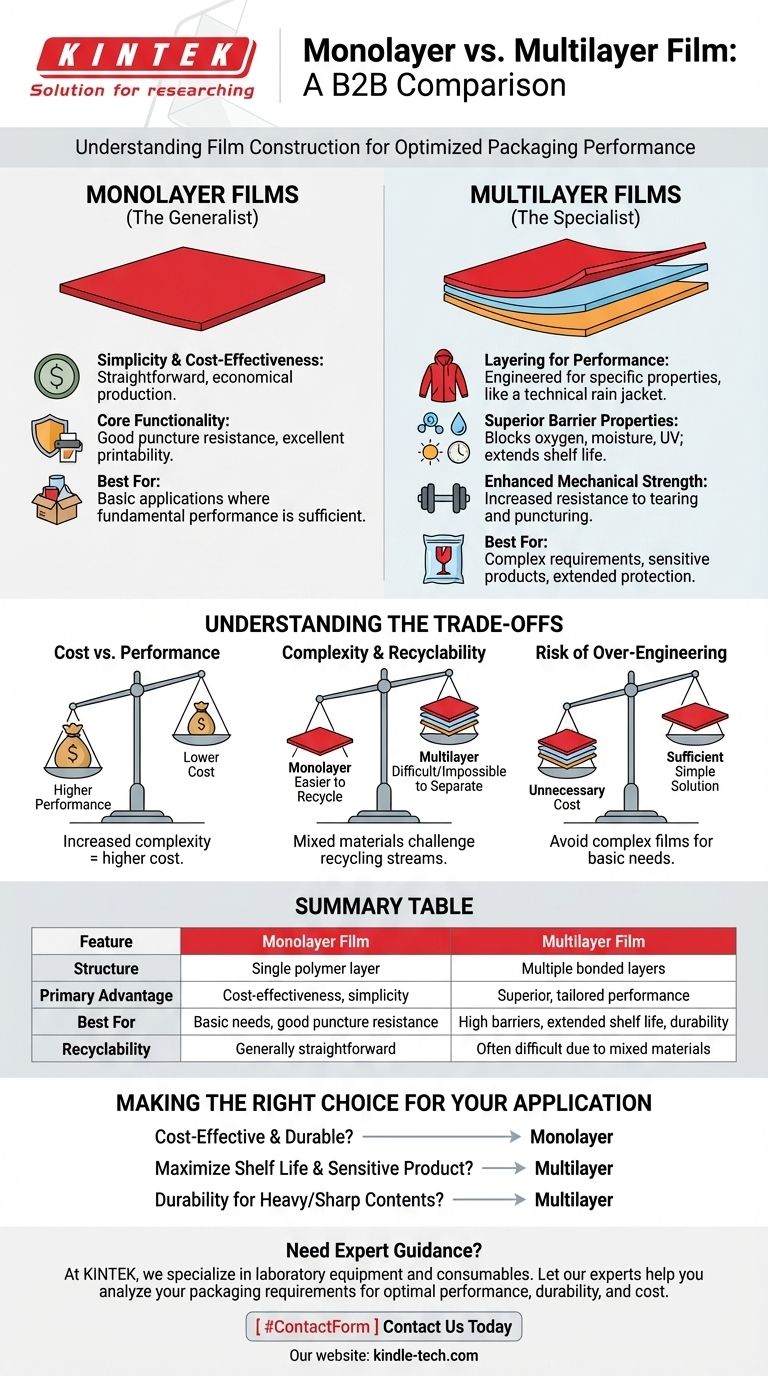
At its core, the difference is in their construction. A monolayer film is a single, uniform sheet of one type of polymer, while a multilayer film is an engineered composite, bonding two or more different layers together to achieve specific performance characteristics that a single layer cannot provide on its own.
The decision between monolayer and multilayer film is not about which is "better," but about defining your specific need. Monolayer films offer simplicity and cost-effectiveness for basic applications, whereas multilayer films provide highly tailored, superior performance for complex requirements.

Deconstructing Monolayer Films
A monolayer film can be thought of as a general-purpose tool. It's made from one material that must handle every job required of it, from providing structure to acting as a barrier.
Simplicity and Cost-Effectiveness
The primary advantage of a monolayer film is its simplicity. Manufacturing a single layer of polymer is a straightforward and well-established process, which makes it a highly cost-effective solution.
Core Functionality
These films are perfectly suitable for applications where basic functionality is sufficient. They can be engineered for good puncture resistance and provide an excellent surface for printability, making them ideal for many common packaging needs.
The Power of Multilayer Construction
Multilayer films are specialists. Each layer is chosen for a specific property, and when combined, they create a high-performance material that is greater than the sum of its parts.
Layering for Performance
Think of a high-performance rain jacket. It has an outer layer for water repellency, a middle layer for breathability, and an inner layer for comfort. Multilayer films work on the same principle, combining materials to achieve distinct goals.
Superior Barrier Properties
This is a key driver for choosing multilayer films. One layer might be excellent at blocking oxygen, while another blocks moisture or UV light. Combining them provides comprehensive protection, extending the shelf life and preserving the quality of sensitive products like food or pharmaceuticals.
Enhanced Mechanical Strength
By layering different polymers, manufacturers can dramatically improve a film's durability. This results in enhanced mechanical strength, making the film more resistant to tearing, dropping, and puncturing during transport and handling.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right film requires acknowledging the inherent compromises between cost, performance, and environmental impact.
Cost vs. Performance
There is a direct relationship between complexity and cost. The specialized performance of a multilayer film comes from a more complex manufacturing process, making it a more expensive option than a simple monolayer film.
Complexity and Recyclability
Monolayer films, being made of a single polymer type, are generally straightforward to recycle. Multilayer films, however, bond different materials together, which can make them difficult or impossible to separate and recycle through conventional streams.
The Risk of Over-Engineering
Using a complex multilayer film when a simple monolayer would suffice is a common mistake. It adds unnecessary cost and environmental burden without providing a tangible benefit to the product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your product's specific needs should be the sole driver of your decision.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for a durable product: A monolayer film offers the necessary puncture resistance and printability without unnecessary expense.
- If your primary focus is maximizing shelf life for a sensitive product: A multilayer film is essential for its superior barrier properties against oxygen, moisture, and light.
- If your primary focus is durability for heavy or sharp contents: The enhanced mechanical strength of a multilayer film provides the reliability you need to prevent package failure.
Ultimately, selecting the correct film is about precisely matching the material's capabilities to your product's requirements.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Monolayer Film | Multilayer Film |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Single polymer layer | Multiple bonded polymer layers |
| Primary Advantage | Cost-effectiveness, simplicity | Superior, tailored performance |
| Best For | Basic applications, good puncture resistance | High barrier properties, extended shelf life, enhanced durability |
| Recyclability | Generally straightforward | Can be difficult due to mixed materials |
Need expert guidance to select the perfect film for your product?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables. Our experts can help you analyze your packaging requirements—whether you need cost-effective monolayer solutions or high-performance multilayer films for sensitive products. We provide the materials and insights to ensure your packaging delivers on performance, durability, and cost.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss your specific needs and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory and packaging challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Aluminum-Plastic Flexible Packaging Film for Lithium Battery Packaging
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Rod Insulated for Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What materials are used in thin film optical coating? Key Materials for Precise Light Control
- What does a layered film mean? Unpacking the Depths of Cinematic Storytelling
- What is the blown film technique? A Guide to High-Strength Plastic Film Production
- What is a sustainable solution to reduce plastic waste? A Guide to the Waste Hierarchy
- What is the difference between single layer film and multi layer film? A Guide to Material Selection








