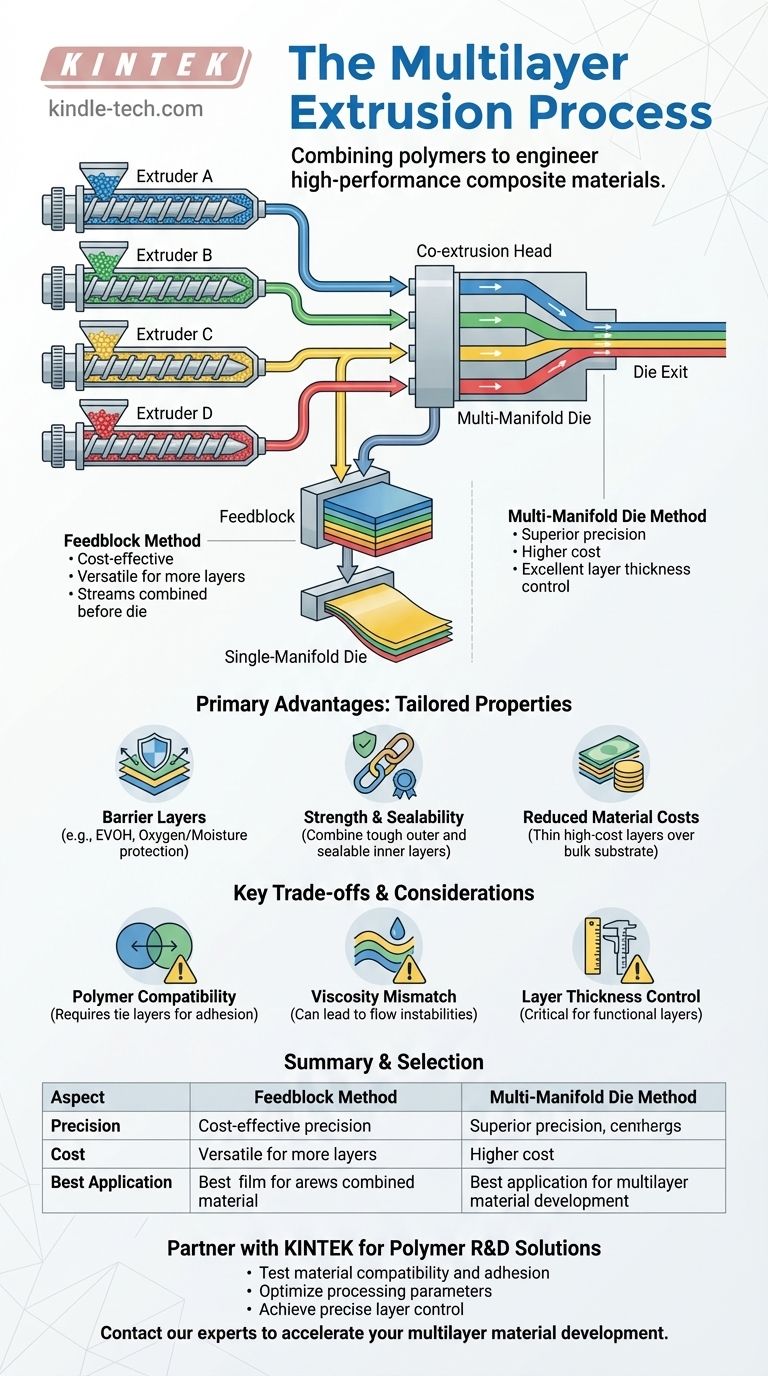
At its core, multilayer co-extrusion is a manufacturing process where two or more different polymers are melted, extruded, and merged into a single, layered structure. This is accomplished before the material is shaped by the final die, allowing for the creation of composite materials with precisely engineered properties that no single polymer could achieve on its own.
The fundamental goal of multilayer extrusion is not just to layer plastics, but to create a new, high-performance material by combining the distinct advantages of each polymer—such as strength, oxygen barrier, and sealability—into one integrated film or sheet.
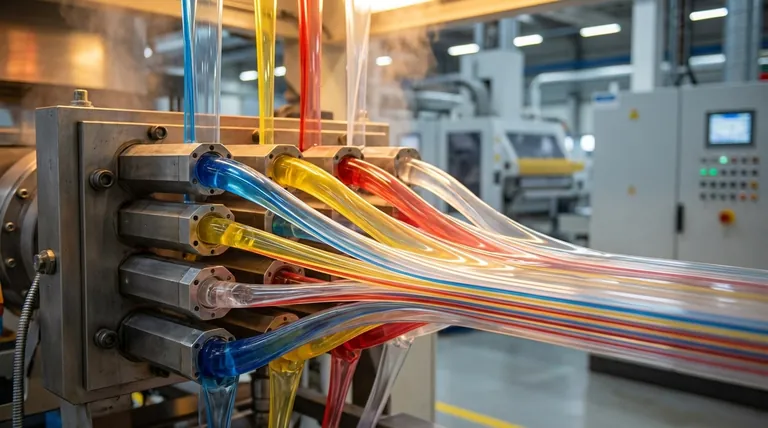

How Multilayer Extrusion Works: The Core Process
The elegance of multilayer extrusion lies in its ability to combine separate material streams into a single, cohesive output. This is managed through a sequence of highly controlled steps.
Individual Extruders: The Starting Point
Each polymer used in the final structure begins in its own dedicated extruder. An extruder is essentially a heated barrel containing a rotating screw that melts, mixes, and pressurizes the raw polymer resin (in pellet form).
The output of each extruder is a uniform stream of molten polymer, with its flow rate and temperature precisely controlled for the specific layer it will form.
The Co-extrusion Head: Where Layers Meet
After leaving their individual extruders, the molten polymer streams are directed into a specialized co-extrusion head. This is the critical junction where the layers are brought together.
There are two primary designs for this head, each with its own methodology for combining the materials.
Two Key Methods for Combining Polymers
The choice of method for combining the polymer streams has a significant impact on cost, complexity, and the level of precision you can achieve in the final product.
The Feedblock Method
In this common approach, the separate molten polymer streams are first combined in a component called a feedblock, which is positioned just before the main die.
The feedblock arranges the streams into a stack of parallel layers. This layered stack then flows into a standard, single-manifold die, which spreads the material out to the desired width while maintaining the distinct layers. This method is versatile and cost-effective for adding more layers.
The Multi-Manifold Die Method
This method is more complex and expensive but offers superior precision. Here, the die itself contains individual channels (manifolds) for each polymer.
The polymers are spread to their full width within their own separate manifolds inside the die. They are only merged together just before the final die exit. This provides extremely precise control over the thickness of each individual layer.
The Primary Advantage: Engineering Unique Properties
Multilayer extrusion is used because it enables the creation of materials with a tailored combination of performance characteristics.
Creating High-Performance Barrier Layers
Many applications, especially in food and medical packaging, require a barrier to oxygen, moisture, or chemicals. A thin, high-cost barrier polymer (like EVOH) can be sandwiched between thicker, lower-cost structural polymers (like polyethylene).
Combining Strength and Sealability
A product may require a tough, puncture-resistant outer layer and a soft, heat-sealable inner layer. Multilayer extrusion allows these two incompatible properties to coexist in a single film.
Reducing Material Costs
A costly polymer with a specific desirable property (e.g., UV resistance) can be used as a very thin outer layer (a "cap layer") over a cheaper, bulk substrate, reducing the total cost of the final product.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the process requires careful management of material science and fluid dynamics to be successful.
Polymer Compatibility
For layers to adhere properly, the polymers must have sufficient intermolecular attraction. If they are not compatible, a thin "tie layer" of an adhesive polymer must be extruded between them.
Viscosity Mismatch
The flow rates of the different molten polymers must be closely matched. A significant mismatch in viscosity can lead to instabilities at the layer interfaces, resulting in defects and non-uniform layer thickness.
Layer Thickness Control
Achieving and maintaining precise thickness for each layer, especially for very thin functional layers, is a significant process control challenge. The multi-manifold die method offers better control but at a higher capital cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct extrusion method depends entirely on your project's specific performance requirements and budget.
- If your primary focus is versatility and cost-efficiency for 3-7 layers: The feedblock method is often the most practical and economical choice.
- If your primary focus is absolute precision for thin, critical layers: The multi-manifold die method provides superior control, justifying its higher cost.
- If your primary focus is creating a structure with many layers (9+): The feedblock method is more scalable and is the standard for producing complex barrier films.
Ultimately, multilayer co-extrusion empowers you to engineer a material perfectly suited to its final application.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Process | Melting and merging multiple polymers into a single, layered structure before shaping. |
| Key Methods | Feedblock (cost-effective, versatile) vs. Multi-Manifold Die (high precision, higher cost). |
| Primary Advantage | Combines distinct polymer properties (e.g., strength, barrier, sealability) into one material. |
| Key Consideration | Polymer compatibility and viscosity matching are critical for layer stability and adhesion. |
Ready to engineer the perfect multilayer film for your application?
The multilayer extrusion process is powerful, but its success depends on precise control and the right equipment. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for polymer research and development, helping you perfect your co-extrusion parameters before scaling up.
We can help you:
- Test material compatibility and layer adhesion.
- Optimize processing parameters for your specific polymer blend.
- Achieve the precise layer control your product demands.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project and discover how our solutions can accelerate your development of high-performance multilayer materials.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Powerful Plastic Crusher Machine
People Also Ask
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What are the drawbacks of PECVD? Understanding the Trade-offs of Low-Temperature Deposition
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What are the disadvantages of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Managing the Trade-offs of Low-Temperature Deposition
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Coating Solution for Sensitive Materials


















