In chemical engineering, a mixing reactor is not merely a container; it is the dynamic environment where chemical potential becomes reality. Its fundamental importance lies in its ability to control the physical conditions—concentration and temperature—that govern the speed, efficiency, quality, and safety of a chemical reaction. Without effective mixing, even the most promising chemical formula will fail to perform predictably at any meaningful scale.
The core purpose of a mixing reactor is to overcome physical transport limitations (mass and heat transfer) so that the chemical reaction's intrinsic speed is the only factor limiting production. This control is the key to achieving efficient, predictable, and safe chemical processes.

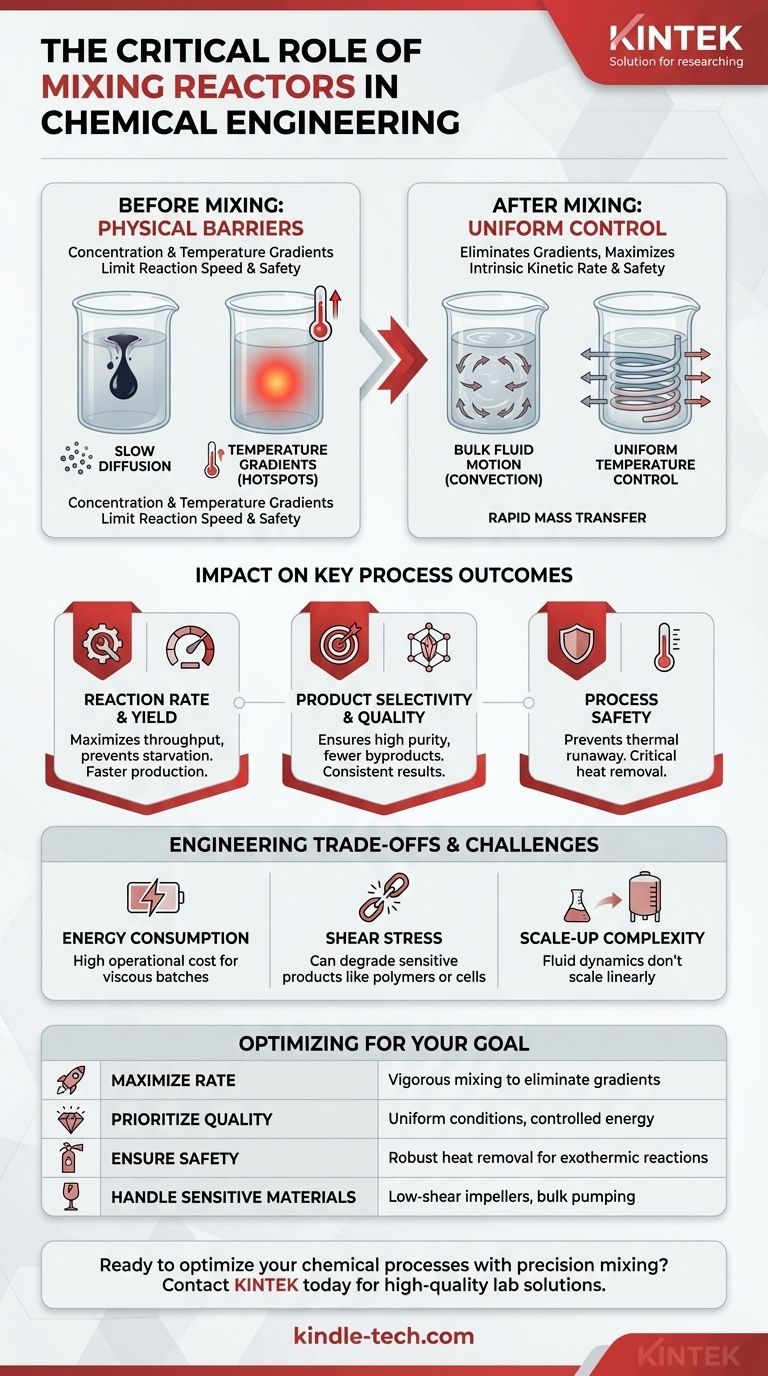
The Core Function: Overcoming Physical Barriers
A chemical reaction can only occur when molecules collide under the right conditions. A mixing reactor's primary job is to create and maintain these conditions uniformly throughout a large volume.
The Problem of Concentration Gradients
Imagine adding a drop of ink to a glass of still water. The color spreads slowly through diffusion, a very slow process. Reactants in an unstirred reactor behave the same way.
The area where the reaction occurs quickly becomes depleted of reactants, creating a "starved" zone. This dramatically slows down or even stops the reaction, regardless of how much reactant is elsewhere in the vessel.
How Mixing Drives Mass Transfer
Effective mixing creates bulk fluid motion (convection), which is thousands of times faster than diffusion at transporting molecules.
This turbulence rapidly reduces concentration gradients, ensuring that fresh reactants are constantly supplied to the reaction zone. For reactions involving different phases (like a gas bubbled through a liquid), mixing is essential for creating and maintaining the interfacial area where the reaction actually happens.
The Problem of Temperature Gradients (Hotspots)
Many reactions release heat (exothermic) or absorb heat (endothermic). In an unstirred exothermic reaction, the heat generated can't escape effectively.
This leads to the formation of localized hotspots where the temperature is dangerously high. These hotspots can cause side reactions, degrade the product, or even lead to a runaway reaction with catastrophic consequences.
How Mixing Enables Heat Transfer
Mixing forces the entire fluid to circulate, moving hot fluid from the reaction zone to the vessel walls, where it can be cooled by a jacket or internal coils.
This forced convection creates uniform temperature control, which is critical for ensuring the reaction produces the desired product (selectivity) and operates safely.
The Impact on Key Process Outcomes
The physical control provided by mixing has a direct and measurable impact on the metrics that define a successful chemical process.
Controlling Reaction Rate and Yield
By eliminating reactant starvation, mixing allows the reaction to proceed at its maximum possible speed, known as its intrinsic kinetic rate.
This means you get more product in less time, directly increasing the throughput and yield of the reactor.
Ensuring Product Selectivity and Quality
Many processes can form unwanted byproducts, especially at the wrong temperatures or concentrations. Uniform conditions prevent this.
By eliminating hotspots and concentration gradients, good mixing ensures the reaction consistently favors the desired product, leading to higher purity and selectivity.
Guaranteeing Process Safety
For highly exothermic reactions, the mixing system is a primary piece of safety equipment. Its ability to facilitate heat removal is what prevents a thermal runaway.
A failure of the mixer (e.g., a broken impeller or power loss) is often a critical emergency scenario in chemical plants precisely because it removes this essential layer of control.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While essential, mixing is not a simple "more is better" solution. It involves critical engineering trade-offs.
Energy Consumption
Mixing requires significant energy input, especially for large, viscous batches. The motor driving the impeller can be a major operational cost.
Over-mixing is not only wasteful but can be detrimental, making the optimization of mixing energy a key design consideration.
Shear Stress and Product Degradation
High-speed impellers create intense shear forces. These forces can be destructive to sensitive products.
For example, high shear can break the long molecular chains of polymers, destroy delicate crystals needed for a drug formulation, or rupture living cells in a bioreactor.
The Challenge of Scale-Up
A mixing strategy that works perfectly in a one-liter lab flask will almost certainly fail in a 10,000-liter production vessel.
Fluid dynamics do not scale linearly. Ensuring that a large-scale reactor has the same level of mass and heat transfer as its lab-scale counterpart is one of the most complex challenges in chemical engineering.
Optimizing Mixing for Your Specific Goal
The "right" level and type of mixing depend entirely on the specific demands of your process. Consider these guiding principles when defining your objective.
- If your primary focus is maximizing reaction rate: You need to ensure the process is kinetically limited, not mass-transfer limited, by providing vigorous mixing to eliminate concentration gradients.
- If your primary focus is product quality and selectivity: Prioritize uniform temperature and concentration profiles to suppress side reactions, which may require controlled, rather than maximum, mixing energy.
- If your primary focus is process safety with highly exothermic reactions: Your mixing system must be robustly designed to guarantee heat removal and prevent hotspots, making it a critical safety device.
- If your primary focus is producing shear-sensitive materials: You must use low-shear impellers and mixing strategies that promote bulk fluid movement (pumping) over high local turbulence.
Ultimately, mastering the mixing reactor is about controlling the physical environment to unlock the full potential of your chemistry.
Summary Table:
| Key Function | Impact on Process |
|---|---|
| Eliminates Concentration Gradients | Maximizes reaction rate and yield by preventing reactant starvation. |
| Prevents Temperature Hotspots | Ensures product selectivity, quality, and safety, especially in exothermic reactions. |
| Overcomes Physical Transport Limitations | Allows the reaction to proceed at its intrinsic kinetic speed for efficient scale-up. |
Ready to optimize your chemical processes with precision mixing?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment, including reactors designed for optimal mass and heat transfer. Whether you are scaling up a reaction or need to ensure the safety and purity of a sensitive synthesis, our solutions are engineered to meet your specific challenges.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can help you achieve efficient, predictable, and safe chemical production.
Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a high-pressure reactor in h-BN magnetic nanocomposite synthesis? Master Precision Deposition
- Why is a High-temperature and High-pressure Autoclave necessary for zirconium alloy testing? Ensure Nuclear Safety.
- How does a high-pressure hydrothermal autoclave facilitate the synthesis of BiVO4@PANI nanocomposites? Unlock Precision.
- Which critical experimental conditions does a high-pressure autoclave provide? Optimize Mixed Sulfide Leaching
- What is the function of a high-pressure static autoclave in biomass HTL? Optimize Your Biomass Conversion Research



















