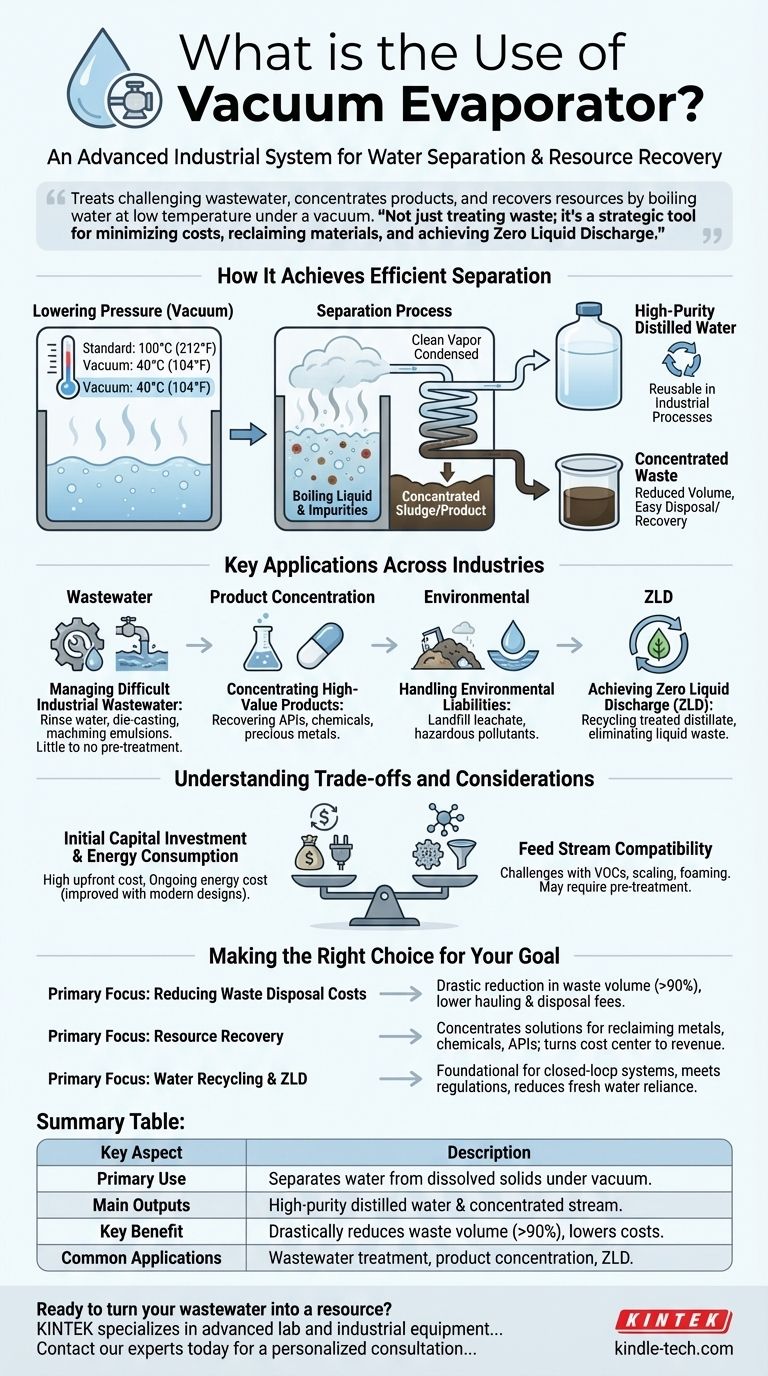
At its core, a vacuum evaporator is an advanced industrial system for separating water from dissolved solids and other contaminants. Its primary use is to treat challenging industrial wastewater, concentrate valuable products, and recover resources by efficiently boiling water at a low temperature under a vacuum. This process produces a high-quality, reusable water distillate and a significantly reduced volume of concentrated waste.
The true value of a vacuum evaporator is not just treating waste; it's a strategic tool for minimizing disposal costs, reclaiming valuable materials, and achieving environmental goals like Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) by turning a liability into a recoverable resource.

How It Achieves Efficient Separation
A vacuum evaporator's effectiveness comes from a simple principle of physics applied with sophisticated engineering. Understanding this process clarifies why it is so widely adopted.
The Principle of Lowering Pressure
By creating a vacuum inside the boiling chamber, the system dramatically lowers the pressure. This allows water to boil at a much lower temperature (e.g., 40°C / 104°F) than the standard 100°C (212°F) at atmospheric pressure.
The Separation Process
This low-temperature boiling is highly energy-efficient. The water turns into vapor, leaving behind non-volatile components like salts, metals, oils, and other contaminants. This clean vapor is then drawn off and condensed back into liquid form in a separate chamber.
The Two Outputs
The process results in two distinct and manageable outputs: a high-purity distilled water that can often be reused in industrial processes, and a small volume of highly concentrated sludge or product, which is far cheaper to dispose of or easier to process for recovery.
Key Applications Across Industries
The versatility of vacuum evaporators allows them to solve critical problems in a diverse range of sectors, handling waste streams that are often difficult or expensive to treat with other methods.
Managing Difficult Industrial Wastewater
Vacuum evaporators are ideal for treating complex waste streams like rinse water from surface treatments, wastewater from die-casting, and exhausted machining emulsions. They handle these difficult mixtures with little to no chemical pre-treatment.
Concentrating High-Value Products
In the pharmaceutical and chemical industries, these systems are used to recover valuable Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) or other components from process water. In metallurgy, they can concentrate solutions to reclaim precious metals.
Handling Environmental Liabilities
A primary application is the treatment of highly contaminated water such as landfill leachate. The evaporator effectively isolates hazardous pollutants, producing clean water and a manageable, low-volume hazardous concentrate.
Achieving Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD)
For facilities aiming to eliminate liquid waste discharge, vacuum evaporation is a cornerstone technology. It allows companies to create a closed-loop system by recycling the treated distillate back into their operations.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, a vacuum evaporator is not a universal solution. An objective assessment requires understanding its limitations to determine if it's the right fit for your specific needs.
Initial Capital Investment
The upfront cost of a high-quality vacuum evaporator system can be significant. This capital expenditure must be weighed against the long-term operational savings in waste disposal, water costs, and resource recovery.
Energy Consumption
While more efficient than atmospheric boiling, evaporation is still an energy-intensive process. The ongoing electrical cost is a key operational factor, though modern heat pump designs have made them significantly more cost-effective.
Feed Stream Compatibility
Although highly versatile, some waste streams can present challenges. Liquids with highly volatile organic compounds (VOCs) or those prone to severe scaling or foaming may require specific pre-treatment steps or more advanced evaporator designs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a wastewater treatment technology depends entirely on your primary objective. A vacuum evaporator offers distinct advantages for specific strategic goals.
- If your primary focus is reducing waste disposal costs: The key benefit is its ability to drastically reduce the volume of liquid waste (often by over 90%), which directly lowers hauling and disposal fees.
- If your primary focus is resource recovery: A vacuum evaporator excels at concentrating solutions to reclaim valuable materials like metals, chemicals, or APIs, potentially turning a cost center into a revenue stream.
- If your primary focus is water recycling and ZLD: This technology is a foundational tool for creating a closed-loop water system, enabling you to meet stringent environmental regulations and reduce your reliance on fresh water.
Ultimately, a vacuum evaporator transforms a wastewater liability into a manageable, and often valuable, operational asset.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Use | Separates water from dissolved solids and contaminants under vacuum. |
| Main Outputs | High-purity distilled water for reuse and a concentrated waste/product stream. |
| Key Benefit | Drastically reduces waste volume (often >90%), lowering disposal costs. |
| Common Applications | Industrial wastewater treatment, product concentration, landfill leachate, ZLD systems. |
Ready to turn your wastewater into a resource?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab and industrial equipment, including vacuum evaporation systems tailored to your needs. Whether your goal is to slash disposal costs, recover valuable materials, or achieve Zero Liquid Discharge, our solutions can help you transform a liability into an asset.
Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation and discover the right vacuum evaporator for your laboratory or facility.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Evaporation Crucible for Organic Matter
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
People Also Ask
- What precautions should be taken in a chemistry lab? Master the RAMP Framework for Ultimate Safety
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the analytical used in laboratory? Choose the Right Tool for Your Lab's Needs
- What temperature does evaporation occur? Unlock the Secrets to Controlling the Rate of Evaporation
- Do cannabinoids evaporate? How to Preserve Potency and Prevent Degradation



















