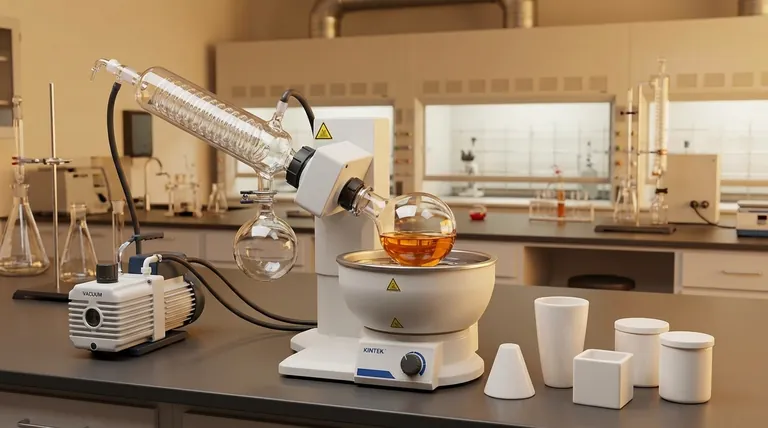
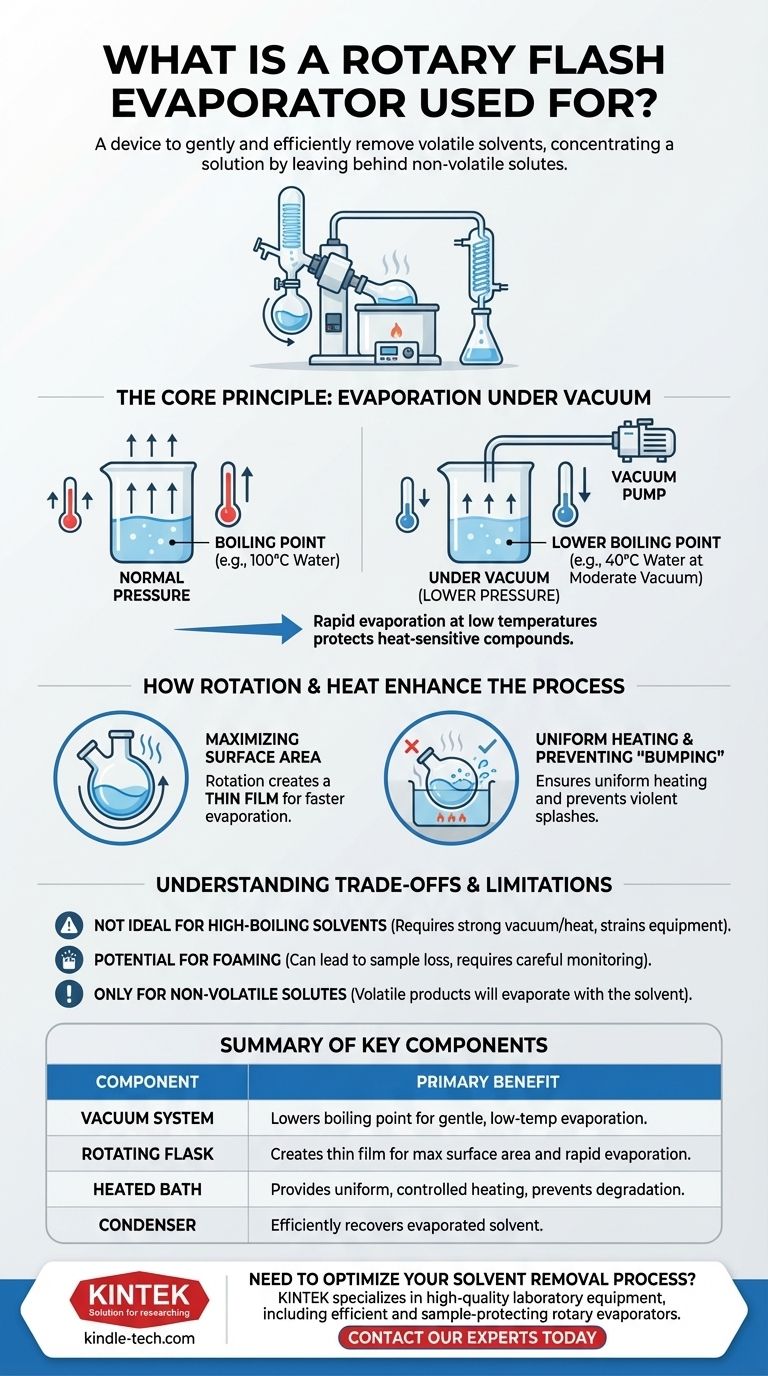
At its core, a rotary flash evaporator, often called a "rotovap," is a device used in chemical laboratories to gently and efficiently remove volatile solvents from a sample. Its primary function is to concentrate a solution by evaporating the liquid, leaving behind the non-volatile solute you wish to isolate.
A rotary evaporator's effectiveness comes from its ability to lower a solvent's boiling point by reducing the pressure inside the system. This allows for rapid evaporation at a low temperature, which is essential for protecting heat-sensitive compounds from thermal degradation.

The Core Principle: Evaporation Under Vacuum
At the heart of the rotary evaporator is the scientific principle that a liquid's boiling point depends on the surrounding pressure. By connecting the apparatus to a vacuum pump, we can dramatically lower the pressure, and thus, lower the temperature needed for the solvent to boil.
Why Lower Pressure Matters
A liquid boils when its vapor pressure equals the pressure of the environment above it. At sea level, water boils at 100°C (212°F). However, if you lower the atmospheric pressure—as you would on a high mountain or with a vacuum pump—water will boil at a much lower temperature.
The Benefit of Lower Boiling Points
This principle is the key advantage of the rotovap. For example, a solvent like dichloromethane, which boils at 40°C under normal pressure, can be evaporated near 0°C under a moderate vacuum.
Protecting Your Sample
This low-temperature evaporation is critical when working with delicate materials. Many compounds in organic chemistry, natural product research, and pharmaceutical development are thermally labile, meaning they decompose or are destroyed when exposed to high heat. A rotovap removes the solvent without damaging the desired product.
How Rotation and Heat Enhance the Process
While the vacuum is essential, the rotation of the flask is what makes the process so efficient. This is combined with a gentle heat source to drive the evaporation.
Maximizing Surface Area
The rotation of the evaporating flask spreads the sample solution into a thin film across the entire inner surface. This dramatically increases the surface area of the liquid exposed to the vacuum, which significantly speeds up the rate of evaporation.
Ensuring Uniform Heating
The rotating flask is typically lowered into a heated water or oil bath. The rotation ensures that the thin film of liquid is constantly and evenly heated, providing the necessary energy for vaporization without creating dangerous hot spots that could degrade the sample.
Preventing "Bumping"
When heating a liquid under vacuum, it can sometimes boil violently in a process called bumping, which can cause a sudden splash of the solution out of the flask, leading to sample loss. The constant agitation and smooth boiling provided by the flask's rotation effectively prevent this.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While incredibly useful, the rotary evaporator is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Not Ideal for High-Boiling Point Solvents
The method is most effective for solvents with low to moderate boiling points. High-boiling point solvents like water or DMSO require a very strong vacuum and/or higher temperatures, which can strain the equipment and begin to defeat the purpose of "gentle" evaporation.
Potential for Foaming
Some solutions, especially those containing soaps or certain biological extracts, have a tendency to foam under vacuum. This foam can be drawn out of the flask and into the condenser, resulting in loss of the target compound. This requires careful monitoring and slow application of the vacuum.
Only for Non-Volatile Solutes
The entire process relies on the assumption that your target compound (the solute) is non-volatile under the operating conditions. If your desired product is also volatile, it will evaporate along with the solvent, making separation impossible with this method.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, the decision to use a rotary evaporator depends on the properties of your sample and your ultimate objective.
- If your primary focus is purifying a heat-sensitive compound: The rotary evaporator is the gold standard for removing a solvent after an extraction or a chemical reaction.
- If your primary focus is separating two volatile liquids: You need fractional distillation, not a rotovap, as it separates components based on their different boiling points.
- If your primary focus is simply concentrating a robust, non-sensitive solute: A simple distillation setup might be sufficient, though a rotovap is almost always faster and more efficient.
Mastering the use of a rotary evaporator comes from understanding its core principles of pressure, temperature, and surface area to achieve gentle and efficient solvent removal.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|
| Vacuum System | Lowers solvent boiling point for gentle, low-temperature evaporation. |
| Rotating Flask | Creates a thin film for maximum surface area and rapid evaporation. |
| Heated Bath | Provides uniform, controlled heating to prevent sample degradation. |
| Condenser | Efficiently recovers the evaporated solvent for reuse or disposal. |
Need to Optimize Your Solvent Removal Process?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality laboratory equipment, including rotary evaporators designed for efficiency and sample protection. Whether you're working in pharmaceutical development, natural product extraction, or organic synthesis, our rotovaps ensure gentle and precise solvent removal for your most heat-sensitive compounds.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect rotary evaporator for your lab's needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Evaporation Crucible for Organic Matter
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Ceramic Evaporation Boat Set Alumina Crucible for Laboratory Use
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What precautions should be taken in a chemistry lab? Master the RAMP Framework for Ultimate Safety
- Do cannabinoids evaporate? How to Preserve Potency and Prevent Degradation
- What are the analytical used in laboratory? Choose the Right Tool for Your Lab's Needs
- What are the 5 factors that affect the rate of evaporation? Master the Process for Your Lab
- Which solvent is normally used in IR spectroscopy? Optimize Your Sample Prep for Clearer Results



















