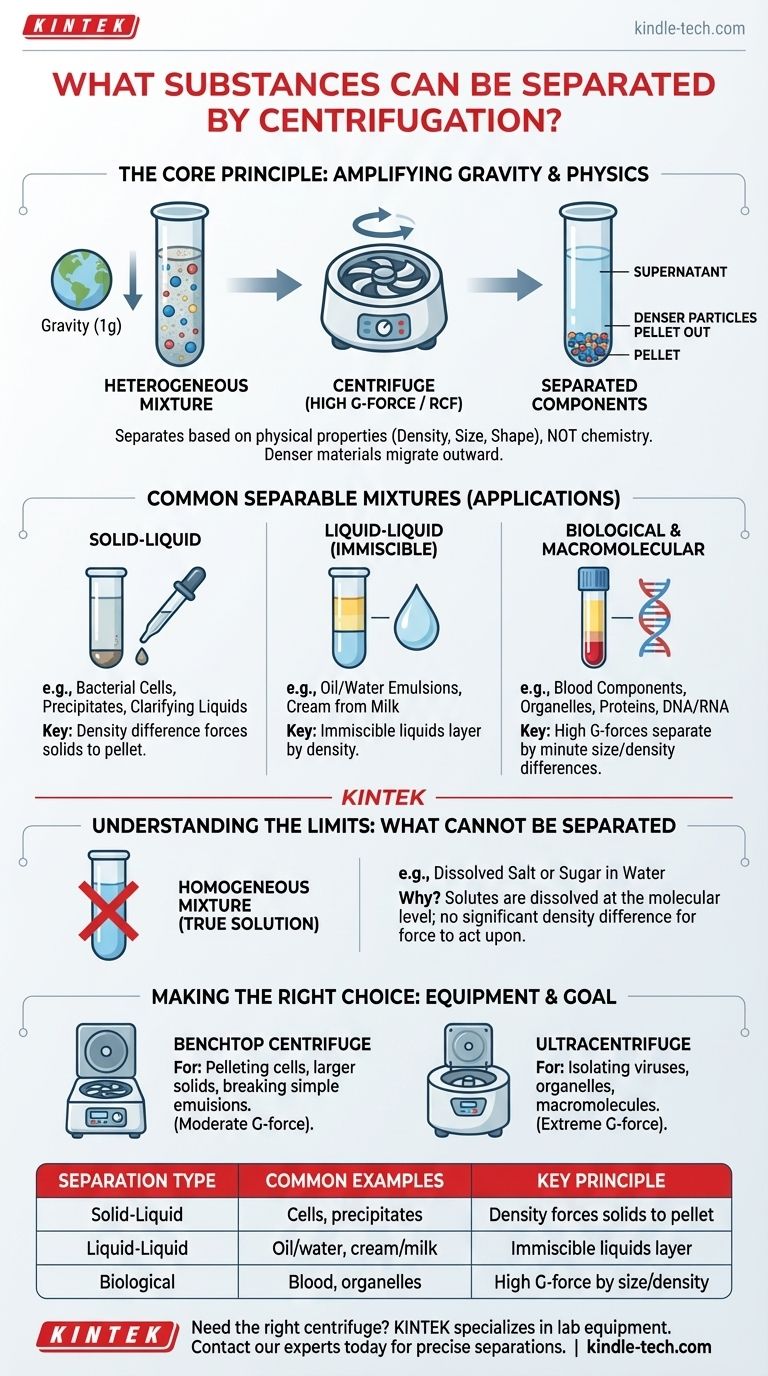
In principle, centrifugation can separate the components of any heterogeneous mixture where those components differ in physical properties like density, size, or shape. It is a powerful laboratory and industrial technique used to separate solids from liquids, immiscible liquids from each other, and even macromolecules from a solvent by dramatically amplifying the force of gravity.
The core principle to understand is that centrifugation does not separate substances based on chemistry; it separates them based on physics. If components in a mixture have different densities, the centrifuge will force the denser material to the bottom, leaving the less dense material on top.

The Fundamental Principle: How Centrifugation Works
Centrifugation is essentially a method of accelerated sedimentation. It replaces the relatively weak force of gravity with a much more powerful centrifugal force generated by high-speed rotation.
Amplifying Gravity's Force
A centrifuge spins samples around a fixed axis, subjecting them to a powerful outward force known as Relative Centrifugal Force (RCF) or G-force. This force can be thousands, or even hundreds of thousands, of times greater than Earth's gravity.
This immense force dramatically speeds up the natural tendency of denser particles to settle out of a mixture.
The Critical Role of Density
The most important factor for separation is density. When a mixture is spun, every component is subjected to the same centrifugal force.
However, the denser components displace the less dense components, forcing the denser material to migrate outward and collect at the bottom of the tube as a pellet. The less dense liquid that remains above is called the supernatant.
The Influence of Particle Size and Shape
While density is primary, the size and shape of particles also play a role. Larger particles will sediment faster than smaller particles of the same density because they have more mass to overcome the liquid's viscous drag.
This principle is the basis for differential centrifugation, a technique used to separate components of different sizes, such as subcellular organelles.
Common Applications and Separable Mixtures
This principle allows for an incredibly wide range of applications across biology, chemistry, and industry.
Solid-Liquid Separations
This is the most common use of centrifugation. It is used to separate solid particles suspended in a liquid.
Examples include pelleting bacterial cells or eukaryotic cells from a growth medium, collecting a precipitate formed during a chemical reaction, or clarifying wine and beer by removing yeast.
Liquid-Liquid Separations
Centrifugation is highly effective for separating two immiscible liquids—liquids that do not mix, like oil and water.
The process rapidly breaks emulsions, forcing the denser liquid to the bottom and the less dense liquid to the top, forming two distinct layers. This is used in dairy processing to separate cream (fat) from milk.
Biological and Macromolecular Separations
With high-speed or ultracentrifuges, it is possible to separate components that are very small and have only slight density differences.
This includes separating blood components (red and white blood cells from plasma), isolating subcellular organelles (like mitochondria, nuclei, and ribosomes), and purifying macromolecules like proteins, DNA, and RNA from cellular extracts.
Understanding the Limitations
Trusting the process means understanding what it cannot do. The physical principles that make centrifugation so powerful also define its limits.
What Centrifugation Cannot Separate
Centrifugation is ineffective on homogeneous mixtures, often called true solutions. In a true solution, such as salt dissolved in water, the solute is broken down to the molecular level and evenly distributed.
There are no significant density differences for the centrifugal force to act upon. The dissolved particles are simply too small and integrated to be separated by physical force alone.
The Importance of Equipment
The type of separation you can achieve is directly tied to the equipment you use. A simple benchtop centrifuge is perfect for pelleting cells.
However, separating tiny viruses or individual proteins requires an ultracentrifuge, a specialized and expensive piece of equipment capable of generating extreme G-forces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Mixture
To apply this knowledge, first identify the nature of your mixture and your goal.
- If your primary focus is separating visible solids from a liquid: A standard centrifuge at moderate speed is almost always the correct tool.
- If your primary focus is breaking an emulsion of two liquids: Centrifugation will dramatically accelerate the layering process based on density.
- If your primary focus is isolating very small biological particles (e.g., organelles, viruses): You will need an ultracentrifuge capable of generating exceptionally high G-forces.
- If your primary focus is separating a dissolved solid from a solvent: Centrifugation will not work; you must use a different method like evaporation, chromatography, or distillation.
Ultimately, centrifugation is a physical tool that exploits physical differences to achieve a separation.
Summary Table:
| Separation Type | Common Examples | Key Principle |
|---|---|---|
| Solid-Liquid | Bacterial cells, precipitates | Density difference forces solids to pellet |
| Liquid-Liquid | Oil/water, cream/milk | Immiscible liquids layer by density |
| Biological | Blood components, organelles, proteins | High G-forces separate by size/density |
Need the right centrifuge for your lab's separation tasks? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Whether you're pelleting cells, purifying proteins, or breaking emulsions, we provide reliable centrifuges tailored to your application. Contact our experts today to enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve precise separations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Automatic Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What is the use of vibrating sieve machine? Achieve Precise Particle Size Analysis for Your Lab
- What does a vibrating sieve do? Automate Particle Size Analysis for Accurate Results
- What are the disadvantages of sieve machine? Key Limitations in Particle Size Analysis
- What is the speed of a sieving machine? Optimize Vibration for Maximum Efficiency and Accuracy
- What are the different types of sieving machines? Choose the Right Motion for Your Material



















