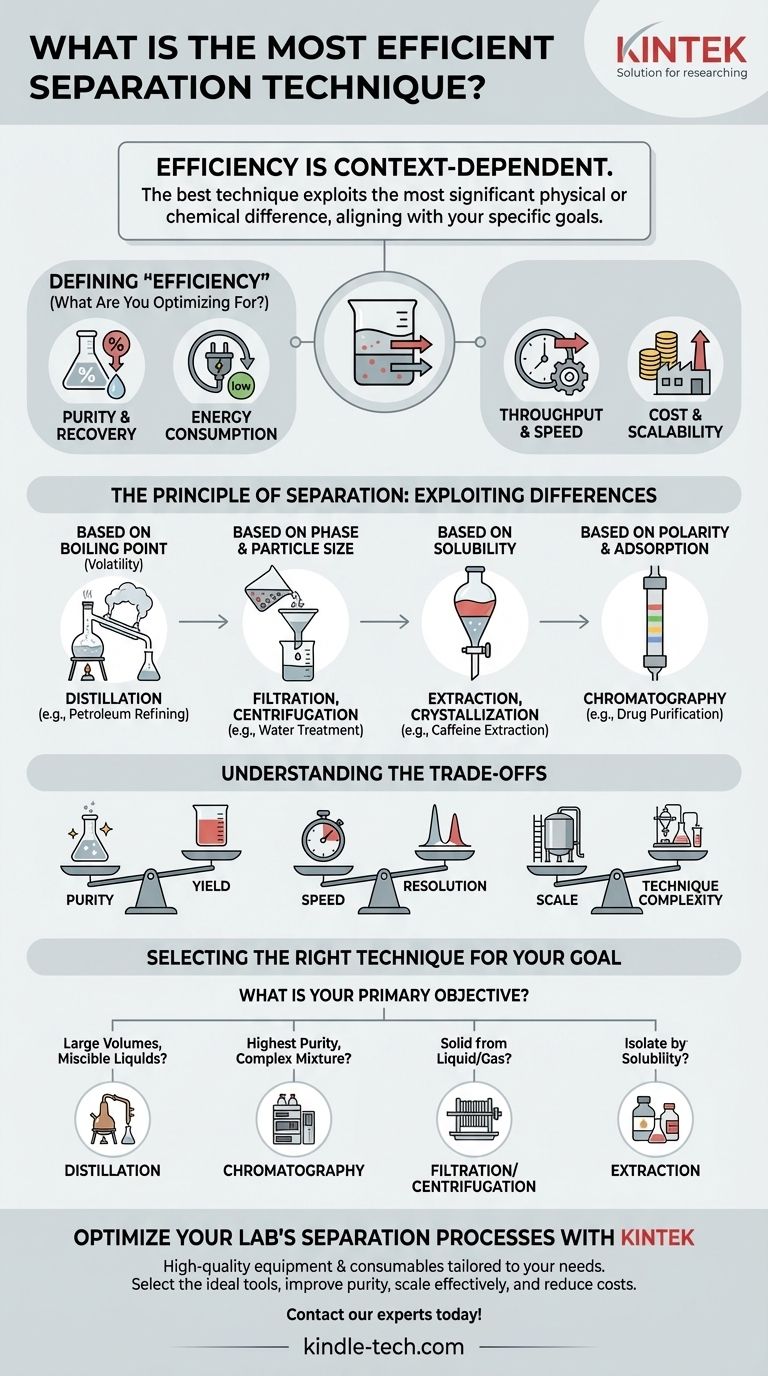
There is no single "most efficient" separation technique. The efficiency of any method is entirely dependent on the specific properties of the mixture you are separating, the desired purity of the final products, and the scale of the operation. A technique that is highly efficient for one task can be completely ineffective or prohibitively expensive for another.
The most efficient separation technique is the one that best exploits the most significant physical or chemical difference between the components of your mixture, aligning with your specific goals for purity, speed, and cost.

Defining "Efficiency": What Are You Optimizing For?
Before you can select a technique, you must first define what "efficient" means for your specific application. These factors are often in competition with one another, requiring a careful balance.
Purity & Recovery
Purity, or resolution, refers to how well a substance is isolated from others. Recovery refers to the amount of your target substance you retrieve. Pushing for extremely high purity often results in lower recovery.
Energy Consumption
Separations are fundamentally fighting against entropy, which requires energy. Techniques like distillation are energy-intensive, while methods like filtration can be very low-energy. This is a critical factor in large-scale industrial processes.
Throughput & Speed
How much material do you need to process in a given amount of time? A high-throughput industrial process has very different requirements than a high-precision laboratory analysis.
Cost & Scalability
The economic viability of a technique is paramount. A method that is simple and affordable in a lab, like certain types of chromatography, can become astronomically expensive at an industrial scale.
The Principle of Separation: Exploiting Differences
The core principle of any separation is to leverage a difference in physical or chemical properties. Your first step is to identify the greatest point of distinction between the components you wish to separate.
Based on Boiling Point (Volatility)
Distillation is the workhorse for separating miscible liquids with different boiling points. By heating the mixture, the component with the lower boiling point (the more volatile one) turns to vapor first, which can then be collected and condensed.
This is the dominant method in industries like petroleum refining and alcohol production due to its effectiveness at separating large volumes.
Based on Phase & Particle Size
When separating solids from liquids or gases, simple mechanical methods are often most efficient.
Filtration uses a medium that allows the fluid to pass through but not the solid. Sieving separates solids of different sizes. Centrifugation uses high-speed rotation to separate components based on density.
Based on Solubility
These methods exploit how differently substances dissolve in various solvents.
Extraction uses a solvent to selectively dissolve and remove a target compound from a mixture. Crystallization purifies a solid by dissolving it in a hot solvent and letting it cool, causing the desired compound to precipitate out in a purer, crystalline form.
Based on Polarity & Adsorption
Chromatography is a powerful family of techniques that separates components based on their differential interaction with a stationary phase (like silica gel) and a mobile phase (a moving liquid or gas).
It offers unparalleled separation power for complex mixtures, making it essential for pharmaceutical analysis and purification, but it is often more complex and costly than bulk methods.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a technique always involves balancing competing priorities. Understanding these trade-offs is key to making an intelligent decision.
The Purity vs. Yield Dilemma
In many processes, achieving higher purity means sacrificing yield. For example, in distillation, you might discard the initial and final fractions of the distillate to ensure the central fraction is exceptionally pure, thereby losing some of your product.
The Speed vs. Resolution Dilemma
Faster is not always better. In chromatography, running the process faster (higher flow rate) almost always reduces the quality of the separation (resolution). You must choose between high throughput with adequate separation or low throughput with excellent separation.
The Scale vs. Technique Dilemma
A technique's efficiency is fundamentally tied to scale. Distillation is highly efficient for separating thousands of barrels of crude oil but is needlessly complex for purifying a few milligrams of protein in a lab, where chromatography would be far more suitable.
Selecting the Right Technique for Your Goal
Your choice must be driven by your primary objective. Evaluate your specific needs to determine the most logical starting point.
- If your primary focus is separating large volumes of miscible liquids with different boiling points (e.g., crude oil, ethanol/water): Distillation is almost always the most economically efficient method.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible purity for a complex, high-value mixture (e.g., purifying a drug): Chromatography provides the best resolution, despite higher costs and lower throughput.
- If your primary focus is removing a solid from a liquid or gas (e.g., water treatment, dust collection): Filtration, sieving, or centrifugation offer the most direct and energy-efficient solution.
- If your primary focus is isolating a target compound from a mixture based on its unique solubility (e.g., extracting caffeine from coffee beans): Liquid-liquid or solid-liquid extraction is the most effective approach.
Ultimately, choosing the right method begins not with a list of techniques, but with a deep understanding of your own mixture and objectives.
Summary Table:
| Separation Goal | Most Efficient Technique | Key Principle | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Large-scale separation of miscible liquids (e.g., crude oil) | Distillation | Differences in boiling point | Petroleum refining, alcohol production |
| High-purity isolation of complex, high-value mixtures (e.g., pharmaceuticals) | Chromatography | Differences in polarity/adsorption | Drug purification, lab analysis |
| Solid-liquid or solid-gas separation (e.g., water treatment) | Filtration, Centrifugation | Differences in particle size/density | Industrial processes, environmental applications |
| Isolating compounds based on solubility (e.g., caffeine extraction) | Extraction, Crystallization | Differences in solubility | Chemical processing, food/beverage industry |
Optimize Your Lab's Separation Processes with KINTEK
Struggling to choose the right separation technique for your specific laboratory needs? The efficiency of your process depends on selecting the correct equipment and consumables tailored to your mixture's properties and your goals for purity, speed, and cost.
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for all your separation needs. Whether you require distillation setups, filtration systems, chromatography columns, or extraction apparatus, we have the solutions to enhance your lab's efficiency and accuracy.
Let us help you:
- Select the ideal equipment for your specific separation challenges
- Improve purity and recovery rates with precision-engineered tools
- Scale your processes effectively from research to production
- Reduce operational costs with durable, reliable laboratory solutions
Don't let an inefficient separation process slow down your research or production. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation and discover how KINTEK can elevate your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Wall Mounted Water Distillation Unit
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Hollow Cleaning Basket and Rack Carrier
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
People Also Ask
- How plasma is created in sputtering? A Step-by-Step Guide to Ionization and Thin Film Deposition
- What is a filter press used for? Achieve Maximum Solid-Liquid Separation Efficiency
- How does a high-power ultrasonic homogenizer assist in the preparation of organic-inorganic nanocomposites?
- Is sintering the same as melting? Master the Critical Thermal Process Distinction
- Is annealing done in a furnace? Mastering the Thermal Process for Material Properties
- How to do magnetron sputtering? A Step-by-Step Guide to Thin Film Deposition
- What heating treatment can be used to strengthen the structure of a metal? Master Hardening, Tempering & More
- What happens in sample preparation? The Critical Step for Accurate Lab Analysis



















