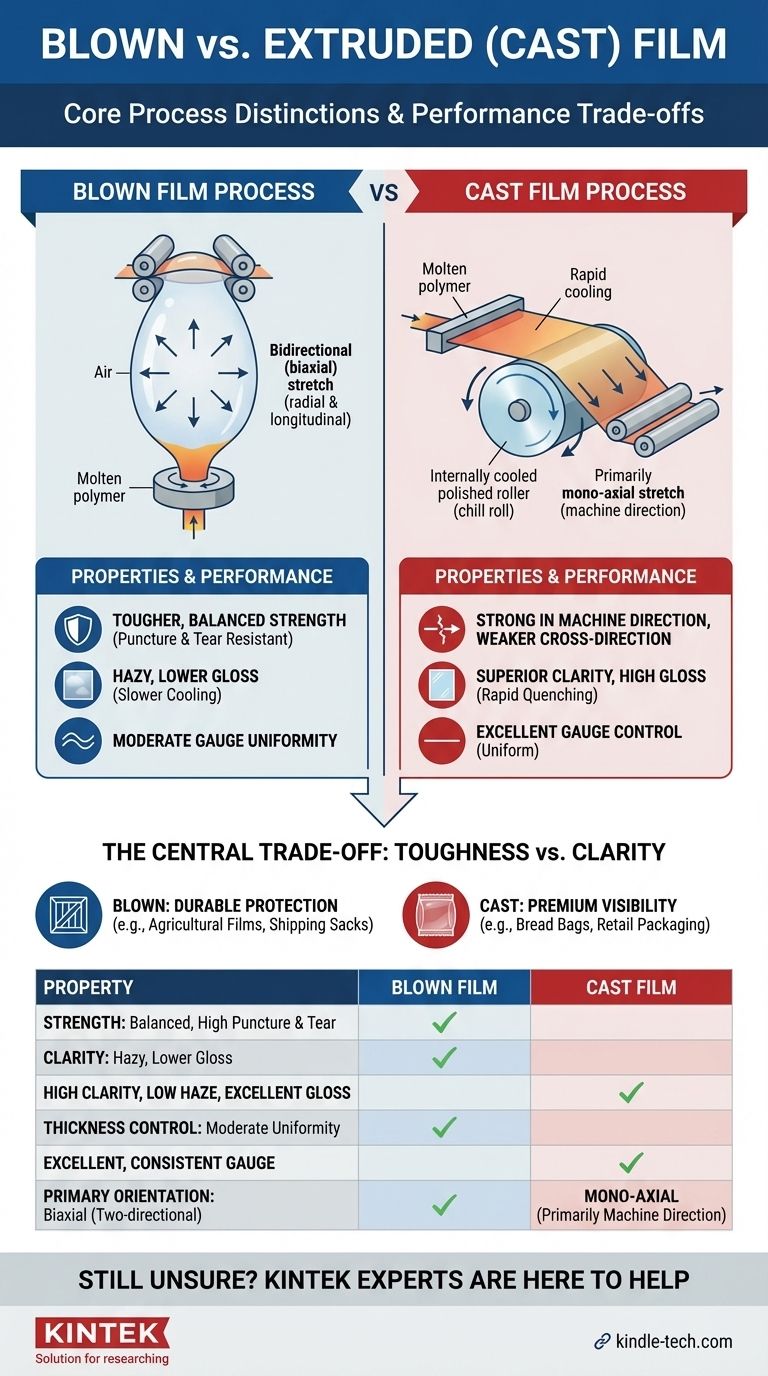
At its core, the difference between blown and extruded film lies in the manufacturing process immediately after the plastic is melted. While both start with extrusion, blown film is inflated vertically like a bubble to stretch it in two directions, whereas cast extruded film is immediately cooled on a flat, chilled roller, stretching it primarily in one direction. This fundamental difference in processing creates films with distinct and predictable properties.
The central trade-off is simple: blown film provides superior toughness and balanced strength at the expense of optical clarity, while cast film delivers exceptional clarity and uniformity at the expense of balanced mechanical strength.
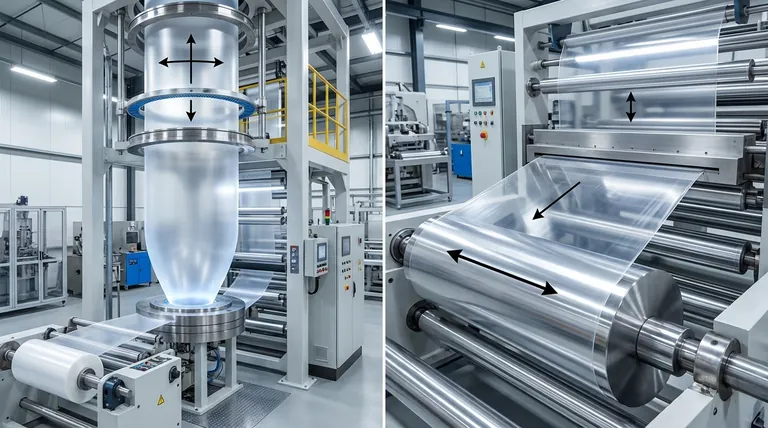

The Core Process Distinction: Bubble vs. Roller
To understand why the films perform so differently, you must first visualize how they are made. The choice of process directly engineers the film's molecular structure and resulting characteristics.
How Blown Film is Made
In the blown film process, molten polymer is pushed through a circular die, forming a thick tube of material. Immediately, air is blown into the center of this tube, causing it to expand like a large, continuous bubble.
This expansion stretches the film in two ways simultaneously: radially (the hoop direction) and longitudinally (the machine direction). This biaxial orientation aligns the polymer molecules in two directions, which is the source of the film's balanced strength.
The bubble is then cooled by the surrounding air, collapsed between rollers, and wound onto a roll.
How Cast Film is Made
The cast film process, often called cast extrusion, uses a flat extrusion die instead of a circular one. The molten polymer emerges as a thin, wide sheet directly onto a large, highly polished, and internally cooled roller, known as a chill roll.
This rapid cooling or "quenching" freezes the polymer molecules in a more random state, which is key to the film's high clarity. The film is stretched primarily in the machine direction as it's pulled through a series of rollers, giving it mono-axial orientation.
Comparing the Final Product: Properties and Performance
The differences in manufacturing directly translate to measurable differences in the finished product. Your application's requirements will determine which set of properties is more valuable.
Strength and Durability
Blown film is the tougher material. The biaxial orientation creates a film with more balanced tensile strength and significantly higher tear resistance, especially against punctures.
Cast film, being oriented primarily in one direction, is strong along its length but can tear more easily in the cross-direction.
Clarity and Gloss
Cast film has superior optical properties. The rapid quenching process prevents the formation of large crystals within the polymer, resulting in much higher clarity, lower haze, and better gloss. It provides a crystal-clear appearance ideal for retail packaging.
Blown film's slower cooling process allows for more crystallization, which makes the film hazier and less transparent.
Thickness Uniformity (Gauge Control)
Cast film offers exceptional gauge control. The direct contact with precision-engineered chill rolls allows for a very consistent and uniform film thickness across the entire web.
Controlling the gauge of blown film is more challenging due to the inherent instabilities of the air-cooled bubble, which can lead to minor variations in thickness.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these films means making a conscious compromise. There is no single "best" film, only the best film for a specific job.
The Toughness vs. Clarity Compromise
This is the most critical trade-off. If your product needs to be seen clearly on a shelf, cast film is the obvious choice. If your product needs durable protection during shipping and handling, blown film is the safer bet.
Directional Strength Imbalances
The mono-axial orientation of cast film makes it perfect for applications where force is applied predictably in the machine direction. However, it can be a point of failure if unexpected cross-directional stress is applied. Blown film's balanced nature makes it more resilient to unpredictable forces.
Cost and Production Speed
Cast film lines typically run at higher speeds than blown film lines, leading to greater output. This can often translate to a lower cost per unit, especially for high-volume applications like stretch wrap. However, the initial capital investment for cast film equipment is generally higher.
Choosing the Right Film for Your Application
Your choice should be dictated entirely by the primary demand of your end-use.
- If your primary focus is puncture resistance and load-bearing strength: Choose blown film for applications like agricultural films, construction liners, and heavy-duty shipping sacks.
- If your primary focus is premium product visibility and aesthetics: Choose cast film for applications like bread bags, magazine overwraps, and high-clarity food packaging.
- If your primary focus is high-speed, automated wrapping with consistent performance: Choose cast film for its superior gauge control and quiet unwind, making it ideal for pallet stretch wrapping.
By understanding the fundamental process differences, you can confidently select the film whose inherent properties align perfectly with your project's demands.
Summary Table:
| Property | Blown Film | Cast Film |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | Balanced, high puncture & tear resistance | Strong in machine direction, weaker cross-direction |
| Clarity | Hazy, lower gloss | High clarity, low haze, excellent gloss |
| Thickness Control | Moderate gauge uniformity | Excellent, consistent gauge |
| Primary Orientation | Biaxial (two-directional) | Mono-axial (primarily machine direction) |
Still unsure which film process is right for your specific application? The experts at KINTEK are here to help. We specialize in providing the right lab equipment and consumables to support your material testing and R&D needs. Whether you're developing new packaging or optimizing film properties, our team can help you make an informed decision.
Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your laboratory's efficiency and success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
People Also Ask
- What technical requirements must specialized pressure-bearing molds meet? Optimize Sulfide Electrolyte Densification
- What role do high-strength graphite molds play during vacuum hot pressing? Enhance Precision in CuAlMn Composites
- Why is hot press molding preferred over traditional solution casting? Expert Comparison for Polymer Electrolytes
- Why is precise temperature and pressure control necessary for combustible cartridge cases? Ensure Structural Integrity
- What is the role of graphite molds during the hot pressing of LSLBO ceramics? Essential for High-Density Electrolytes



















