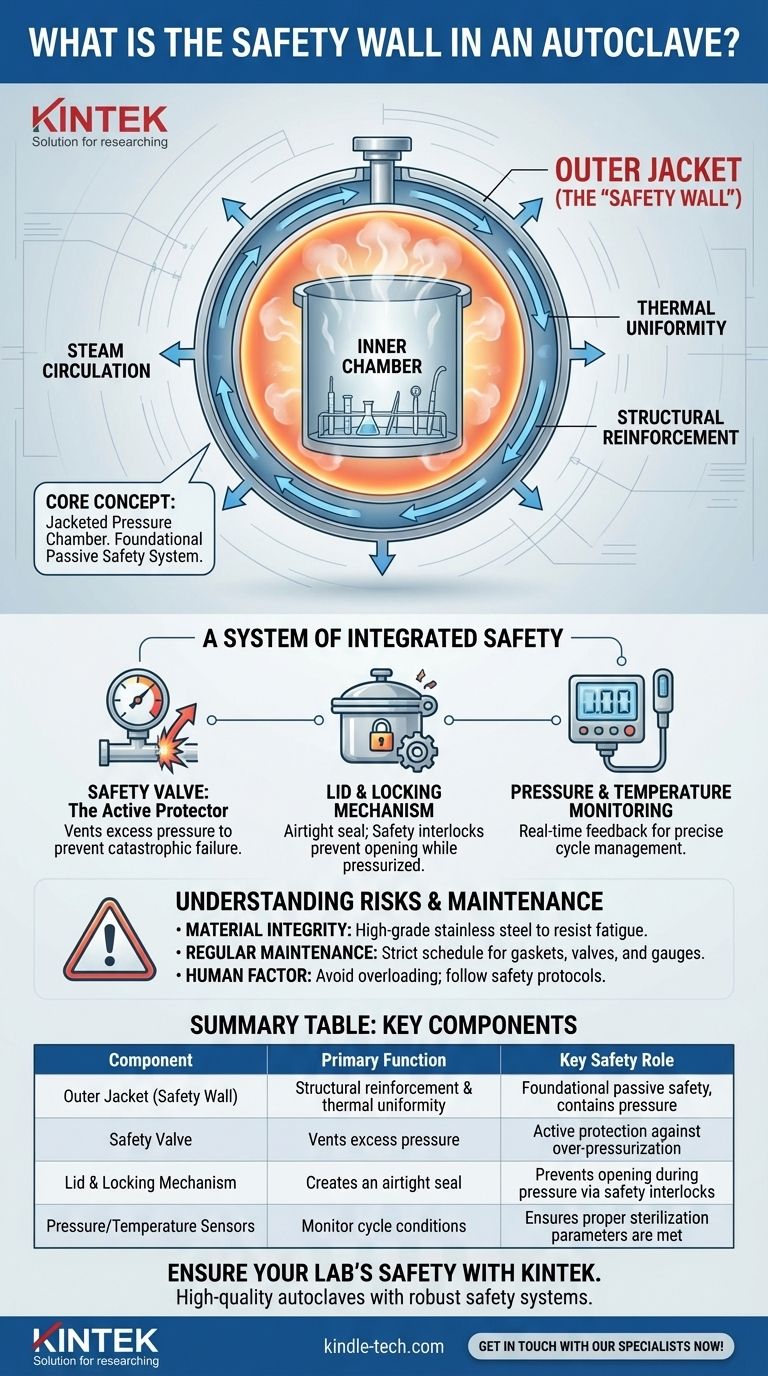
While "safety wall" is not a standard technical term for an autoclave component, it almost certainly refers to the double-walled construction of the pressure chamber, specifically the outer jacket. This design is a fundamental safety and performance feature, providing the structural integrity needed to contain extreme pressure and ensuring uniform heat distribution for effective sterilization.
The core concept you're looking for is the autoclave's jacketed pressure chamber. While the safety valve is the primary active safety device, the robust, double-walled design of the chamber itself is the foundational passive safety system that makes the entire process possible.

The Autoclave's Core: The Pressure Chamber
An autoclave's primary function is to contain high-pressure, high-temperature steam. The design of its central chamber is therefore critical to both its effectiveness and its safety.
The Inner Chamber
The inner chamber is the primary container where you place instruments, media, or other materials for sterilization. Its main role is to provide a sealed environment that can be filled with saturated steam.
The Outer Jacket (The "Safety Wall")
Surrounding this inner chamber is an outer wall, or jacket. This is the component most accurately described as a "safety wall." It creates a space between the two walls that serves two critical purposes:
- Structural Reinforcement: The jacket provides immense structural strength, enabling the vessel to safely withstand the high internal pressures required for sterilization (often exceeding 30 PSI).
- Thermal Uniformity: Steam is often circulated within this jacket to preheat the inner chamber walls. This prevents condensation and ensures the temperature is consistent throughout the chamber, leading to more reliable sterilization.
A System of Integrated Safety
True autoclave safety does not come from a single wall but from a system of interconnected components designed to prevent failure. The chamber's robust construction is just the starting point.
The Safety Valve: The Active Protector
Every autoclave is equipped with a safety valve. This is a non-negotiable, critical component. If the pressure inside the chamber exceeds a predetermined safe limit due to a malfunction, this valve automatically opens to vent excess steam, preventing a catastrophic failure.
The Lid and Locking Mechanism
The door or lid is engineered to create an airtight seal. Modern autoclaves feature safety interlocks that prevent the cycle from starting if the door isn't properly locked and, more importantly, prevent the door from being opened while the chamber is still pressurized.
Pressure and Temperature Monitoring
Pressure gauges and temperature sensors provide constant, real-time feedback on the conditions inside the chamber. These allow the control system to manage the cycle precisely and enable operators to verify that proper sterilization conditions have been met.
Understanding the Inherent Risks
While modern autoclaves are exceptionally safe, their safety relies on both design and proper maintenance. Understanding the potential points of failure is key to mitigating risk.
Material Integrity is Paramount
Autoclave chambers are built from high-grade materials like stainless steel or gunmetal for a reason. These materials are chosen for their ability to resist corrosion and withstand repeated cycles of high pressure and temperature without fatiguing.
Regular Maintenance is Non-Negotiable
The most robust design can be compromised by neglect. Gaskets on the door wear out, safety valves can become clogged, and gauges can lose calibration. A strict, documented maintenance schedule is essential for ensuring all safety systems function as intended.
The Human Factor
Operator error remains a significant risk. Overloading the chamber can impede steam circulation, leading to incomplete sterilization. Attempting to bypass safety interlocks or improperly securing the lid can lead to dangerous failures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding these components allows you to operate and select equipment with confidence.
- If your primary focus is routine operation: Trust the autoclave's integrated system, but always verify that the cycle has reached the target pressure and temperature before confirming a successful run.
- If your primary focus is purchasing new equipment: Prioritize models with a certified, jacketed stainless steel chamber and clearly documented safety valve specifications.
- If your primary focus is long-term safety: Implement and follow a rigorous maintenance and calibration schedule for door seals, safety valves, and monitoring gauges.
Ultimately, recognizing that autoclave safety comes from a complete system—not just one "wall"—is the key to ensuring safe, effective, and reliable sterilization.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Key Safety Role |
|---|---|---|
| Outer Jacket (Safety Wall) | Structural reinforcement & thermal uniformity | Foundational passive safety, contains pressure |
| Safety Valve | Vents excess pressure | Active protection against over-pressurization |
| Lid & Locking Mechanism | Creates an airtight seal | Prevents opening during pressure via safety interlocks |
| Pressure/Temperature Sensors | Monitor cycle conditions | Ensures proper sterilization parameters are met |
Ensure your lab's safety and achieve reliable sterilization with equipment you can trust.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab autoclaves and consumables, designed with robust safety systems like jacketed chambers and certified safety valves. Our equipment helps you maintain strict sterilization protocols and protect your valuable work.
Contact us today to find the perfect autoclave solution for your laboratory's needs. Let our experts help you enhance your lab's safety and efficiency.
Get in touch with our specialists now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of an autoclave system in SiC corrosion research? Simulate BWR conditions accurately.
- Why is autoclaving rather than boiling water used for sterilization? Achieve True Sterility for Your Lab
- What is the pressure required in an autoclave? Achieve Sterile Results with 15 PSI
- What are the 3 methods of sterilization? Choose the Right Method for Your Lab Needs
- What temperature does an autoclave open? The Critical Safety Rule for Lab Sterilization
- What are the minimum temperature and pressure requirements for autoclave steam sterilization? Ensure Complete Sterility in Your Lab
- What is the difference between gravity and pre vacuum autoclave? Choose the Right Sterilization Method
- Why is a laboratory autoclave necessary for Postgate Medium B (PMB)? Ensure Pure SRB Cultures & Accurate MIC Research



















