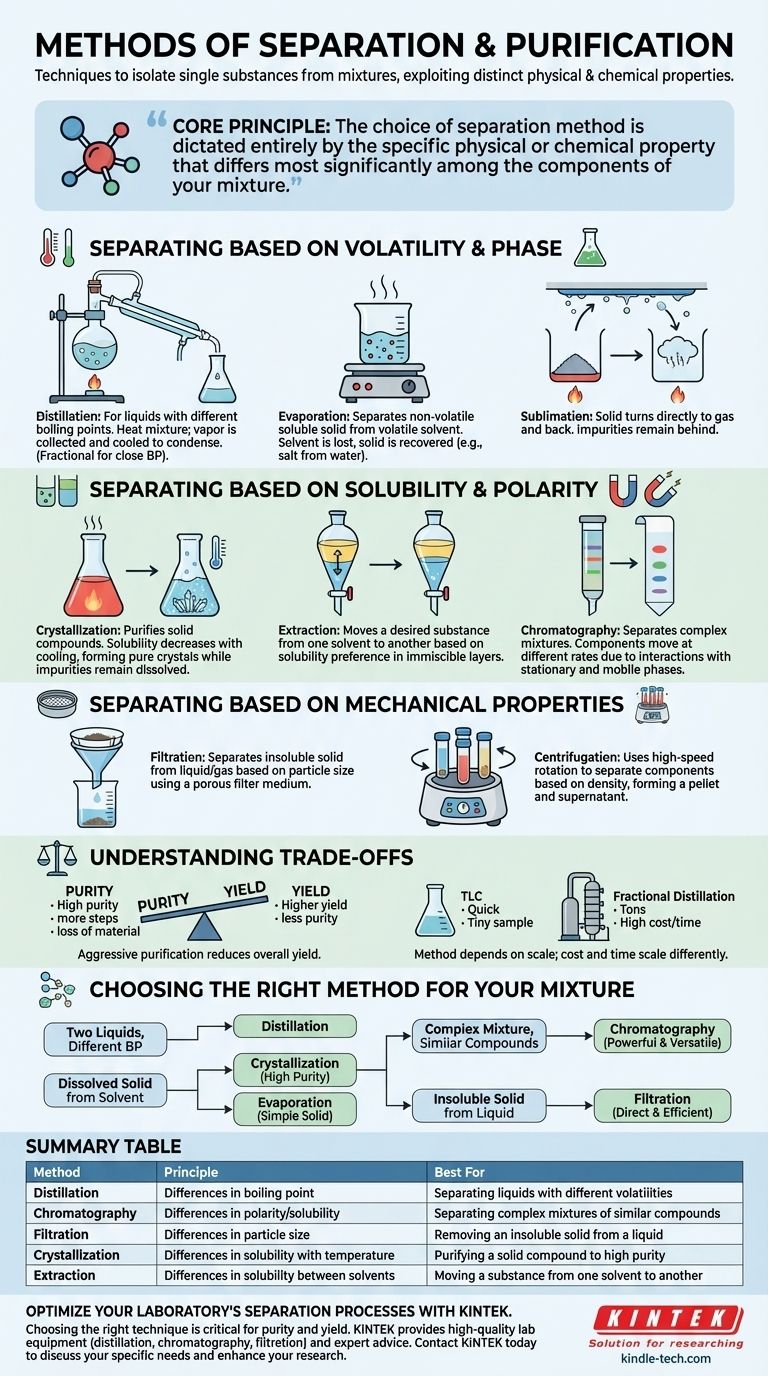
At their core, separation and purification methods are a set of techniques used to isolate a single substance from a mixture. These methods exploit the distinct physical and chemical properties of the mixture's components, such as differences in boiling point, solubility, size, or charge, allowing for their selective removal. Key techniques include distillation for separating liquids with different volatilities and chromatography for separating complex mixtures based on polarity.
The single most important principle to understand is that the choice of a separation method is not arbitrary. It is dictated entirely by the specific physical or chemical property that differs most significantly among the components of your mixture.

Separating Based on Volatility and Phase
The most fundamental differences between substances are often their boiling points and states of matter (solid, liquid, gas) at a given temperature and pressure. These techniques leverage those differences.
Distillation
Distillation is the workhorse for separating liquid mixtures where components have different boiling points. The mixture is heated until the more volatile component (the one with the lower boiling point) begins to boil and turn into vapor.
This vapor is then channeled into a separate container and cooled, causing it to condense back into a pure liquid. Fractional distillation is a more precise version used when boiling points are very close, employing a fractionating column to achieve better separation.
Evaporation
This is a simpler technique used to separate a non-volatile soluble solid from a volatile liquid solvent. A common example is obtaining salt from salt water.
By heating the solution, the solvent (water) evaporates into the air, leaving the solid solute (salt) behind. This method is effective for recovery of the solid, but the solvent is typically lost to the atmosphere.
Sublimation
Sublimation is a unique process where a solid turns directly into a gas without first passing through a liquid phase. This property can be used for purification.
If a solid mixture contains a substance that can sublime (like iodine), heating the mixture will turn only that substance into a gas. This gas can then be collected on a cold surface, where it will deposit back into a pure solid, leaving impurities behind.
Separating Based on Solubility and Polarity
Many separations rely on how differently substances interact with various solvents. This is governed by the chemical principle of "like dissolves like," where polar substances dissolve in polar solvents and nonpolar substances dissolve in nonpolar solvents.
Crystallization
Crystallization is a highly effective technique for purifying solid compounds. It operates on the principle that the solubility of most solids increases with temperature.
A crude solid is dissolved in a minimal amount of a hot solvent. As the solution cools slowly, the solubility of the desired compound decreases, causing it to form pure crystals. Impurities, which are present in smaller amounts, remain dissolved in the cold solvent.
Extraction
Liquid-liquid extraction is used to move a desired substance from one solvent to another. It relies on the substance being more soluble in the second solvent than in the first.
The two immiscible solvents (like oil and water) are shaken together in a separatory funnel. The target compound partitions, or moves, into the solvent in which it has higher solubility. The layers are then separated, effectively isolating the compound.
Chromatography
Chromatography is a powerful family of techniques for separating complex mixtures. All forms of chromatography operate on the same basic principle involving two phases: a stationary phase (a solid or a liquid supported on a solid) and a mobile phase (a liquid or gas).
The mixture is passed through the stationary phase by the flow of the mobile phase. Components that interact more strongly with the stationary phase move slower, while components that are more soluble in the mobile phase move faster. This difference in movement causes the components to separate over time.
Separating Based on Mechanical Properties
Sometimes, the simplest properties like particle size and density are all that's needed to achieve a clean separation.
Filtration
This is a straightforward mechanical method used to separate an insoluble solid from a liquid or gas. The mixture is passed through a filter medium (like filter paper).
The pores in the filter are small enough to let the liquid or gas pass through (the filtrate) but large enough to trap the solid particles (the residue).
Centrifugation
Centrifugation uses high-speed rotation to separate components based on their density. The intense centrifugal force causes denser particles to migrate to the bottom of the container, forming a pellet.
The less dense liquid supernatant can then be carefully poured off. This is much faster and more efficient than relying on gravity alone for sedimentation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a method involves balancing competing priorities. No single technique is perfect for every situation.
Purity vs. Yield
There is almost always a trade-off between the purity of your final product and the amount you recover (yield).
Aggressive purification steps, such as repeated crystallizations, will result in a very pure product but will inevitably lead to some loss of material at each stage, reducing the overall yield.
Scale, Cost, and Time
The appropriate technique heavily depends on the amount of material you are working with. Thin-Layer Chromatography (TLC) is excellent for quickly analyzing tiny amounts of a sample.
In contrast, industrial production might require a massive fractional distillation column to separate tons of material. The cost, complexity, and time required for each method scale differently.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Mixture
Your selection must be guided by the properties of the substances you wish to separate.
- If your primary focus is separating two liquids with different boiling points: Your best choice is distillation, using fractional distillation if the boiling points are close.
- If your primary focus is isolating a dissolved, non-volatile solid from a liquid solvent: Use crystallization for high purity or simple evaporation if you only need the solid.
- If your primary focus is separating a complex mixture of similar compounds: Chromatography is the most powerful and versatile tool for this demanding task.
- If your primary focus is removing an insoluble solid from a liquid: Simple filtration is the most direct and efficient method.
Ultimately, effective separation is about identifying the key difference between your target substance and its contaminants and choosing the tool designed to exploit that specific difference.
Summary Table:
| Method | Principle | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Distillation | Differences in boiling point | Separating liquids with different volatilities |
| Chromatography | Differences in polarity/solubility | Separating complex mixtures of similar compounds |
| Filtration | Differences in particle size | Removing an insoluble solid from a liquid |
| Crystallization | Differences in solubility with temperature | Purifying a solid compound to high purity |
| Extraction | Differences in solubility between solvents | Moving a substance from one solvent to another |
Optimize your laboratory's separation and purification processes with KINTEK.
Choosing the right technique is critical for achieving high purity and yield. Whether you need a robust distillation setup for solvent recovery, chromatography columns for complex separations, or reliable filtration systems, KINTEK provides the high-quality lab equipment and consumables you need.
Our experts can help you select the perfect tools to exploit the specific physical or chemical differences in your mixture, saving you time and resources.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your laboratory's specific needs and discover how our solutions can enhance your research and production outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Wall Mounted Water Distillation Unit
- Automatic Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Customizable Laboratory High Temperature High Pressure Reactors for Diverse Scientific Applications
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
People Also Ask
- Does THC distillate lose potency? A guide to preserving your product's power.
- What is the delta 20 rule of evaporation? Master Safe and Effective Spraying
- What factors affect evaporation and condensation? Master the Science of Water's Phase Changes
- What is the difference between THC extract and distillate? A Guide to Full-Spectrum vs. Pure Potency
- What temperature does evaporation occur? Unlock the Secrets to Controlling the Rate of Evaporation



















