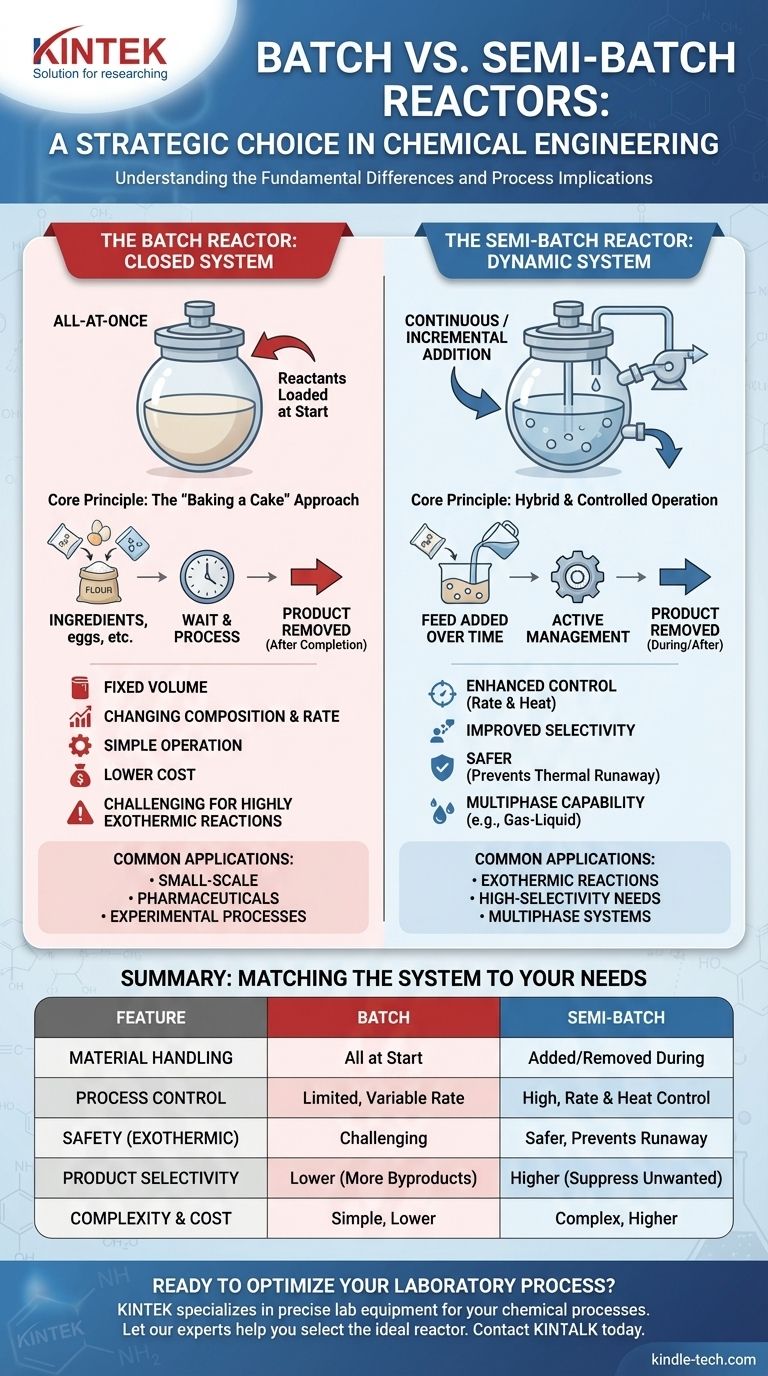
In chemical engineering, the fundamental difference between batch and semi-batch reactors lies in how materials are handled during the reaction. A batch reactor is a closed system where all reactants are loaded at the beginning, and the products are removed only after the reaction is complete. In contrast, a semi-batch reactor allows for one or more reactants to be added, or products to be removed, while the reaction is in progress, creating a more dynamic operating environment.
The choice between batch and semi-batch is not merely a design preference; it is a strategic decision rooted in the need for process control. Batch reactors offer operational simplicity, while semi-batch reactors provide critical control over reaction rate, heat generation, and product selectivity.

The Batch Reactor: A Closed-System Approach
A batch reactor operates much like baking a cake: you place all your ingredients into the bowl at the start, mix them, and then wait for the process to finish before you take the final product out.
Core Operating Principle
In a batch reactor, the vessel is charged with all necessary reactants and catalysts. The system is then sealed, and conditions like temperature and pressure are set. The reaction proceeds over time until it reaches the desired conversion.
Key Characteristics
The volume within a batch reactor is fixed. As the reaction progresses, the concentration of reactants decreases while the concentration of products increases. This dynamic change in composition means the reaction rate itself changes over the course of the batch.
Common Applications
Batch reactors are ideal for small-scale production, manufacturing high-value products like pharmaceuticals, and conducting experimental or new processes in a laboratory. They are most suitable when reactions are not dangerously fast or exothermic.
The Semi-Batch Reactor: A Dynamic, Controlled System
A semi-batch reactor introduces a level of active management during the reaction itself. It is a hybrid system that combines elements of both batch and continuous operation.
Core Operating Principle
In the most common semi-batch configuration, the reactor begins with some reactants, and one or more additional reactants are fed in continuously or in measured increments over time. In other cases, a volatile product might be continuously removed to shift the reaction equilibrium.
Key Advantages of Dynamic Control
The ability to add a reactant over time provides several critical advantages.
Temperature Control for Exothermic Reactions
For reactions that release a large amount of heat (exothermic), adding a limiting reactant slowly prevents a rapid, dangerous temperature spike. This is a crucial safety feature to avoid thermal runaway.
Concentration and Selectivity Control
By keeping the concentration of one reactant low, you can often suppress the formation of unwanted byproducts. This improves the reaction's selectivity, leading to a purer final product and higher yield.
Handling Multiphase Systems
Semi-batch operation is essential for reactions involving different phases, as noted in multiphase substrate use cases. A common example is bubbling a gas (like hydrogen for hydrogenation) through a liquid slurry, where the gas is the continuously fed "reactant."
Understanding the Trade-offs: Control vs. Simplicity
Choosing between these two reactor types involves a clear trade-off between the simplicity of a closed system and the precision of a dynamic one.
Batch Reactor: Pros and Cons
A batch reactor's main advantage is its simplicity in design and operation, which generally translates to lower capital costs. Its versatility allows for the production of many different products in the same vessel.
However, its primary drawback is a lack of in-process control. The initial high concentration of reactants can lead to unwanted side reactions, and managing heat from highly exothermic reactions is difficult and can be unsafe.
Semi-Batch Reactor: Pros and Cons
The key strength of a semi-batch reactor is superior control over the reaction environment. This enhances safety, improves product selectivity, and allows for operations that are impossible in a batch system.
The downside is increased complexity. Semi-batch systems require additional equipment like pumps, flow controllers, and control logic, making them more expensive and complex to operate and scale up.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your decision should be guided by the specific chemical and safety requirements of your reaction.
- If your primary focus is simple, small-scale production: A batch reactor is often the most straightforward and cost-effective choice, especially if heat generation is manageable.
- If your primary focus is safety with a highly exothermic reaction: A semi-batch reactor is essential to prevent thermal runaway by controlling the feed rate of a limiting reactant.
- If your primary focus is maximizing product yield or selectivity: A semi-batch reactor provides the concentration control needed to favor the desired reaction pathway and minimize byproducts.
- If your primary focus is a multiphase reaction (e.g., gas-liquid): A semi-batch configuration is the standard approach for continuously introducing one phase into another.
Ultimately, selecting the right reactor is about matching the operational capabilities of the system to the fundamental demands of your chemical reaction.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Batch Reactor | Semi-Batch Reactor |
|---|---|---|
| Material Handling | All reactants loaded at start | Reactants added/removed during reaction |
| Process Control | Limited, reaction rate changes over time | High, control over reaction rate & heat |
| Safety | Challenging for highly exothermic reactions | Safer, prevents thermal runaway |
| Product Selectivity | Can lead to more byproducts | Higher, suppresses unwanted reactions |
| Complexity & Cost | Simple design, lower cost | More complex, higher cost |
| Ideal For | Small-scale, high-value products (e.g., pharma) | Exothermic, multiphase, or high-selectivity needs |
Ready to optimize your laboratory process with the right reactor?
The choice between batch and semi-batch systems is critical for safety, yield, and efficiency. KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment you need to succeed. Our reactors are designed to meet the demanding requirements of modern chemical processes, ensuring control and reliability.
Let our experts help you select the ideal reactor for your application. Contact KINTALK today to discuss your specific needs and discover how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a constant temperature hydrothermal reactor? Master Coal Fly Ash Activation
- Why are sealed laboratory reaction vessels necessary in the hydrothermal synthesis of zeolites? Ensure Purity and Yield
- What is the role of high-pressure reactors in the study of alloy oxidation? Essential Tools for Supercritical Research
- What is the contribution of a hydrothermal reactor to graded pore construction? Precision Templates for TAS
- What roles do autoclaves play in MFI zeolite synthesis? Master Hydrothermal Crystalline Growth



















