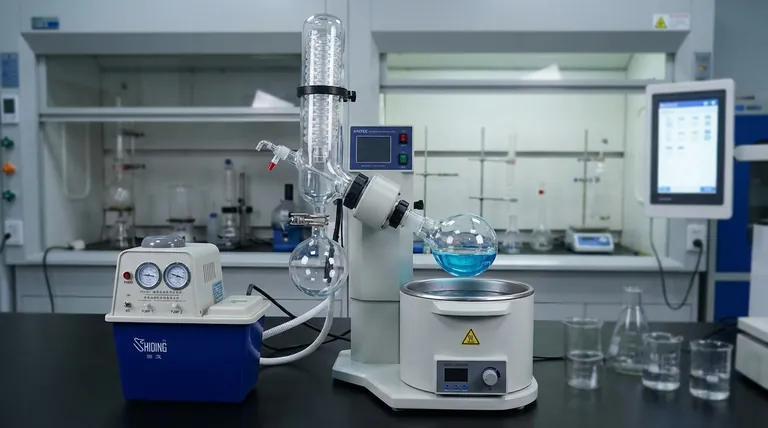
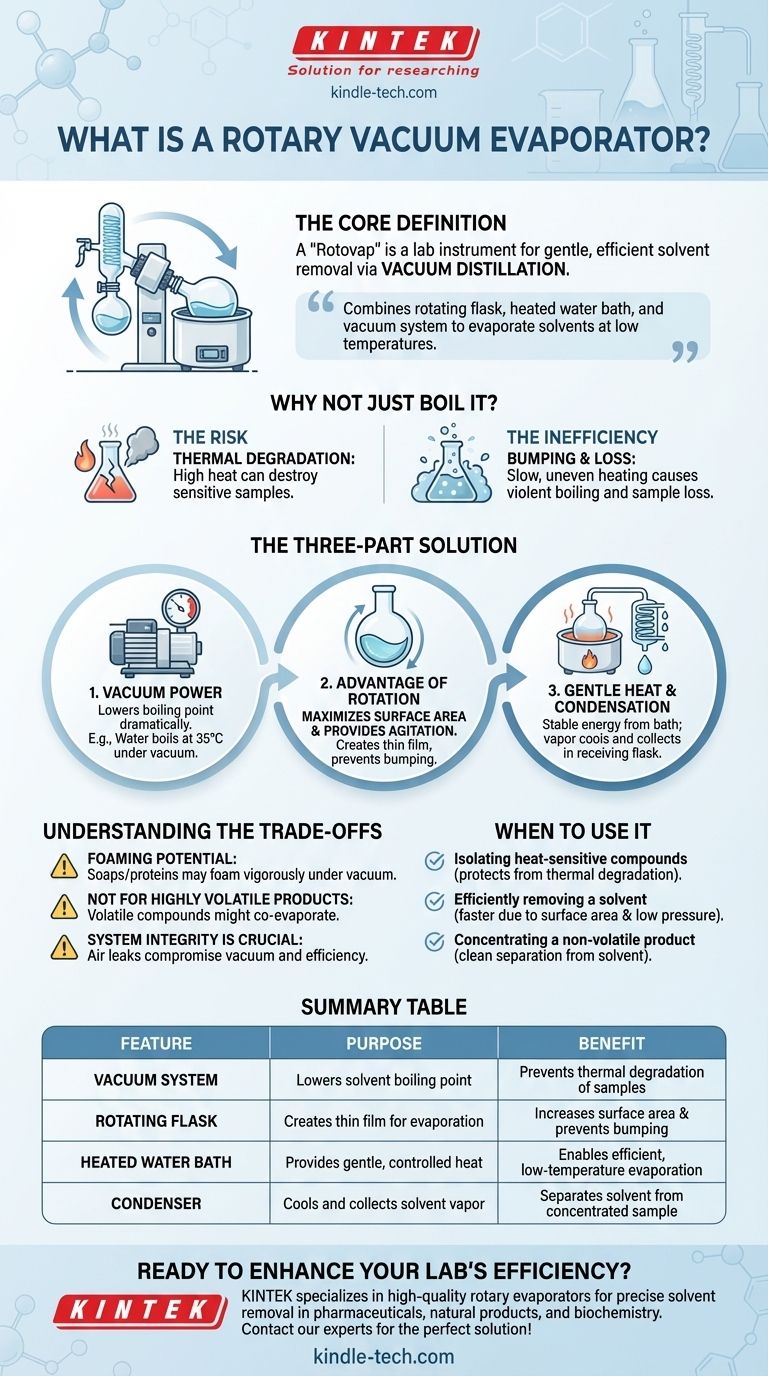
At its core, a rotary vacuum evaporator, often called a "rotovap," is a laboratory instrument designed for the gentle and efficient removal of solvents from a sample. It accomplishes this through a process known as vacuum distillation, which combines a rotating flask, a heated water bath, and a vacuum system to evaporate solvents at temperatures far below their normal boiling points.
The central principle of a rotary evaporator is its ability to lower a solvent's boiling point by reducing the pressure. This allows for rapid evaporation at a low, controlled temperature, preserving the integrity of heat-sensitive samples.

Why Not Just Boil Off the Solvent?
Before understanding how a rotovap works, it's crucial to understand the problem it solves. Simply heating a sample to boil away a solvent is often not a viable option in a professional laboratory setting.
The Risk of Thermal Degradation
Many chemical compounds, particularly in natural product chemistry, pharmaceuticals, and biochemistry, are thermally sensitive. The high temperatures required for standard boiling can easily destroy or alter the sample you are trying to isolate.
The Inefficiency of Standard Distillation
Even for stable compounds, standard distillation can be slow and inefficient. It often leads to uneven heating and a phenomenon called "bumping," where the liquid boils violently and unevenly, which can result in sample loss.
The Rotovap's Three-Part Solution
A rotary evaporator elegantly overcomes these challenges by manipulating three key physical principles simultaneously.
Principle 1: The Power of Vacuum
The defining feature of the system is the vacuum pump. By reducing the atmospheric pressure inside the apparatus, the boiling point of the solvent is dramatically lowered. For example, water boils at 100°C (212°F) at sea level but boils at just 35°C (95°F) under a moderate vacuum.
Principle 2: The Advantage of Rotation
The sample is held in a round-bottom flask that is continuously rotated. This rotation serves two critical purposes:
- Maximizes Surface Area: It constantly spreads the sample mixture into a thin film on the flask's inner surface, vastly increasing the area available for evaporation.
- Provides Agitation: The rotation gently and constantly mixes the sample, ensuring even heat distribution from the bath and preventing bumping.
Principle 3: Gentle Heat and Condensation
A heated water bath provides a gentle and stable source of energy to the rotating flask, facilitating the evaporation process. As the solvent evaporates, the vapor travels into a chilled glass condenser coil. Here, the vapor cools, turns back into a liquid, and is collected in a separate receiving flask, effectively separating it from your now-concentrated sample.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly useful, the rotary evaporator is a specialized tool with specific limitations.
Potential for Foaming
Some samples, particularly those containing soaps or proteins, can foam vigorously under vacuum. This requires careful and slow application of the vacuum to prevent the sample from being pulled through the system.
Not for Highly Volatile Products
If the compound you wish to isolate is itself volatile, it may co-evaporate with the solvent. In these cases, other purification techniques are required.
System Integrity is Crucial
The entire process depends on a well-sealed system. Any air leaks will compromise the vacuum, causing the solvent's boiling point to rise and significantly reducing the evaporator's efficiency.
When to Use a Rotary Evaporator
Choosing the right tool is essential for success in the lab. The rotary evaporator is the definitive choice for specific, common scenarios.
- If your primary focus is isolating heat-sensitive compounds: The rotovap is the ideal tool, as its low-temperature operation protects your sample from thermal degradation.
- If your primary focus is efficiently removing a solvent: The combination of increased surface area from rotation and low-pressure evaporation makes the process much faster than other methods.
- If your primary focus is concentrating a non-volatile product: The rotovap excels at cleanly separating your desired solid or oil from the volatile solvent it was dissolved in.
Ultimately, the rotary evaporator is an indispensable instrument that enables chemists to perform delicate separations with both speed and precision.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Purpose | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum System | Lowers solvent boiling point | Prevents thermal degradation of samples |
| Rotating Flask | Creates thin film for evaporation | Increases surface area & prevents bumping |
| Heated Water Bath | Provides gentle, controlled heat | Enables efficient, low-temperature evaporation |
| Condenser | Cools and collects solvent vapor | Separates solvent from the concentrated sample |
Ready to enhance your lab's efficiency and protect your sensitive samples? KINTEK specializes in high-quality laboratory equipment, including reliable rotary evaporators designed for precise solvent removal. Our rotovaps are perfect for applications in pharmaceuticals, natural product chemistry, and biochemistry. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory's needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Benchtop Water Circulating Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Ceramic Evaporation Boat Set Alumina Crucible for Laboratory Use
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What types of gases can a water circulating vacuum pump handle? Safely Manage Flammable, Condensable & Dirty Gases
- What are the preventive maintenance of hydraulic systems? Extend Equipment Life and Maximize Uptime
- Why must a laboratory vacuum pump be used to evacuate a PM-HIP capsule before it is sealed? Ensure Material Integrity
- Why is a high-precision vacuum pump system essential for iCVD? Achieve Superior Film Purity and Uniformity
- What factors affect evaporation and condensation? Master the Science of Water's Phase Changes



















