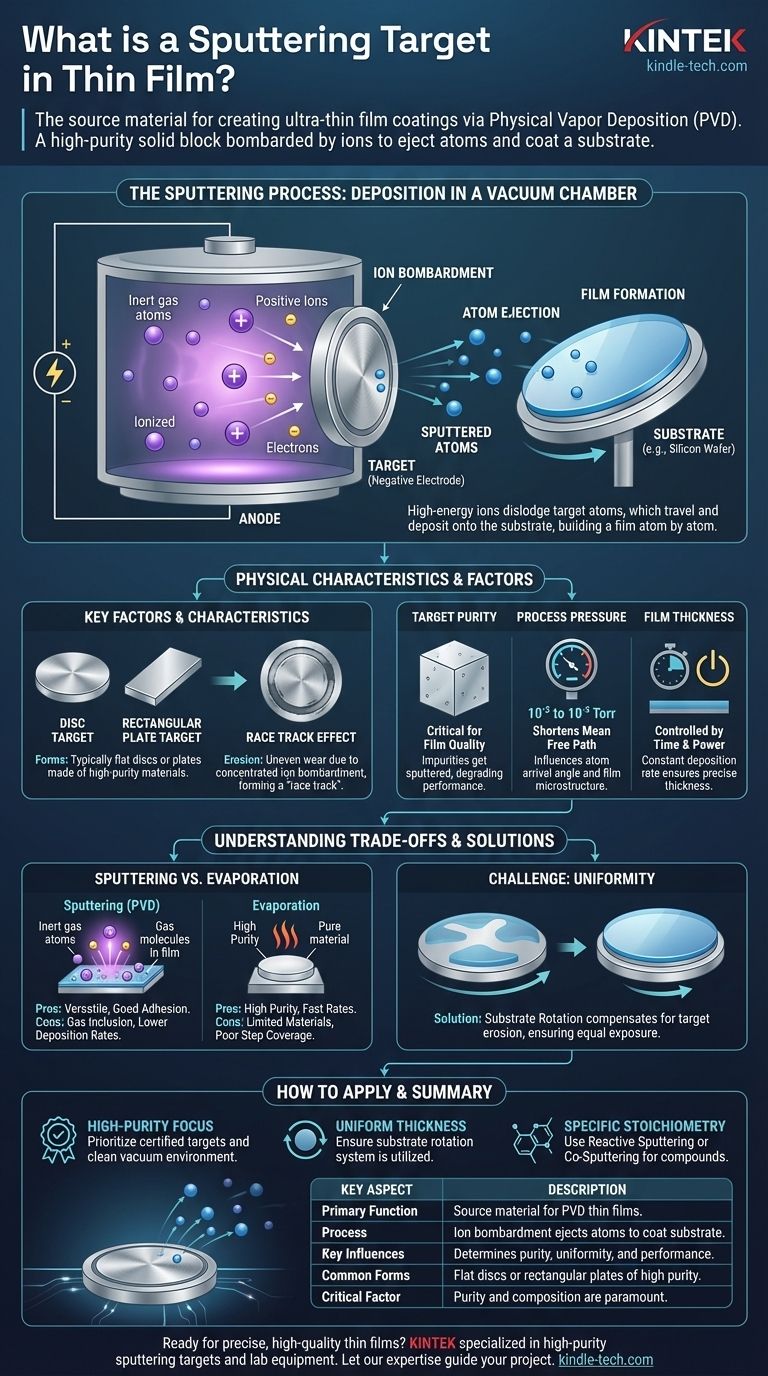
In the world of advanced manufacturing, a sputtering target is the source material used to create an ultra-thin film coating on another object, known as a substrate. It is a solid, high-purity block or plate of the desired coating material. During the sputtering process, this target is bombarded with energized ions, which physically knock atoms off its surface and deposit them onto the substrate to form the film.
The sputtering target is more than just a piece of raw material; it is the fundamental starting point of the thin film. Its purity, composition, and physical form, combined with the sputtering process parameters, directly determine the quality, uniformity, and performance of the final coating.

The Role of the Target in the Sputtering Process
To understand the target, you must first understand the process it enables. Sputtering is a Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) technique used across industries like semiconductors, optics, and medical devices.
How Sputtering Works
The process takes place inside a vacuum chamber. After reducing the pressure, a small amount of an inert gas, typically Argon, is introduced.
A high voltage is applied to the target, causing it to function as a cathode. This voltage ignites the Argon gas, creating a glowing plasma of positive ions and electrons.
These positively charged Argon ions are then accelerated with immense force toward the negatively charged target.
The Bombardment and Deposition Cycle
The impact of these high-energy ions on the target surface is a purely physical collision. It has enough force to dislodge or "sputter" individual atoms from the target material.
These ejected atoms travel across the low-pressure chamber and land on the substrate (such as a silicon wafer or a lens), gradually building up a thin, uniform film atom by atom.
Physical Characteristics of a Target
Sputtering targets are typically manufactured as flat discs or rectangular plates. Their surface area must be larger than the intended area of bombardment to protect other components inside the deposition system.
Over time, the areas of the target hit most intensely by the ion beam will erode more quickly, often forming a distinct groove known as a "race track."
Key Factors Influencing Film Quality
The target itself is the first variable in a successful coating. However, its interaction with the process environment is what truly defines the final film's characteristics.
Target Purity and Composition
The final film can only be as pure as its source. The purity of the sputtering target is therefore critical. Any impurities within the target material will be sputtered along with the desired atoms and incorporated into the growing film, potentially degrading its performance.
Process Pressure
Sputtering requires a higher operating pressure (10⁻² to 10⁻³ Torr) than other methods like thermal evaporation. This is necessary to sustain the plasma.
This higher pressure shortens the "mean free path"—the average distance an atom can travel before colliding with a gas molecule. These collisions can randomize the arrival angle of atoms at the substrate, which can influence the film's microstructure.
Controlling Film Thickness
The thickness of the deposited film is a direct function of time and power. By maintaining a constant deposition rate (a stable plasma and power level), the final thickness is precisely controlled by the duration of the process. Once the desired thickness is reached, the power is cut, the plasma extinguishes, and deposition stops.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, sputtering is a process with specific advantages and limitations that a technical professional must understand.
Sputtering vs. Evaporation
Unlike thermal evaporation, which can operate in a very high vacuum, sputtering's need for a process gas introduces a potential downside. Gas molecules can become trapped or absorbed into the growing film.
This can be a source of contamination or can alter the film's structural properties, a factor that must be carefully managed.
The Challenge of Uniformity
The "race track" effect, where the target erodes unevenly, means that material is not sputtered uniformly across the entire target face.
To achieve a highly uniform coating on the substrate, this effect is typically counteracted by rotating the substrate during deposition. This ensures all parts of the substrate are exposed equally to the flux of sputtered atoms.
Material Deposition Control
The sputtering process offers excellent control over deposition rates and can be used for a vast range of materials, including alloys and compounds. This versatility is a key reason for its widespread adoption in complex manufacturing.
How to Apply This to Your Project
The selection of a target and process parameters is driven entirely by the desired properties of your thin film.
- If your primary focus is high-purity films: Your top priority must be sourcing a certified, high-purity sputtering target and maintaining an exceptionally clean vacuum environment.
- If your primary focus is uniform thickness: Ensure your sputtering system is equipped with substrate rotation to compensate for the inherent non-uniformity of target erosion.
- If your primary focus is a specific stoichiometry for a compound film: You may need to use techniques like reactive sputtering (introducing a reactive gas) or co-sputtering from multiple targets to achieve the correct chemical composition.
Ultimately, viewing the sputtering target as the foundational source of your film empowers you to control the entire deposition process with greater insight and precision.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Source material for physical vapor deposition (PVD) of thin films |
| Process | Bombarded by ions to eject atoms that coat a substrate |
| Key Influences | Determines film purity, uniformity, and performance |
| Common Forms | Flat discs or rectangular plates made of high-purity materials |
| Critical Factor | Purity and composition are paramount for final film quality |
Ready to achieve precise, high-quality thin films for your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-purity sputtering targets and lab equipment, ensuring your coatings meet the strictest standards for semiconductors, optics, and medical devices. Let our expertise guide your project from material selection to process optimization. Contact us today to discuss your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Culture Dish and Evaporation Dish
- Vacuum Cold Trap Direct Cold Trap Chiller
People Also Ask
- How do Mass Flow Controllers (MFCs) influence LDIP properties during CVD? Achieve Precise Isotropic Carbon Synthesis
- What is the process of chemical solution deposition? A Guide to the Sol-Gel Method
- What are the disadvantages of LPCVD? Understanding the Trade-offs for High-Quality Thin Films
- What hardware is used in the carbon nanotube (CNT) modification process? Essential Tools for Li-ion Anode Innovation
- What is the chemical vapor deposition process for thin film? Grow Superior, Conformal Coatings
- What are the 2 methods of deposition? PVD vs. CVD Explained for Your Lab
- How do you prepare carbon nanotubes using CVD? A Step-by-Step Guide to Controlled Synthesis
- What is CVD process in semiconductor? A Guide to Building Microchips from Gas












