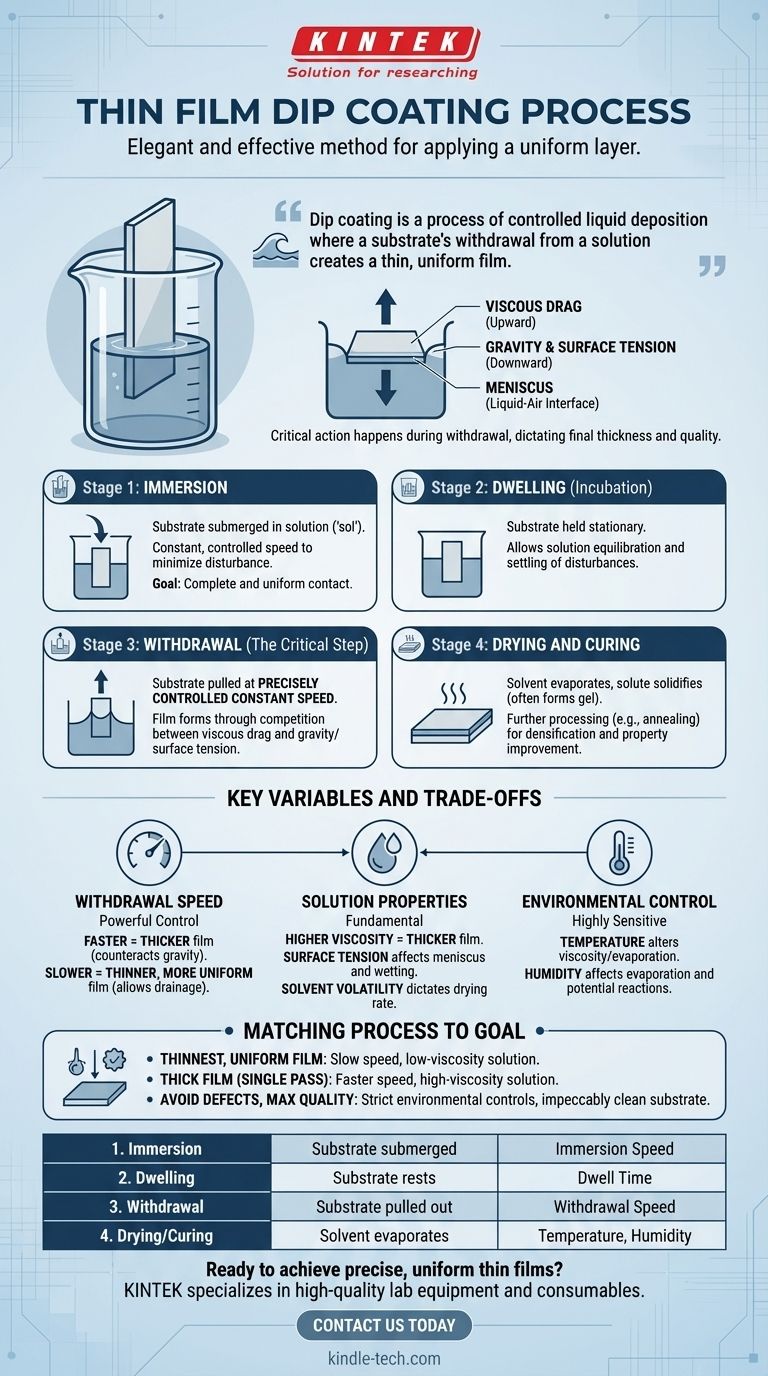
At its core, the thin film dip coating process is a remarkably elegant and effective method for applying a uniform layer of material onto a substrate. It consists of four primary stages: immersing the substrate in a solution, allowing it to dwell, withdrawing it at a constant speed, and finally, drying the resulting film. The critical action happens during withdrawal, where a delicate balance of physical forces dictates the final thickness and quality of the coating.
Dip coating is a process of controlled liquid deposition where a substrate's withdrawal from a solution creates a thin, uniform film. The thickness of this film is primarily governed by the withdrawal speed and the physical properties of the liquid, such as its viscosity and surface tension.

Deconstructing the Dip Coating Process
To truly understand dip coating, we must look at each stage not as an isolated step, but as a part of a continuous physical process. The success of the final film depends on precise control at every point.
Stage 1: Immersion
The process begins by fully submersing the substrate into the coating solution, often called the "sol." This is typically done at a constant, controlled speed to minimize any disturbance or wave generation in the liquid. The goal is to ensure the entire surface to be coated makes complete and uniform contact with the solution.
Stage 2: Dwelling (Incubation)
Once immersed, the substrate is held stationary within the solution for a predetermined period. This dwelling time allows the solution to equilibrate on the substrate's surface, ensuring complete wetting and allowing any initial disturbances from the immersion to settle.
Stage 3: Withdrawal (The Critical Step)
This is the most crucial stage where the film is actually formed. The substrate is pulled out of the solution at a precisely controlled, constant speed.
As the substrate is withdrawn, a thin layer of the liquid clings to its surface and is drawn upward. The thickness of this entrained layer is determined by a competition between viscous drag (pulling the liquid up with the substrate) and the forces of gravity and surface tension (pulling the liquid back down into the bath). A visible curve, known as the meniscus, forms at the intersection of the liquid, substrate, and air.
Stage 4: Drying and Curing
As the substrate is withdrawn, the solvent in the adhered layer begins to evaporate. This evaporation causes the solute material to solidify, often forming a gel. This solid film may then undergo further processing, such as annealing or heat treatment, to densify the material, remove residual organic compounds, and improve its final structural and chemical properties.
Understanding the Key Variables and Trade-offs
The apparent simplicity of dip coating is deceptive. Achieving a high-quality, reproducible film requires careful management of several interconnected variables.
Withdrawal Speed
This is the most powerful control parameter. A faster withdrawal speed counteracts gravity more effectively, resulting in a thicker film. Conversely, a slower withdrawal speed allows more liquid to drain back into the bath, producing a thinner, more uniform film. However, excessively high speeds can lead to instability and defects.
Solution Properties
The viscosity and surface tension of the coating solution are fundamental. Higher viscosity leads to a thicker entrained film, while surface tension influences the shape of the meniscus and the wetting behavior. The volatility of the solvent also plays a critical role, as it dictates the rate of drying and solidification.
Environmental Control
The entire process is highly sensitive to the surrounding environment. Changes in temperature can alter the solution's viscosity and evaporation rate. Humidity can significantly affect solvent evaporation and potentially introduce unwanted reactions, especially for moisture-sensitive materials.
Matching the Process to Your Goal
Your specific objective will determine how you balance these variables.
- If your primary focus is creating the thinnest, most uniform film: Use a slow, highly stable withdrawal speed and a low-viscosity solution.
- If your primary focus is producing a relatively thick film in a single pass: Use a faster withdrawal speed and a higher-viscosity solution.
- If your primary focus is avoiding defects and maximizing quality: Implement strict environmental controls for temperature and humidity, and ensure the substrate is impeccably clean before immersion.
Ultimately, mastering dip coating is about understanding and controlling the delicate interplay of forces during the withdrawal phase.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Action | Primary Control Parameter |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Immersion | Substrate is submerged in solution | Immersion Speed |
| 2. Dwelling | Substrate rests in solution | Dwell Time |
| 3. Withdrawal | Substrate is pulled out | Withdrawal Speed |
| 4. Drying/Curing | Solvent evaporates, film solidifies | Temperature, Humidity |
Ready to achieve precise, uniform thin films in your lab? The dip coating process requires control and the right equipment to be successful. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for all your coating and material processing needs. Our experts can help you select the perfect solution for your specific application. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and ensure reproducible, high-quality results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- What is microwave plasma CVD? A Guide to High-Purity Diamond and Material Synthesis
- How does PACVD equipment improve DLC coatings? Unlock Low Friction and High Heat Resistance
- What is the specific function of the metal filament in HF-CVD? Key Roles in Diamond Growth
- How does a Hot Filament Chemical Vapor Deposition (HFCVD) reactor function? Expert Guide to Diamond Film Fabrication
- What machine is used to make lab-grown diamonds? Discover the HPHT & CVD Technologies



















