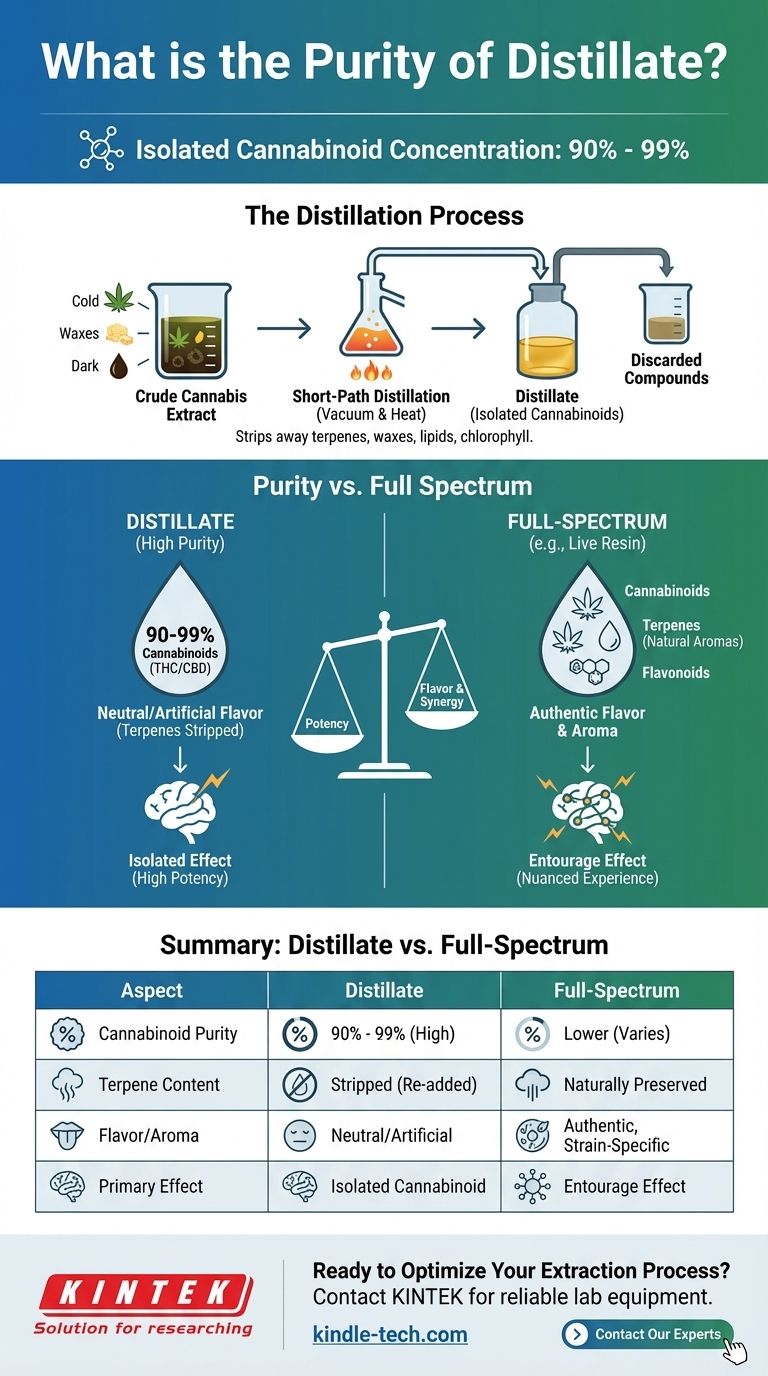
In the world of cannabis concentrates, distillate represents one of the purest forms available. Typically, cannabis distillate tests between 90% and 99% in total cannabinoids, making it a highly potent product. This level of purity is achieved through a complex scientific process that isolates the target cannabinoid, such as THC or CBD, from nearly all other plant matter.
The critical takeaway is that distillate's "purity" refers specifically to its high concentration of a single cannabinoid. This purity is achieved by removing other valuable compounds, most notably the terpenes responsible for flavor, aroma, and nuanced effects.

What "Purity" Really Means for Distillate
The term "purity" can be misleading. In the context of distillate, it does not necessarily mean "better" or "cleaner" in an absolute sense. It simply means the final product is a highly refined and isolated compound.
A Focus on Cannabinoid Isolation
The primary goal of creating distillate is to isolate one specific cannabinoid, like delta-9-THC or CBD, in its most concentrated form.
The process strips away virtually everything else: waxes, lipids, chlorophyll, flavonoids, and, most importantly, terpenes. The resulting product is a thick, translucent oil that is nearly odorless and tasteless.
The Distillation Process in Brief
Distillate is made using a process called short-path distillation. It works by heating a crude cannabis extract under a vacuum.
Because different compounds have different boiling points, the desired cannabinoid (e.g., THC) can be evaporated, collected, and condensed, leaving behind the less desirable materials. This is similar to how distilleries produce high-proof spirits like vodka from a fermented base.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Purity vs. Full Spectrum
The high cannabinoid purity of distillate comes with significant trade-offs, primarily related to the loss of other compounds that contribute to the overall experience.
The Loss of Terpenes
Terpenes are the aromatic compounds that give different cannabis strains their unique scent and flavor profiles, from citrusy and piney to earthy and floral.
The high heat used in distillation destroys these volatile molecules. The result is a highly potent but one-dimensional product that lacks the authentic flavor and aroma of the original plant.
The "Entourage Effect"
Many experts and consumers believe in the "entourage effect"—the theory that cannabinoids and terpenes work synergistically to produce a more nuanced and effective experience.
By removing the terpenes, distillate provides the isolated effect of a single cannabinoid. In contrast, full-spectrum extracts that retain their terpenes are thought to offer an effect that is closer to that of the original flower.
The Role of Re-introduced Terpenes
To compensate for the lack of flavor, producers often add terpenes back into the distillate after the purification process.
These can be cannabis-derived terpenes (CDTs), which are extracted from actual cannabis plants, or botanically-derived terpenes (BDTs), which are sourced from other plants. While this improves taste, the resulting flavor profile is an approximation, not a true representation of the original strain.
How to Apply This to Your Project
The "best" concentrate depends entirely on what you value most in your experience. There is no single correct answer, only the right choice for a specific goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum potency and versatility: Distillate is the clear choice, as it provides a high, reliable dose of a single cannabinoid that can be used in edibles, vapes, and topicals without adding unwanted flavor.
- If your primary focus is authentic flavor and a nuanced effect: You should explore full-spectrum extracts like live resin or live rosin, which prioritize preserving the plant's natural terpenes over achieving maximum THC percentage.
- If your primary focus is a solventless and natural product: Rosin is the ideal option, offering a clean extraction method that uses only heat and pressure to balance potency with terpene preservation.
Understanding that distillate's purity is about cannabinoid isolation—not overall quality—empowers you to select the product that truly aligns with your desired outcome.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Distillate | Full-Spectrum (e.g., Live Resin) |
|---|---|---|
| Cannabinoid Purity | 90% - 99% | Lower (varies) |
| Terpene Content | Stripped (often re-added) | Naturally preserved |
| Flavor/Aroma | Neutral/Artificial | Authentic, strain-specific |
| Primary Effect | Isolated cannabinoid | Entourage effect |
| Best For | Maximum potency, versatility | Authentic experience, nuanced effects |
Ready to Optimize Your Extraction Process?
Whether your goal is to produce high-purity distillates or preserve the full spectrum of cannabinoids and terpenes, having the right equipment is fundamental to achieving consistent, high-quality results. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables for the cannabis industry, from precise heating elements for distillation setups to solvent recovery systems.
Our expertise can help you scale your production while maintaining the purity and quality your customers expect. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific project needs and help you select the perfect equipment for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Buchner Funnel and Triangular Funnel
- Lab Sterile Slapping Type Homogenizer for Tissue Mashing and Dispersing
- Automatic Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine Cold Isostatic Pressing
- RRDE rotating disk (ring disk) electrode / compatible with PINE, Japanese ALS, Swiss Metrohm glassy carbon platinum
People Also Ask
- What are heated hydraulic presses used for? Molding Composites, Vulcanizing Rubber, and More
- What is a hydraulic hot press? Unlock the Power of Heat and Pressure for Advanced Materials
- What is the purpose of using a laboratory hydraulic press for LGVO synthesis? Achieve High-Purity Solid Electrolytes
- What is a heated hydraulic press used for? Essential Tool for Curing, Molding, and Laminating
- What is a hydraulic hot press machine? A Guide to Force and Heat for Material Transformation







