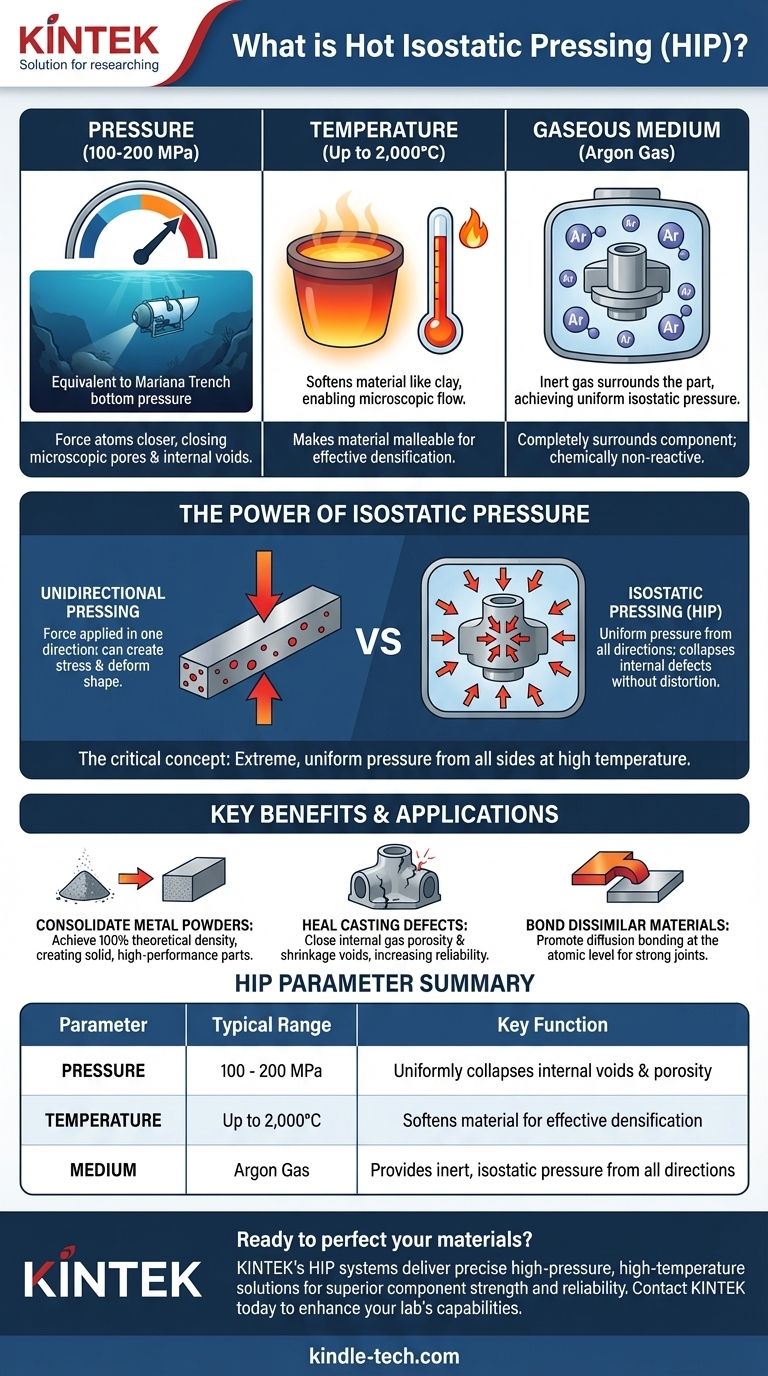
In short, Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) uses isostatic gas pressure that typically ranges from several tens of megapascals (MPa) up to 200 MPa, which is roughly 1,000 to 2,000 times standard atmospheric pressure. This immense pressure is applied uniformly in all directions in conjunction with high temperatures, often reaching 2,000°C, to densify materials and eliminate internal defects.
The critical concept is not just the high pressure, but its isostatic nature. By applying extreme, uniform pressure from all sides at high temperatures, HIP can collapse internal voids and create fully dense, high-performance components without distorting their shape.

The Core Parameters of HIP
Hot Isostatic Pressing is a manufacturing process defined by the precise interplay of three key factors: pressure, temperature, and a pressurizing medium.
Defining the Pressure Range
The pressure in a HIP cycle typically falls between 100 MPa and 200 MPa. To put this in perspective, 100 MPa is equivalent to the pressure found at the bottom of the Mariana Trench, the deepest point in the ocean.
This level of pressure is necessary to physically force atoms closer together, closing up microscopic pores, cracks, and other internal voids within a material.
The Role of High Temperature
Pressure alone is not enough. HIP systems also apply temperatures ranging from a few hundred degrees Celsius up to 2,000°C.
This intense heat makes the material malleable, almost like clay. In this softened state, the material can flow on a microscopic level, allowing the high pressure to effectively weld internal voids shut.
The Gaseous Medium
The pressure is not applied by a physical piston but by a gas. Argon is the most common choice because it is inert, meaning it will not chemically react with the material being processed, even at extreme temperatures.
The gas completely surrounds the part, which is how it achieves uniform, isostatic pressure.
What "Isostatic" Pressure Actually Means
The term "isostatic" is fundamental to understanding how HIP works and why it is so effective. It distinguishes the process from conventional pressing methods.
Uniform Pressure from All Directions
Isostatic means the pressure is applied equally and simultaneously on every single surface of the component.
Imagine submerging an object deep in the ocean. The water pressure pushes on it from the top, bottom, and all sides with the same force. This is a perfect analogy for the isostatic gas pressure inside a HIP vessel.
Why Uniformity Is Critical
This uniform pressure squeezes the part without distorting its overall shape. Because the force is perfectly balanced, it collapses internal porosity and defects inward.
This allows for the creation of components with complex geometries that are processed to full theoretical density, dramatically improving their mechanical properties like strength and fatigue resistance.
Contrast with Unidirectional Pressing
A traditional forge or press applies force in one direction (uniaxially). While this is effective for shaping metal, it can create internal stresses and cannot eliminate pre-existing internal voids as effectively as HIP can.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the HIP process involves balancing key variables and understanding its inherent limitations.
Pressure vs. Temperature Balance
The specific combination of pressure and temperature is tailored to the material. A material with a lower melting point may require less heat but more pressure, while a high-strength superalloy might need extreme temperatures to become pliable enough for the pressure to work.
Cycle Time and Cost
HIP is a batch process, not a continuous one. Loading, heating, pressurizing, holding, and cooling cycles can take many hours. This makes it more expensive and time-consuming than some other manufacturing methods.
Part Preparation
For the process to work on powders or to prevent surface reactions, parts must often be sealed within a gas-tight container or "can." This adds an extra step and cost to the manufacturing workflow.
How Parameters Are Matched to the Goal
The precise pressure and temperature settings are selected based on the specific manufacturing objective.
- If your primary focus is consolidating metal powders: The goal is to achieve 100% theoretical density, creating a solid part from loose powder that has properties superior to cast or forged equivalents.
- If your primary focus is healing defects in castings: Lower pressures and temperatures might be used just to close internal gas porosity and shrinkage voids, significantly increasing the part's reliability and service life.
- If your primary focus is bonding dissimilar materials: The process parameters are chosen to promote diffusion at the atomic level, creating a bond between two different materials that is as strong as the parent materials themselves.
Ultimately, Hot Isostatic Pressing leverages the combined power of uniform pressure and high heat to perfect materials from the inside out.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Typical Range | Key Function |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure | 100 - 200 MPa | Uniformly collapses internal voids and porosity |
| Temperature | Up to 2,000°C | Softens material for effective densification |
| Medium | Argon Gas | Provides inert, isostatic pressure from all directions |
Ready to perfect your materials from the inside out?
KINTEK's Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) systems deliver the precise combination of extreme pressure (up to 200 MPa) and high temperature (up to 2,000°C) needed to achieve 100% theoretical density, eliminate internal defects in castings, and consolidate metal powders. This results in components with superior strength, fatigue resistance, and reliability.
Whether your goal is to heal casting defects, create fully dense parts from powder, or bond dissimilar materials, our HIP solutions are tailored to your specific material and performance requirements.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our lab equipment and consumables can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and material performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of hot isostatic pressing? Achieve 100% Density and Superior Performance
- What is the HIP material process? Achieve Near-Perfect Density and Reliability
- How much energy does hot isostatic pressing consume? Unlock Net Energy Savings in Your Process
- What are some of the attractive properties of hot isostatic pressed products? Achieve Perfect Density and Superior Performance
- Is hot isostatic pressing a heat treatment? A Guide to Its Unique Thermomechanical Process



















