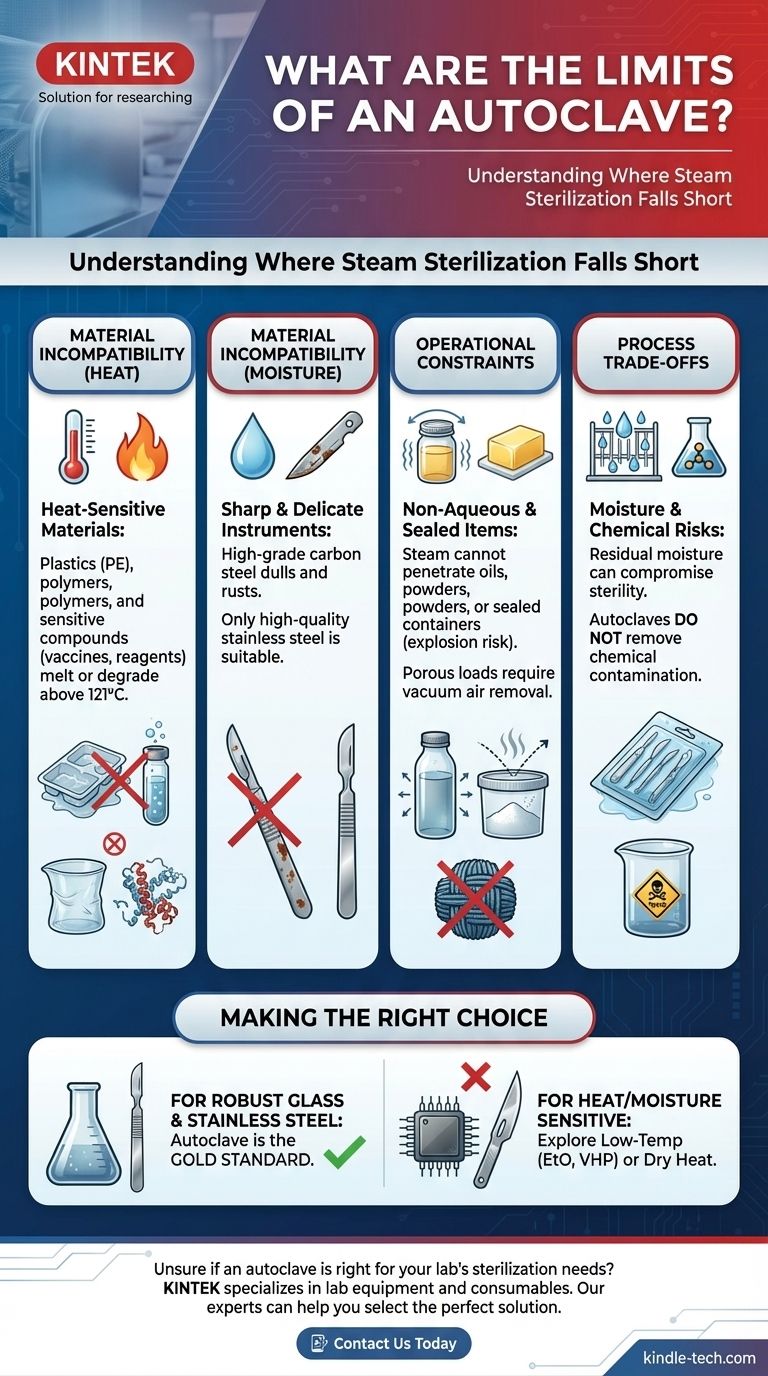
At its core, an autoclave's primary limitation is its reliance on high-pressure, high-temperature steam. This means it is fundamentally unsuitable for any material that is sensitive to heat or moisture. Consequently, it cannot sterilize items like heat-labile plastics, sharp carbon steel instruments that would dull or rust, and anhydrous materials like oils or powders that steam cannot penetrate.
The power of an autoclave—using superheated steam to kill microorganisms—is also its greatest weakness. Any material that cannot withstand temperatures above 121°C (250°F) or direct exposure to moisture is at risk of being damaged or failing to be sterilized.
Material Incompatibility: The Primary Limitation
The most common reason an autoclave is the wrong choice for a task is that the material itself cannot survive the process. This limitation falls into several key categories.
Heat-Sensitive Materials
Many common materials, especially plastics and polymers, will melt, warp, or degrade under the intense heat of an autoclave. For example, polyethylene trays are known to melt and can cause significant damage to the autoclave chamber itself. Only plastics specifically rated for autoclaving can be used.
Sharp and Delicate Instruments
High heat and moisture create a corrosive environment for certain metals and can ruin the temper of sharp edges. High-grade carbon steel, often used for scalpels and scissors, will become dull and is prone to rusting. Only instruments made from high-quality stainless steel are appropriate for steam sterilization.
Sensitive Compounds and Solutions
The sterilization process is not limited to physical objects. Many chemical and biological compounds are denatured or destroyed by excessive heat. High-protein solutions like vaccines and serums, as well as certain reagents like urea, will degrade and lose their efficacy, requiring filtration or other non-heat-based sterilization methods.
Operational Constraints and Substance Type
Beyond simple material compatibility, an autoclave's effectiveness is limited by the physical nature of the items being sterilized and how the chamber is loaded.
Non-Aqueous and Waterproof Substances
Steam sterilization works through direct contact and condensation, which transfers heat efficiently. Oily substances, greases, and powders are hydrophobic (repel water) and cannot be penetrated by steam. This means an autoclave is completely ineffective for sterilizing these materials; dry heat is the appropriate alternative.
Porous Loads and Hollow Items
Achieving sterilization in textiles, dense porous loads, or long, thin hollow tubes requires the complete removal of air so steam can penetrate every surface. Basic autoclaves (such as Class N) do not have a vacuum cycle to actively remove air, making them unsuitable for these types of loads. This failure to penetrate can lead to a failed sterilization cycle.
Sealed Containers
Never autoclave liquids in a tightly sealed container. The buildup of steam pressure inside the container with no means of escape creates an explosion hazard. Containers must be loosely capped or vented to allow pressure to equalize. Similarly, wrapping items completely in aluminum foil is counterproductive as it shields them from steam contact.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While effective, steam sterilization is not a perfect process. Recognizing its inherent drawbacks is critical for safe and effective use.
The Risk of Moisture Retention
A significant disadvantage is moisture retention. If items are not allowed to dry properly within a drying cycle, the residual moisture can compromise the sterile barrier of packaging or promote corrosion on instruments.
No Chemical Decontamination
An autoclave is a sterilization tool, not a chemical purification system. It will effectively kill biological organisms but will not remove or neutralize chemical contamination. If an item is contaminated with a toxic chemical, it will remain chemically contaminated after autoclaving.
The Human Factor in Operation
The effectiveness of an autoclave is highly dependent on the operator. Overcrowding the chamber prevents steam circulation, mixing clean items with biohazardous waste creates cross-contamination risks, and failing to add the correct amount of water can lead to cycle failure or equipment damage. These operational errors are a practical limit on its reliability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct sterilization method, you must match the process to the material and the objective.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing robust glassware and stainless steel surgical tools: The autoclave is the economical, rapid, and highly effective gold standard.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing heat-sensitive plastics or complex electronics: The autoclave is unsuitable; you must explore low-temperature methods like Ethylene Oxide (EtO) or vaporized hydrogen peroxide (VHP).
- If your primary focus is sterilizing sharp carbon steel instruments: An autoclave will cause damage; dry heat sterilization is a more appropriate choice to preserve the sharpness and integrity of the metal.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing oils, powders, or other anhydrous materials: Steam sterilization is ineffective; you must use dry heat, as steam cannot penetrate these substances.
Ultimately, understanding an autoclave's limitations is the key to using it safely and effectively.

Summary Table:
| Limitation Category | Key Examples | Alternative Method |
|---|---|---|
| Heat-Sensitive Materials | Plastics (e.g., polyethylene), sensitive compounds | Low-temperature sterilization (e.g., EtO, VHP) |
| Moisture-Sensitive Items | Sharp carbon steel (rusts), anhydrous oils/powders | Dry heat sterilization |
| Operational Constraints | Porous loads, sealed containers, improper loading | Use appropriate autoclave class (e.g., Class B with vacuum) |
| Chemical Contamination | Toxic chemicals (not neutralized) | Chemical decontamination prior to sterilization |
Unsure if an autoclave is right for your lab's sterilization needs?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the perfect sterilization solution—whether it's an autoclave for robust instruments or an alternative method for heat-sensitive materials.
Contact us today (#ContactForm) to ensure your lab operates safely and efficiently with the right equipment!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Laboratory Horizontal Autoclave Steam Sterilizer Lab Microcomputer Sterilizer
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
People Also Ask
- What is an autoclave used for in a lab? Achieve Total Sterilization for Lab Safety and Integrity
- What are the do's and don'ts in using autoclave? A Guide to Safe and Effective Sterilization
- Can autoclave sterilize liquid? Master Safe and Effective Liquid Sterilization
- What is the most common sterilization technique used in labs? Mastering the Autoclave for Unmatched Safety
- What is the function of autoclave in tissue culture laboratory? Ensure Absolute Sterility for Successful Cell Growth



















