There is no single size for an autoclave. Instead, the size of an autoclave is directly determined by its design and intended application. Autoclaves are fundamentally categorized into two types: smaller, top-loading vertical models and larger, front-loading horizontal units, each suited for different sterilization volumes and workflows.
The critical factor is not a standard measurement but the autoclave's orientation. A vertical autoclave is typically small and ideal for laboratory settings, while a horizontal autoclave is large and built for high-capacity industrial or medical use.
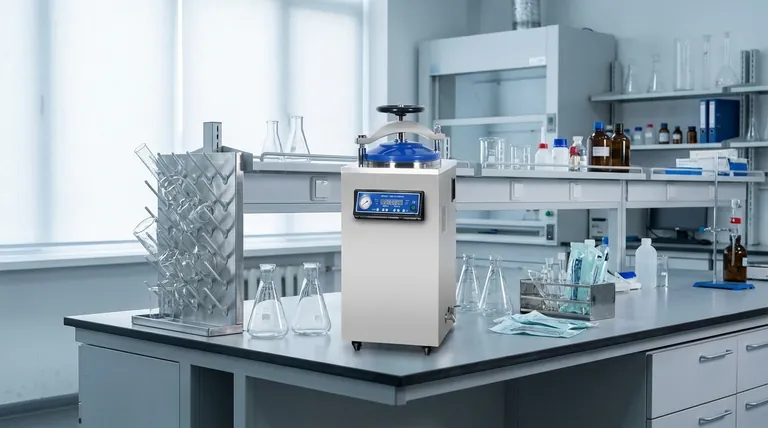

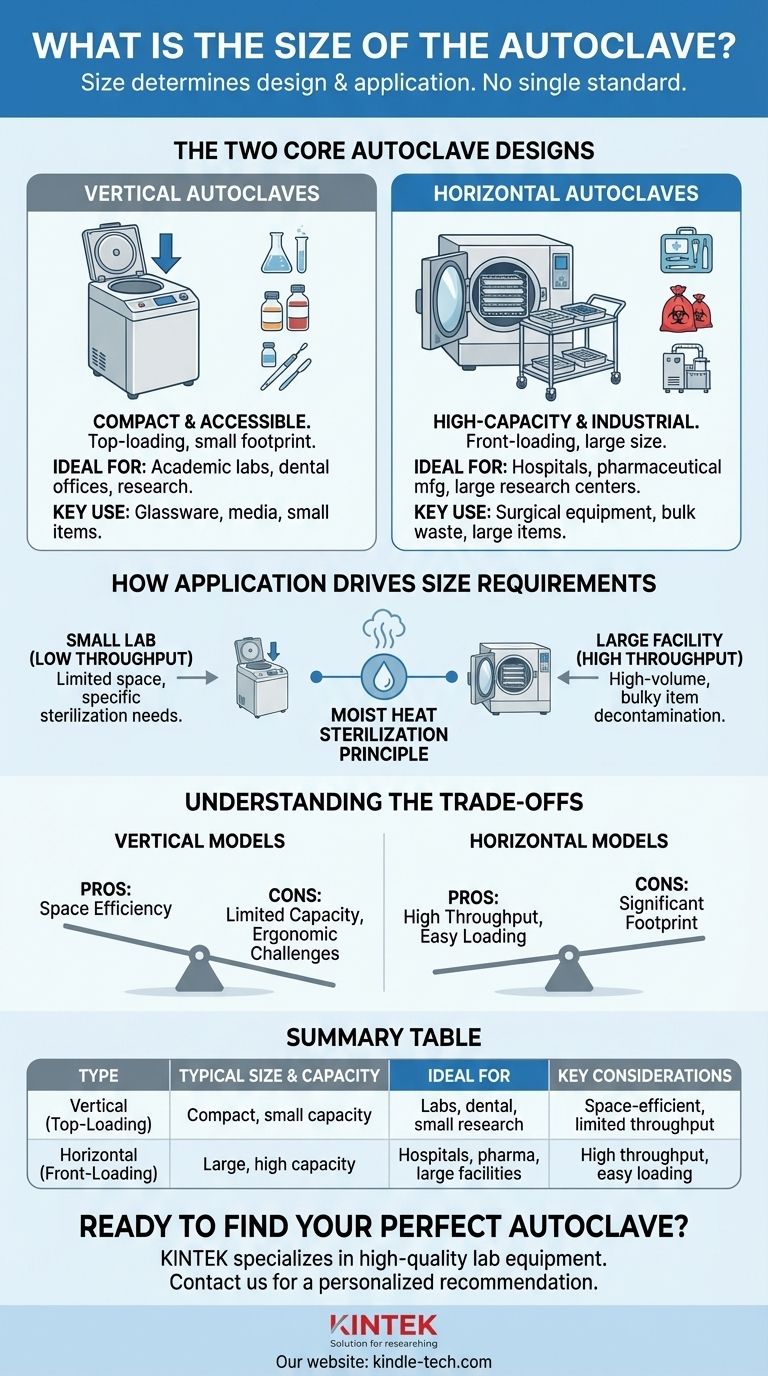
The Two Core Autoclave Designs
The primary determinant of an autoclave's size and capacity is its physical orientation. This design choice influences everything from the unit's footprint to the types of materials it can efficiently sterilize.
Vertical Autoclaves: Compact and Accessible
A vertical autoclave is loaded from the top, much like a pressure cooker. This design is inherently suited for smaller footprints.
These units are most commonly found in small sizes, making them ideal for academic labs, dental offices, or research facilities with limited space and lower throughput needs. They excel at sterilizing items like glassware, media, and small laboratory instruments.
Horizontal Autoclaves: High-Capacity and Industrial Scale
A horizontal autoclave features a door that opens outward, allowing items to be loaded from the front, often using carts or trays.
This design is necessary for high-volume applications and is therefore available in much larger sizes. Hospitals, pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities, and large-scale research centers rely on horizontal autoclaves to sterilize surgical equipment, large quantities of medical waste, and bulky items.
How Application Drives Size Requirements
The function of an autoclave—to sterilize materials using steam under high pressure—is consistent across all models. However, the specific items being sterilized dictate the necessary size and design.
The Principle of Moist Heat Sterilization
Every autoclave operates on the principle of moist heat sterilization. It uses high-pressure steam to reach temperatures that effectively kill bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms.
Matching Size to the Sterilization Load
The vast range of applications directly influences the required capacity.
A microbiology lab sterilizing media and petri dishes has vastly different needs than a hospital that must decontaminate surgical carts and large bags of biohazard waste. The former is served by a small vertical unit, while the latter requires a large horizontal model.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between a vertical and horizontal model involves balancing space, capacity, and workflow efficiency. This is the most critical decision when selecting an autoclave.
Vertical Models: Space Efficiency vs. Limited Capacity
The primary advantage of a vertical autoclave is its smaller physical footprint, making it easy to fit into a crowded laboratory.
However, its capacity is limited, and loading or unloading heavy or bulky items from the top can be ergonomically challenging.
Horizontal Models: High Throughput vs. Significant Footprint
A horizontal autoclave offers superior capacity and is far easier to load, especially for heavy or awkwardly shaped items.
The clear drawback is the significant floor space and utility infrastructure required to operate such a large piece of equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the appropriate autoclave, you must first define your primary sterilization task.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing small lab equipment like glassware and media: A compact, top-loading vertical autoclave is the most efficient choice for your space and workflow.
- If your primary focus is high-volume decontamination or sterilizing bulky surgical instruments: A large, front-loading horizontal autoclave is necessary to handle the required capacity and throughput.
- If your primary focus is a versatile solution for a growing facility: Investing in a horizontal model may provide the scalability needed to meet future sterilization demands.
Choosing the right autoclave begins with understanding that its size and orientation are direct functions of your specific sterilization task.
Summary Table:
| Autoclave Type | Typical Size & Capacity | Ideal For | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vertical (Top-Loading) | Compact, small capacity | Academic labs, dental offices, small-scale research | Space-efficient, limited throughput, ergonomic challenges |
| Horizontal (Front-Loading) | Large, high capacity | Hospitals, pharmaceutical manufacturing, large-scale facilities | High throughput, easy loading, requires significant floor space |
Ready to Find Your Perfect Autoclave?
Choosing the right autoclave is critical for your lab's efficiency and safety. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment, including a range of autoclaves tailored to your specific capacity and workflow needs.
Whether you're sterilizing glassware in a research lab or managing high-volume decontamination, we have the solution. Our experts will help you select the ideal vertical or horizontal model to ensure reliable performance.
Contact us today to discuss your requirements and get a personalized recommendation. Let KINTEK be your partner in laboratory excellence.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- How often should autoclave maintenance be performed? A Guide to Reliable Sterilization
- What media cannot be autoclaved? Protect Heat-Sensitive Reagents from Sterilization Damage
- What criteria must be followed when loading the autoclave to help ensure sterility will be achieved? Master the Key to Reliable Sterilization
- Why is a Teflon-lined stainless steel autoclave necessary for BixIn2-xO3 synthesis? Enhance Your Nanocrystal Purity
- What specific reaction conditions does a PTFE-lined autoclave provide for NVP/C synthesis? Optimize Battery Cathodes
- How does an industrial autoclave work? Unlock the Power of High-Pressure Steam for Sterilization
- Why is a high-pressure hydrothermal synthesis autoclave necessary for MnO2 nanowires? Precision Catalyst Growth
- How are autoclaves checked and maintained? Ensure Sterilization Safety and Compliance



















