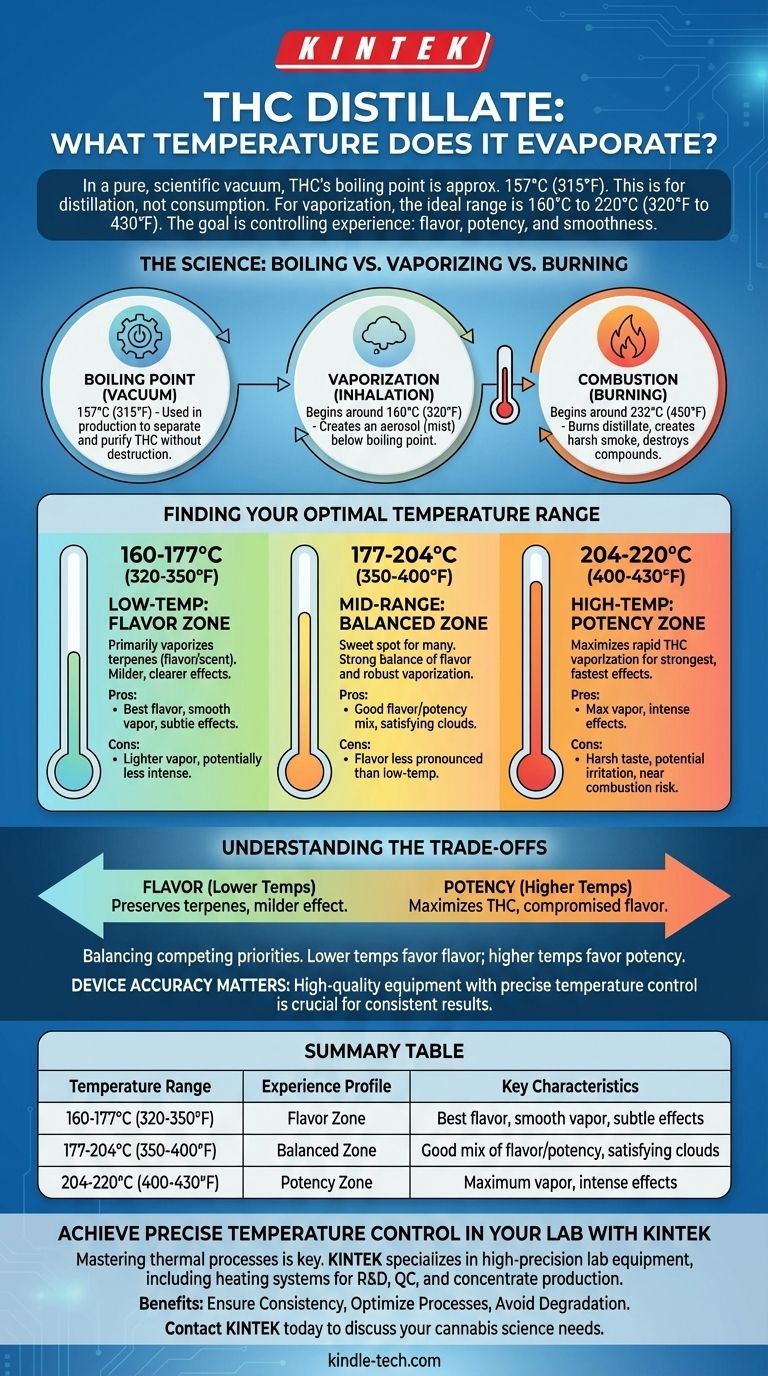
In a pure, scientific vacuum, THC's boiling point—the temperature at which it turns from a liquid to a gas—is approximately 157°C (315°F). However, this number is relevant for the distillation process itself, not for consumption. For effective vaporization when using a vape pen or dab rig, the ideal temperature range is significantly higher, typically between 160°C and 220°C (320°F and 430°F).
The search for a single evaporation temperature is misleading. The real goal is to understand that temperature is a dial you use to control your experience, balancing flavor, potency, and smoothness to achieve your desired outcome.
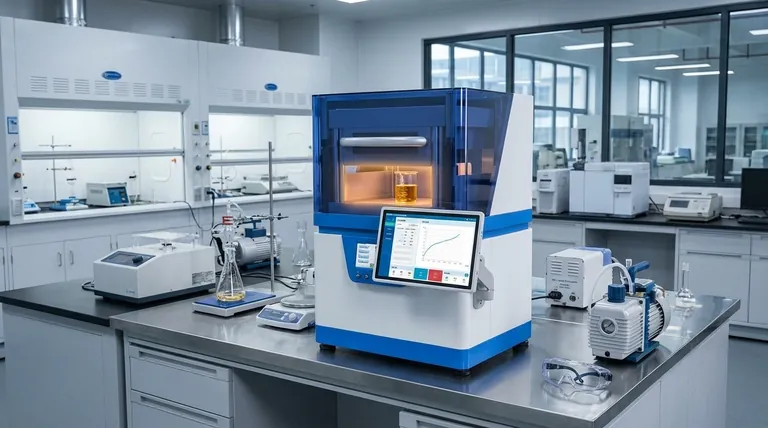

The Science: Boiling vs. Vaporizing vs. Burning
To use distillate effectively, you must understand the difference between three key thermal processes. The temperature you choose directly impacts the chemical compounds you inhale and the resulting effects.
Boiling Point in a Vacuum
The 157°C (315°F) figure refers to the boiling point of THC under vacuum pressure. This specific condition is used by producers during the refinement process to separate and purify THC into a distillate without destroying it. This is a manufacturing specification, not a user guide.
Vaporization for Inhalation
Vaporization is the process of heating a substance until it creates an aerosol (a fine mist of liquid droplets) that can be inhaled. This happens below the true boiling point. For THC distillate, this process begins around 160°C (320°F) and becomes more robust as the temperature increases.
The Enemy: Combustion
Combustion, or burning, begins around 232°C (450°F). At this point, you are no longer vaporizing the distillate; you are burning it. This creates harsh smoke, introduces potentially harmful byproducts like benzene, and destroys the delicate terpenes and cannabinoids, resulting in a less pleasant taste and a different, often less desirable, effect.
Finding Your Optimal Temperature Range
Different temperatures vaporize different compounds at different rates. By adjusting the temperature of your device, you are essentially choosing which compounds to prioritize.
Low-Temperature Vaping: The Flavor Zone (160-177°C / 320-350°F)
In this range, you primarily vaporize terpenes—the aromatic compounds responsible for flavor and scent. Because you are just above THC's lowest vaporization point, the effect is often milder, clearer, and more gradual.
- Pros: Best possible flavor, smooth vapor, subtle and clean effects.
- Cons: Lighter vapor production, potentially less intense psychoactive effects per draw.
Mid-Range Vaping: The Balanced Zone (177-204°C / 350-400°F)
This is the sweet spot for many users. It offers a strong balance between good flavor and robust THC vaporization. You get noticeable terpene expression along with significant vapor production and a potent effect.
- Pros: Good mix of flavor and potency, satisfying vapor clouds.
- Cons: Flavor is less pronounced than at lower temperatures.
High-Temperature Vaping: The Potency Zone (204-220°C / 400-430°F)
This range maximizes the rapid vaporization of THC, delivering the strongest and fastest-acting effects. However, this intensity comes at the cost of flavor, as most terpenes are quickly burned off at these temperatures.
- Pros: Maximum vapor production, most intense and immediate effects.
- Cons: Harsh taste, potential for irritation, risk of nearing combustion.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a temperature is an act of balancing competing priorities. There is no single "best" setting, only the best setting for your specific goal.
Flavor vs. Potency
This is the central trade-off. Lower temperatures favor flavor; higher temperatures favor potency. Terpenes have lower boiling points than THC, so a gentle heat preserves them. A higher heat ensures you are vaporizing as much THC as possible with every draw, but the flavor will be compromised.
Device Accuracy Matters
The temperature setting on your device is an approximation. Inexpensive vape pens with simple voltage settings (e.g., low, medium, high) offer far less precision than a high-quality e-nail or portable vaporizer with digital temperature control. Your results will vary based on your equipment's ability to hold a stable and accurate temperature.
Efficiency and Waste
A temperature that is too low may leave behind un-vaporized THC, wasting product. A temperature that is too high (combustion) actively destroys the THC. The most efficient range is typically the middle zone, where you achieve full vaporization without burning the material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Experimentation is key, but you can use these principles as your starting point. Begin at a lower temperature and gradually increase it during your session to experience the full spectrum of effects and flavors.
- If your primary focus is preserving flavor and terpenes: Start at the low end of the spectrum (~160°C / 320°F) and work your way up slowly.
- If your primary focus is a balanced experience: Aim for the middle range (~185°C / 365°F) as a reliable and effective default setting.
- If your primary focus is maximum potency and cloud production: Use the higher range (~210°C / 410°F), but be careful not to exceed 220°C (430°F) to avoid a harsh, burnt taste.
By mastering temperature, you move from being a passive consumer to an active participant in shaping your own experience.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Experience Profile | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| 160-177°C (320-350°F) | Flavor Zone | Best flavor, smooth vapor, subtle effects |
| 177-204°C (350-400°F) | Balanced Zone | Good mix of flavor and potency, satisfying clouds |
| 204-220°C (400-430°F) | Potency Zone | Maximum vapor production, intense effects |
Achieve Precise Temperature Control in Your Lab
Mastering thermal processes is key to product quality and user experience. KINTEK specializes in high-precision lab equipment, including temperature-controlled heating systems ideal for R&D, quality control, and production of concentrates like THC distillate.
Our reliable and accurate heating solutions help you:
- Ensure Consistency: Reproduce exact thermal profiles for uniform product quality.
- Optimize Processes: Fine-tune vaporization or distillation parameters for maximum efficiency.
- Avoid Degradation: Precisely control temperatures to prevent combustion and preserve delicate compounds.
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities? Contact KINTALK today to discuss your specific needs and discover how our equipment can support your work in cannabis science, pharmaceuticals, or material testing.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory plate hot press play in the vulcanization and molding of fluorosilicone rubber (F-LSR)?
- What role does a hot press play in treating the CAL-GPE interface? Optimize Performance for Flexible Lithium Batteries
- What is a hydraulic floor press used for? A Versatile Tool for Industrial and Lab Applications
- How is pressure generated and applied in a hot press? Master High-Intensity Hydraulic & Pneumatic Systems
- What are the advantages of using a hot press for Li7P2S8I0.5Cl0.5? Boost Conductivity with Precision Densification



















