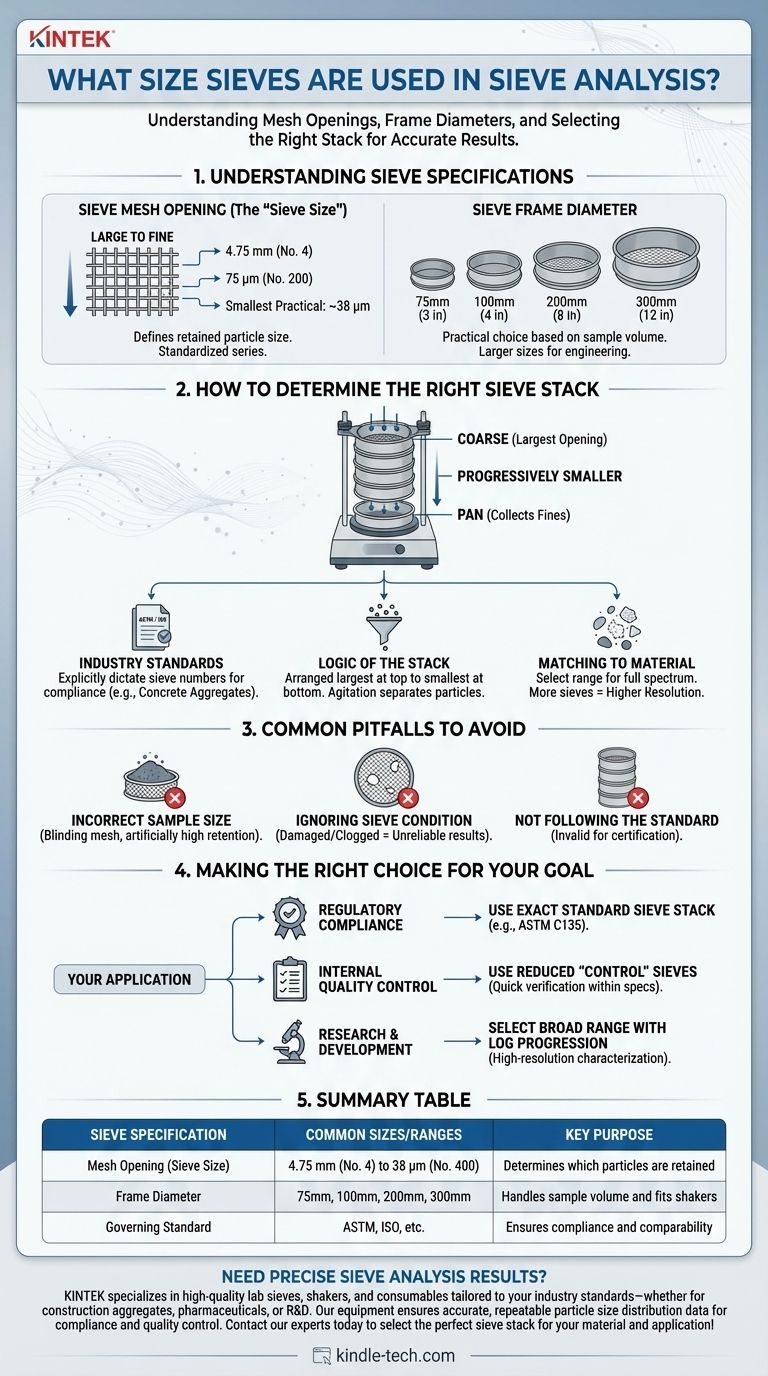
In sieve analysis, the mesh openings range from large gravel sizes down to very fine powders, typically from several inches to as small as 38 microns (0.0015 inches). The physical sieve frames also come in standard diameters, commonly 75mm (3 in), 100mm (4 in), 200mm (8 in), and 300mm (12 in), to fit sieve shakers and accommodate different sample volumes.
The critical takeaway is that sieve sizes are not chosen randomly. They are selected as a specific "stack" based on the material being tested and, most importantly, the governing industry standard (e.g., for concrete, soils, or pharmaceuticals) to ensure results are accurate, repeatable, and comparable.

Understanding Sieve Specifications
To select the correct sieves, you must understand the two primary measurements that define them: the mesh opening and the frame diameter.
Sieve Mesh Opening (The "Sieve Size")
This is the most critical specification. It defines the size of the openings in the wire mesh and determines what size particles are retained.
These sizes are standardized, with common series ranging from coarse to fine. A typical stack might include sieves with openings from 4.75 mm (a No. 4 sieve) down to 75 µm (a No. 200 sieve), depending on the material.
The smallest practical mesh size for standard dry sieve analysis is around 38 microns. Below this, particles are more effectively measured by other means like laser diffraction or hydrometer analysis.
Sieve Frame Diameter
This refers to the physical diameter of the circular frame holding the mesh. The choice is primarily practical.
- Smaller diameters (75mm, 100mm): Best for small sample sizes or rare, valuable materials.
- Larger diameters (200mm, 300mm): The most common sizes for civil engineering and aggregate testing, as they can handle the larger sample volumes needed to be representative of the bulk material.
How to Determine the Right Sieve Stack
The goal of sieve analysis is to determine the particle size distribution, or "gradation," of a material. This requires using a series of sieves with progressively smaller openings.
The Role of Industry Standards
For most engineering and quality control applications, you do not choose the sieve sizes yourself. They are explicitly dictated by standards organizations.
For example, testing aggregate for concrete follows specific ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) or other national standards. These documents prescribe the exact sieve numbers you must use in your stack to ensure the aggregate meets the required gradation for strength and workability.
The Logic of the Sieve Stack
Sieves are arranged in a stack with the largest mesh opening at the top and the smallest at the bottom. A solid "pan" is placed at the very bottom to collect all particles that pass through the final sieve.
During a test, the material is placed in the top sieve, and the entire stack is agitated. Particles fall through the mesh until they are retained on a sieve with openings smaller than their diameter.
Matching Sieves to Your Material
If you are not following a specific standard (e.g., for research purposes), you should select a range of sieves that covers the full spectrum of particle sizes you expect in your sample.
The number of sieves in your stack determines the "resolution" of your analysis. More sieves provide a more detailed and accurate particle size distribution curve.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
The accuracy of sieve analysis depends heavily on correct procedure. Choosing the right sieve sizes is the first step, but a poor process will invalidate the results.
Using an Incorrect Sample Size
The references correctly highlight that sample size is critical. A sample that is too large will "blind" the mesh, preventing particles from having a chance to pass through the openings. This results in an artificially high amount of material being retained on coarser sieves. A sample of 25-100 grams is a common starting point for finer materials.
Ignoring Sieve Condition
Damaged sieves with bent wires, clogged openings, or tears in the mesh will produce completely unreliable results. Sieves must be regularly inspected, cleaned, and calibrated to ensure the mesh openings are accurate.
Not Following the Standard
If your goal is to certify a material for a specific use (like road base or filter sand), you must use the sieve stack defined by the relevant standard. Using a different set of sieves makes your results invalid for certification and incomparable to other tests.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application dictates your sieve selection strategy. After obtaining a representative sample of your material, use the following guidelines.
- If your primary focus is regulatory compliance or certification: You must use the exact sieve stack specified by the governing industry standard (e.g., ASTM C136 for aggregates).
- If your primary focus is internal quality control: You can use a reduced set of "control" sieves that bracket the key upper and lower size limits for your product to quickly verify if it is within specification.
- If your primary focus is research and development: Select a broad range of sieves with logarithmic progression in size to create a high-resolution particle distribution curve for detailed material characterization.
Choosing the correct sieve sizes is the foundation for obtaining meaningful and reliable particle analysis data.
Summary Table:
| Sieve Specification | Common Sizes/Ranges | Key Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Mesh Opening (Sieve Size) | 4.75 mm (No. 4) to 38 µm (No. 400) | Determines which particles are retained |
| Frame Diameter | 75mm, 100mm, 200mm, 300mm | Handles sample volume and fits shakers |
| Governing Standard | ASTM, ISO, etc. | Ensures compliance and comparability |
Need precise sieve analysis results? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab sieves, shakers, and consumables tailored to your industry standards—whether for construction aggregates, pharmaceuticals, or R&D. Our equipment ensures accurate, repeatable particle size distribution data for compliance and quality control. Contact our experts today to select the perfect sieve stack for your material and application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
People Also Ask
- How is a vibratory sieve shaker used in the particle size analysis of mechanically alloyed powders? Expert Guide
- What is the primary purpose of using standard sieves? Master Particle Uniformity for High-Quality Catalyst Preparation
- What is the role of standard sieves in gold scrap leaching kinetic studies? Ensure Precision in Particle Classification
- What are the factors affecting sieving performance and efficiency? Optimize Your Particle Separation Process
- What are the specifications for test sieves? A Guide to ASTM & ISO Standards for Accurate Particle Analysis



















