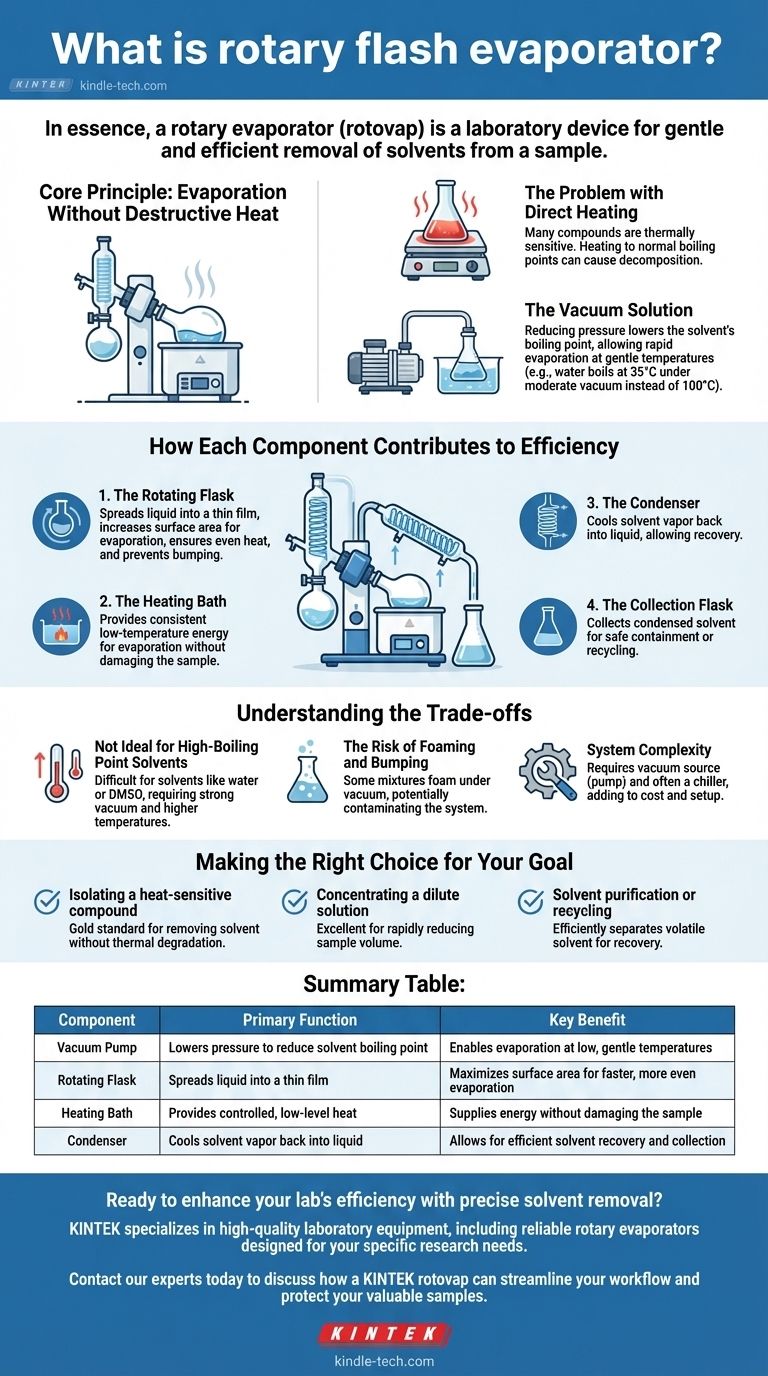
In essence, a rotary evaporator, often called a "rotovap," is a laboratory device designed for the gentle and efficient removal of solvents from a sample. It works by reducing the pressure over a liquid, which lowers its boiling point, allowing for rapid evaporation at a low temperature. The rotation of the flask maximizes the surface area of the liquid, further speeding up the process.
The core principle of a rotary evaporator is vacuum distillation. By combining reduced pressure with rotation and gentle heating, it allows chemists to remove volatile solvents from a sample without using high temperatures that could damage the desired, non-volatile compounds left behind.

The Core Principle: Evaporation Without Destructive Heat
In many chemical processes, the final product is dissolved in a solvent that needs to be removed. Simply boiling it away at atmospheric pressure is often not a viable option.
The Problem with Direct Heating
Many organic and biological compounds are thermally sensitive. Heating them to the normal boiling point of a solvent (like 78°C for ethanol or 100°C for water) can cause them to decompose or undergo unwanted side reactions, destroying the final product.
The Vacuum Solution
A rotary evaporator solves this problem by connecting the system to a vacuum pump. Reducing the pressure above a liquid dramatically lowers its boiling point. For example, water boils at 35°C (95°F) under a moderate vacuum, a far gentler temperature than its standard 100°C (212°F).
This allows for the rapid evaporation of the solvent at or near room temperature, preserving the integrity of the valuable compound left in the flask.
How Each Component Contributes to Efficiency
The genius of the rotovap lies in how its parts work together to create a gentle yet highly efficient system for solvent removal.
The Rotating Flask
The flask containing the sample is rotated by a motor. This rotation continuously spreads the liquid into a thin film on the interior surface of the flask. This action accomplishes three critical tasks: it dramatically increases the surface area for evaporation, ensures even and gentle heating, and provides agitation to prevent violent "bumping."
The Heating Bath
The rotating flask is lowered into a heated water bath. This bath provides a consistent and low-temperature source of energy to drive the evaporation process. Its temperature is carefully controlled to be just warm enough to facilitate evaporation without damaging the sample.
The Condenser
As the solvent evaporates into a vapor, it travels into a condenser, which is a glass coil chilled with circulating cold water or another coolant. This cold surface causes the solvent vapor to immediately condense back into a liquid.
The Collection Flask
The condensed, purified solvent then drips down from the condenser and is collected in a separate receiving flask. This allows the removed solvent to be safely contained, measured, or even recycled for future use.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While indispensable, the rotary evaporator is not a universal solution for all separation tasks. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Not Ideal for High-Boiling Point Solvents
The system is most effective for solvents with low to moderate boiling points (e.g., acetone, ethanol, ethyl acetate). Removing very high-boiling point solvents like water or DMSO requires a very strong vacuum and higher temperatures, reducing the "gentle" advantage of the technique.
The Risk of Foaming and Bumping
Some mixtures, particularly those containing soaps or fine solids, can foam vigorously under vacuum. This foam can travel through the system and contaminate the condenser and collection flask, leading to product loss. Careful control of the vacuum and rotation speed is required to manage this.
System Complexity
A rotary evaporator is not a standalone device. It requires a stable vacuum source (usually a diaphragm pump) and often a chiller to supply cold fluid to the condenser. These ancillary components add to the cost and complexity of the setup.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The rotary evaporator is a versatile tool, but its primary benefit is centered on controlled, low-temperature solvent removal.
- If your primary focus is isolating a heat-sensitive compound: The rotovap is the gold standard, allowing you to remove solvent without risking thermal degradation of your product.
- If your primary focus is concentrating a dilute solution: This is an excellent tool for rapidly reducing the volume of a sample to increase the concentration of your solute before further analysis or reaction.
- If your primary focus is solvent purification or recycling: The rotovap efficiently separates a volatile solvent from non-volatile solutes, allowing for the recovery and reuse of expensive or specialized solvents.
Ultimately, the rotary evaporator is a foundational tool for any chemist needing precise, gentle control over solvent removal.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Pump | Lowers pressure to reduce solvent boiling point | Enables evaporation at low, gentle temperatures |
| Rotating Flask | Spreads liquid into a thin film | Maximizes surface area for faster, more even evaporation |
| Heating Bath | Provides controlled, low-level heat | Supplies energy without damaging the sample |
| Condenser | Cools solvent vapor back into liquid | Allows for efficient solvent recovery and collection |
Ready to enhance your lab's efficiency with precise solvent removal?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality laboratory equipment, including reliable rotary evaporators designed for your specific research needs. Whether you are concentrating samples, purifying solvents, or working with thermally sensitive compounds, our solutions ensure gentle and effective processing.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK rotovap can streamline your workflow and protect your valuable samples.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Benchtop Water Circulating Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Evaporation Crucible for Organic Matter
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What factors affect evaporation and condensation? Master the Science of Water's Phase Changes
- Why must a laboratory vacuum pump be used to evacuate a PM-HIP capsule before it is sealed? Ensure Material Integrity
- What are the advantages of a water circulating vacuum pump? Superior Durability for Demanding Lab Environments
- How does the impeller rotation affect the gas flow in a water circulating vacuum pump? A Guide to the Liquid Ring Principle
- What types of gases can a water circulating vacuum pump handle? Safely Manage Flammable, Condensable & Dirty Gases



















